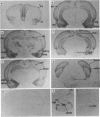
Abstract
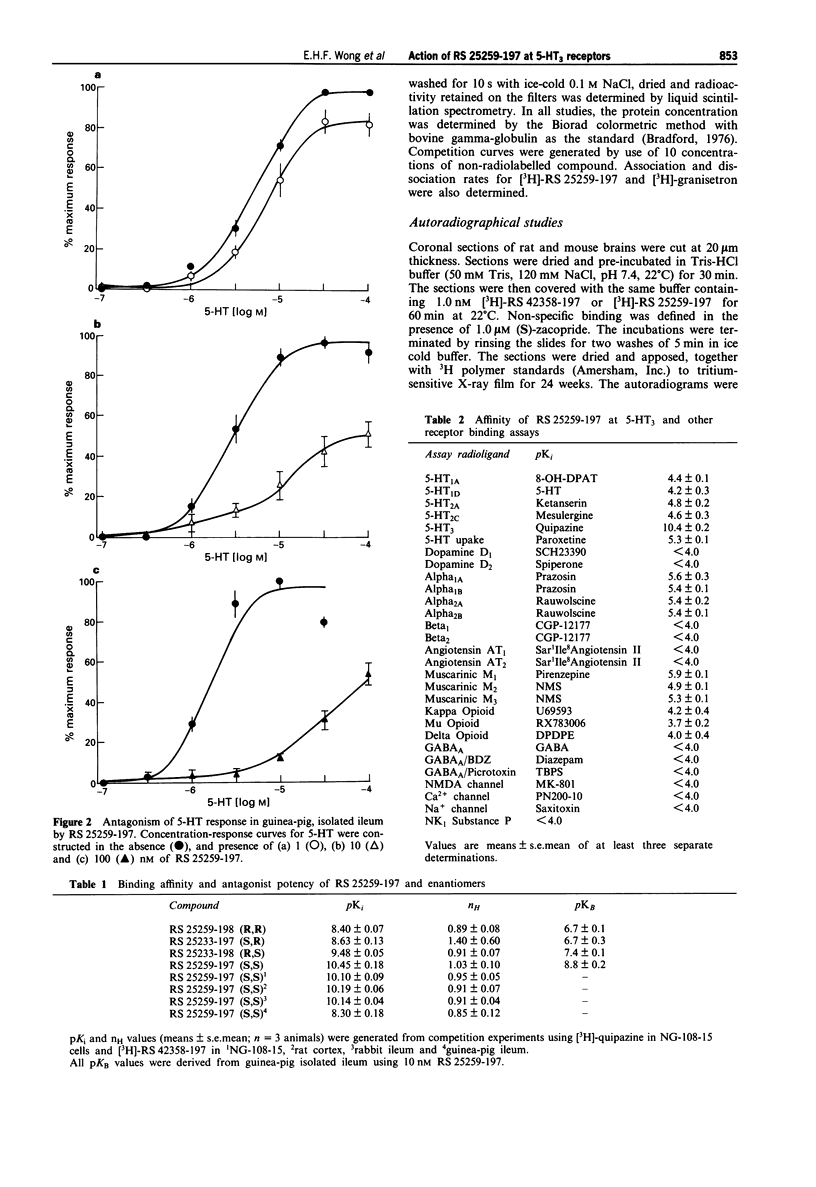
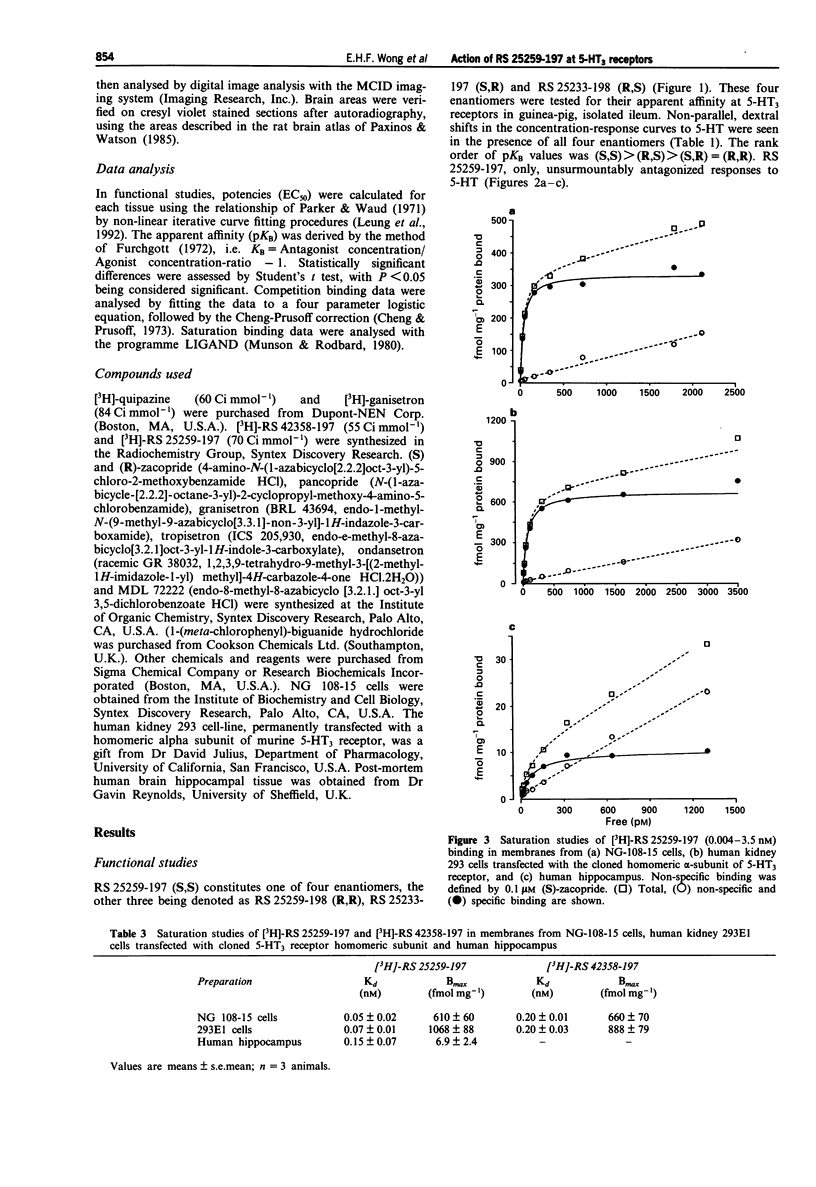
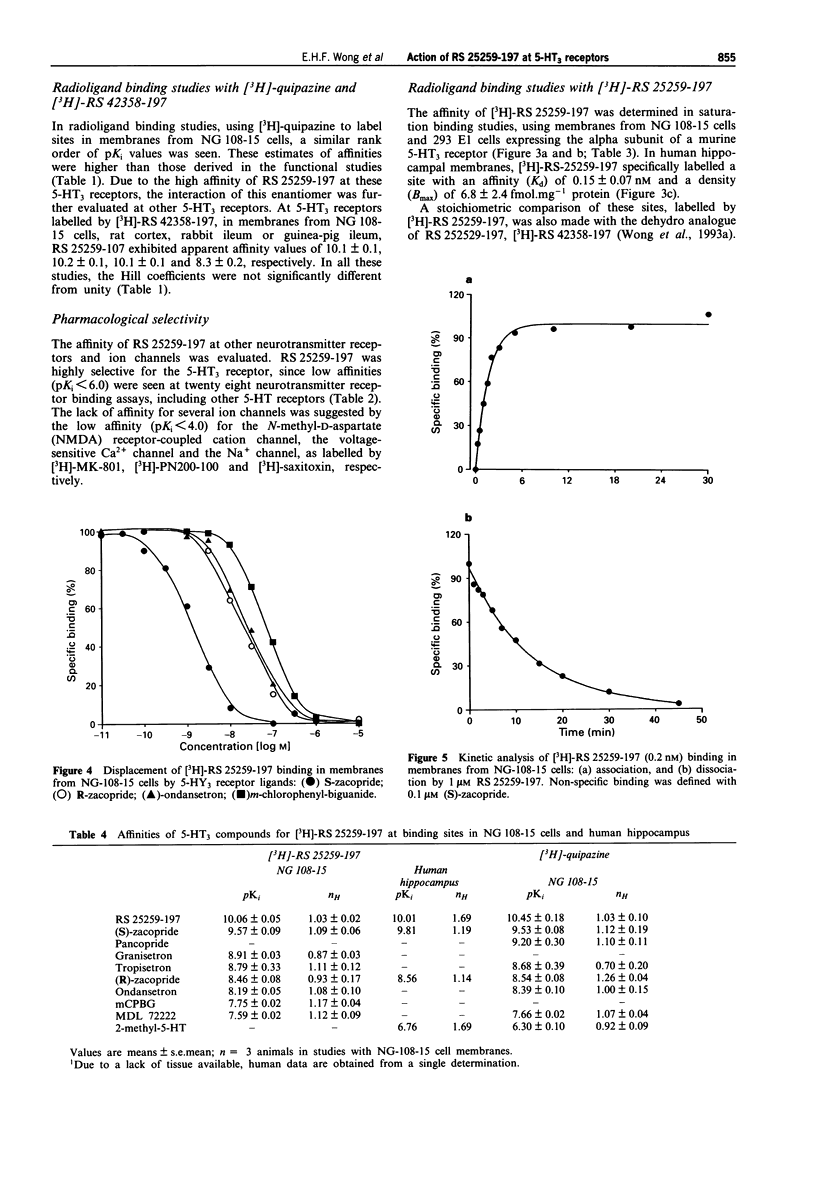
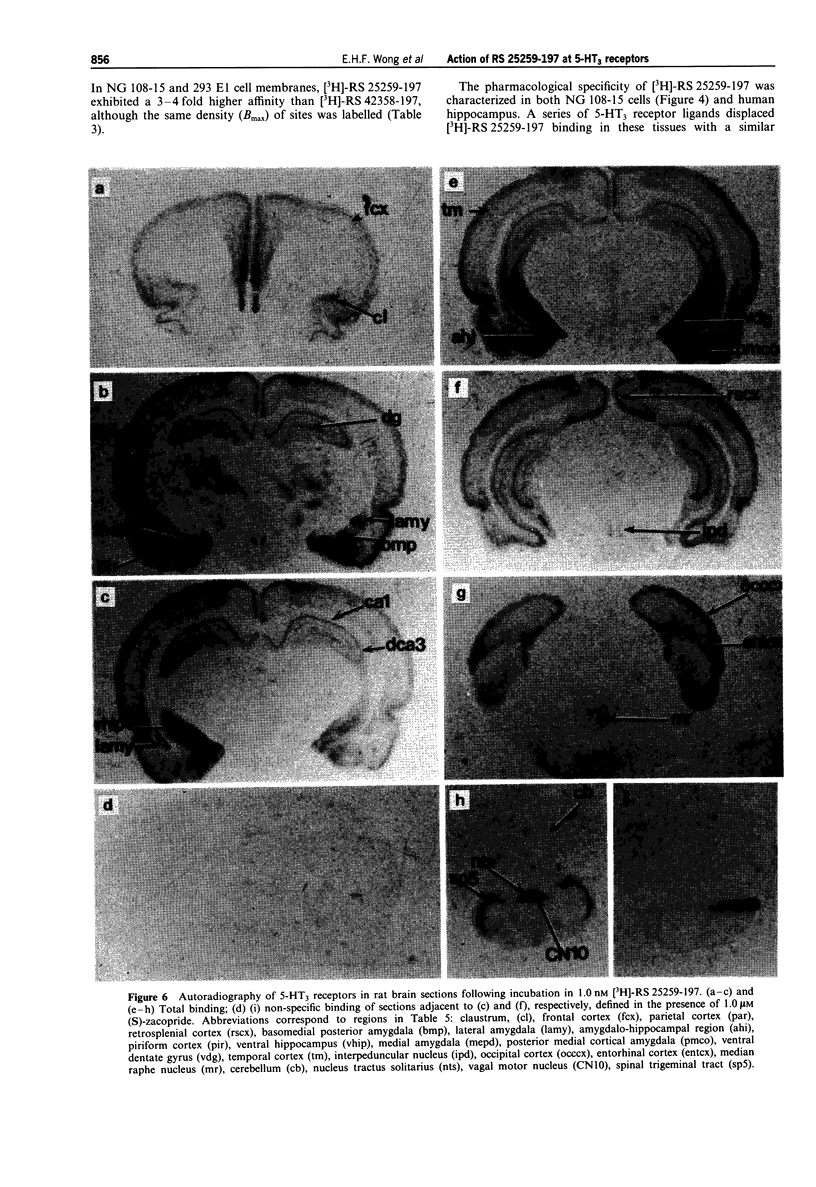
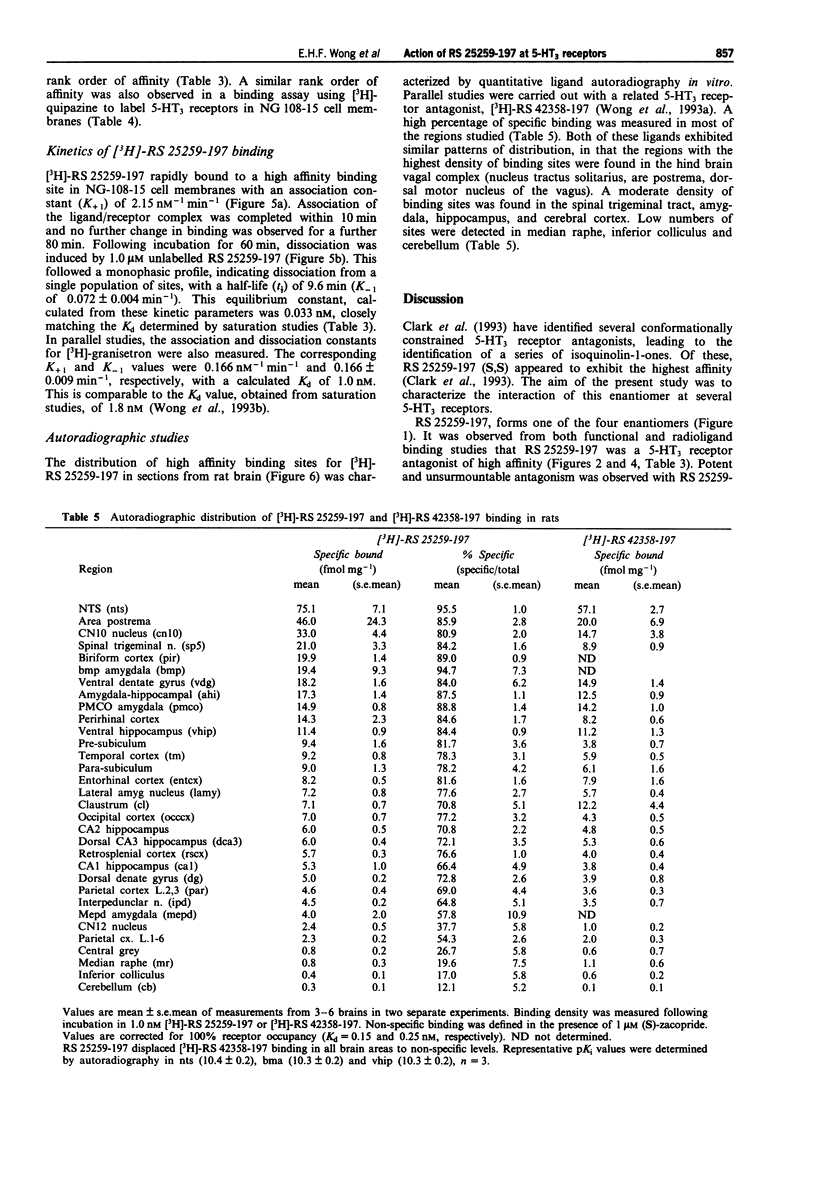
1. A series of isoquinolines have been identified as 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. One of these, RS 25259-197 [(3aS)-2-[(S)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2,3,3a,4,5,6-hexahydro- 1- oxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-hydrochloride], has two chiral centres. The remaining three enantiomers are denoted as RS 25259-198 (R,R), RS 25233-197 (S,R) and RS 25233-198 (R,S). 2. At 5-HT3 receptors mediating contraction of guinea-pig isolated ileum, RS 25259-197 antagonized contractile responses to 5-HT in an unsurmountable fashion and the apparent affinity (pKB), estimated at 10 nM, was 8.8 +/- 0.2. In this tissue, the -log KB values for the other three enantiomers were 6.7 +/- 0.3 (R,R), 6.7 +/- 0.1 (S,R) and 7.4 +/- 0.1 (R,S), respectively. The apparent affinities of RS 25259-197 and RS 25259-198, RS 25233-197 and RS 25233-198 at 5-HT3 receptors in membranes from NG-108-15 cells were evaluated by a [3H]-quipazine binding assay. The -log Ki values were 10.5 +/- 0.2, 8.4 +/- 0.1, 8.6 +/- 0.1 and 9.5 +/- 0.1, respectively, with Hill coefficients not significantly different from unity. Thus, at these 5-HT3 receptors, the rank order of apparent affinities was (S,S) > (R,S) > (S,R) = (R,R). 3. RS 25259-197 displaced the binding of the selective 5-HT3 receptor ligand, [3H]-RS 42358-197, in membranes from NG-108-15 cells, rat cerebral cortex, rabbit ileal myenteric plexus and guinea-pig ileal myenteric plexus, with affinity (pKi) values of 10.1 +/- 0.1, 10.2 +/- 0.1, 10.1 +/- 0.1 and 8.3 +/- 0.2, respectively.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abi-Dargham A., Laruelle M., Wong D. T., Robertson D. W., Weinberger D. R., Kleinman J. E. Pharmacological and regional characterization of [3H]LY278584 binding sites in human brain. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):730–737. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. L., Bhandari P. The 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor antagonists as antiemetics: preclinical evaluation and mechanism of action. Eur J Cancer. 1993;29A Suppl 1:S11–S16. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(05)80254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Barnes N. M., Costall B., Ironside J. W., Naylor R. J. Identification and characterisation of 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 recognition sites in human brain tissue. J Neurochem. 1989 Dec;53(6):1787–1793. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Barnes N. M., Costall B., Naylor R. J., Tyers M. B. 5-HT3 receptors mediate inhibition of acetylcholine release in cortical tissue. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):762–763. doi: 10.1038/338762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boess F. G., Martin I. L. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):275–317. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonhaus D. W., Wong E. H., Stefanich E., Kunysz E. A., Eglen R. M. Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptors in murine brain and ileum using the novel radioligand [3H]RS-42358-197: evidence for receptor heterogeneity. J Neurochem. 1993 Nov;61(5):1927–1932. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb09835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A., Elswood C. J., Burridge J., Ireland S. J., Bunce K. T., Kilpatrick G. J., Tyers M. B. The pharmacological characterization of 5-HT3 receptors in three isolated preparations derived from guinea-pig tissues. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):591–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
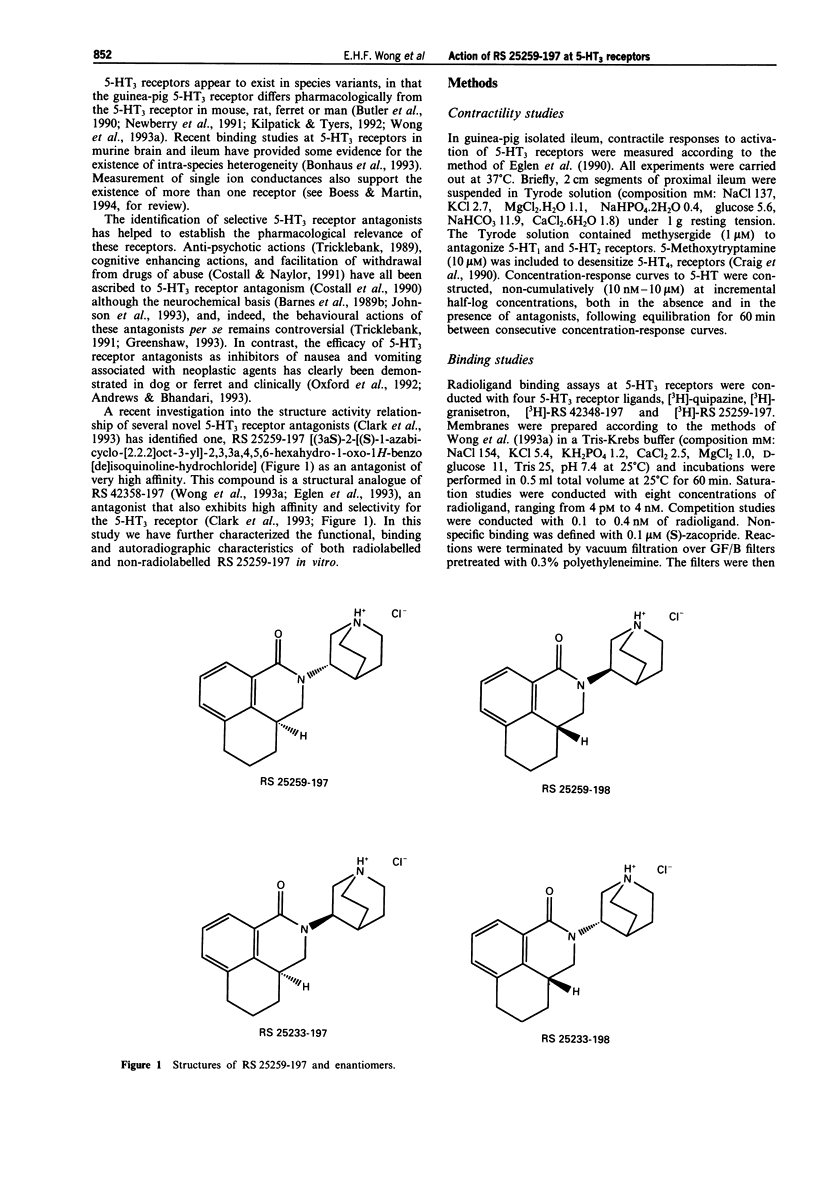
- Clark R. D., Miller A. B., Berger J., Repke D. B., Weinhardt K. K., Kowalczyk B. A., Eglen R. M., Bonhaus D. W., Lee C. H., Michel A. D. 2-(Quinuclidin-3-yl)pyrido[4,3-b]indol-1-ones and isoquinolin-1-ones. Potent conformationally restricted 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1993 Sep 3;36(18):2645–2657. doi: 10.1021/jm00070a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costall B., Naylor R. J. Pharmacological properties and functions of central 5-HT3 receptors. Therapie. 1991 Nov-Dec;46(6):437–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costall B., Naylor R. J., Tyers M. B. The psychopharmacology of 5-HT3 receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;47(2):181–202. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90086-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig D. A., Eglen R. M., Walsh L. K., Perkins L. A., Whiting R. L., Clarke D. E. 5-Methoxytryptamine and 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine-induced desensitization as a discriminative tool for the 5-HT3 and putative 5-HT4 receptors in guinea pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;342(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00178965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkach V., Surprenant A., North R. A. 5-HT3 receptors are membrane ion channels. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):706–709. doi: 10.1038/339706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Lee C. H., Smith W. L., Johnson L. G., Clark R., Whiting R. L., Hegde S. S. Pharmacological characterization of RS 25259-197, a novel and selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Feb;114(4):860–866. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Lee C. H., Smith W. L., Johnson L. G., Whiting R. L., Hegde S. S. RS 42358-197, a novel and potent 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Aug;266(2):535–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Swank S. R., Walsh L. K., Whiting R. L. Characterization of 5-HT3 and 'atypical' 5-HT receptors mediating guinea-pig ileal contractions in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):513–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R. Neuronal 5-HT receptors in the periphery. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Dec;23(12B):1473–1486. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenshaw A. J. Behavioural pharmacology of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists: a critical update on therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jul;14(7):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Clarke D. E., Fozard J. R., Hartig P. R., Martin G. R., Mylecharane E. J., Saxena P. R., Humphrey P. P. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin). Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):157–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Neijt H. C. Identification of serotonin 5-HT3 recognition sites in membranes of N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells by radioligand binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;33(3):303–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Inouye G. T., Eglen R. M., Wong E. H. 5-HT3 receptor ligands lack modulatory influence on acetylcholine release in rat entorhinal cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;347(3):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00167441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick G. J., Jones B. J., Tyers M. B. Binding of the 5-HT3 ligand, [3H]GR65630, to rat area postrema, vagus nerve and the brains of several species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 10;159(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90700-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick G. J., Jones B. J., Tyers M. B. The distribution of specific binding of the 5-HT3 receptor ligand [3H]GR65630 in rat brain using quantitative autoradiography. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 22;94(1-2):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick G. J., Tyers M. B. Inter-species variants of the 5-HT3 receptor. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Feb;20(1):118–121. doi: 10.1042/bst0200118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte A. M., Koscielniak T., Ponchant M., Vergé D., Hamon M., Gozlan H. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of 5-HT3 receptors in the rat CNS using [125I]iodo-zacopride and [3H]zacopride as radioligands. Synapse. 1992 Apr;10(4):271–281. doi: 10.1002/syn.890100402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung E., Michelson S., Villarubia C., Perkins L. A., Eglen R. M. Analysis of concentration-response relationships by seemingly unrelated nonlinear regression (SUNR) technique. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1992 Dec;28(4):209–216. doi: 10.1016/1056-8719(92)90006-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq A. V., Peterson A. S., Brake A. J., Myers R. M., Julius D. Primary structure and functional expression of the 5HT3 receptor, a serotonin-gated ion channel. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1718042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Humphrey P. P. Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine: current perspectives on classification and nomenclature. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKernan R. M., Gillard N. P., Quirk K., Kneen C. O., Stevenson G. I., Swain C. J., Ragan C. I. Purification of the 5-hydroxytryptamine 5-HT3 receptor from NCB20 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13572–13577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn C. M., Peroutka S. J. Characterization of [3H]quipazine binding to 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptors in rat brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1989 Jun;52(6):1787–1792. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Thomas D. R. [3H]-BRL 43694 (Granisetron), a specific ligand for 5-HT3 binding sites in rat brain cortical membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1693–1695. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Cheshire S. H., Gilbert M. J. Evidence that the 5-HT3 receptors of the rat, mouse and guinea-pig superior cervical ganglion may be different. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):615–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford A. W., Bell J. A., Kilpatrick G. J., Ireland S. J., Tyers M. B. Ondansetron and related 5-HT3 antagonists: recent advances. Prog Med Chem. 1992;29:239–270. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. B., Waud D. R. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D. C. Autoradiography of [3H]quipazine in rodent brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct 2;187(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90342-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus L. M., Sarbin N. S., Barefoot D. S., Gordon J. C. Association of [3H]zacopride with 5-HT3 binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 22;168(3):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The kinetics of action of acetylcholine antagonists in smooth muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Apr 19;164(996):488–510. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. P., Engel G., Donatsch P., Stadler P. A. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):126–131. doi: 10.1038/316126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif N. A., Wong E. H., Loury D. N., Stefanich E., Michel A. D., Eglen R. M., Whiting R. L. Characteristics of 5-HT3 binding sites in NG108-15, NCB-20 neuroblastoma cells and rat cerebral cortex using [3H]-quipazine and [3H]-GR65630 binding. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):919–925. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricklebank M. D. Interactions between dopamine and 5-HT3 receptors suggest new treatments for psychosis and drug addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):127–129. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber C., Hoyer D., Palacios J. M. 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptors in the human brain: autoradiographic visualization using [3H]ICS 205-930. Neuroscience. 1989;31(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90382-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber C., Pinkus L. M., Palacios J. M. The (S)-isomer of [3H]zacopride labels 5-HT3 receptors with high affinity in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 8;181(3):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90090-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling K. J., Aspley S., Swain C. J., Saunders J. [3H]quaternised ICS 205-930 labels 5-HT3 receptor binding sites in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 10;149(3):397–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90677-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Robertson D. W., Reid L. R. Specific [3H]LY278584 binding to 5-HT3 recognition sites in rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul 4;166(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90689-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Bonhaus D. W., Lee J. A., Wu I., Loury D. N., Eglen R. M. Different densities of 5-HT3 receptors are labeled by [3H]quipazine, [3H]GR 65630 and [3H]granisetron. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Sep;32(9):869–875. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90142-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Bonhaus D. W., Wu I., Stefanich E., Eglen R. M. Labelling of 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptors with a novel 5-HT3 receptor ligand, [3H]RS-42358-197. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):921–930. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]