Abstract
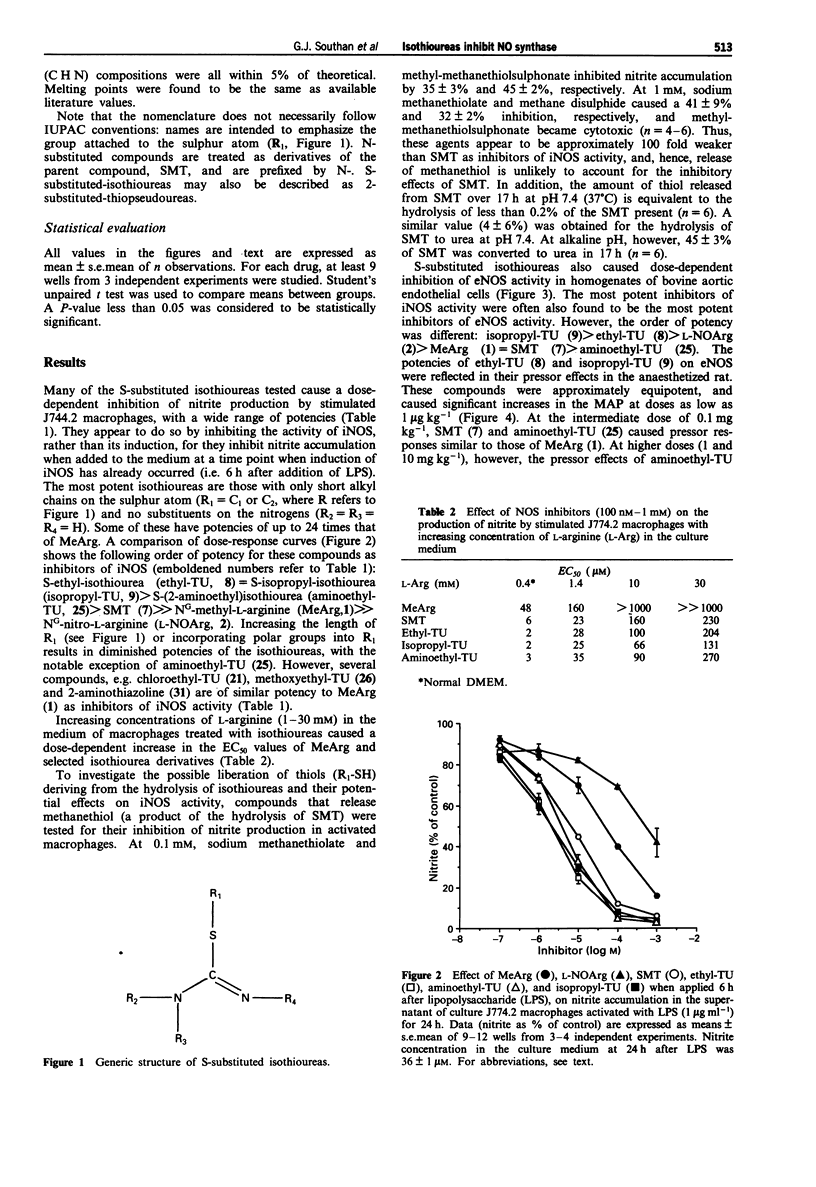
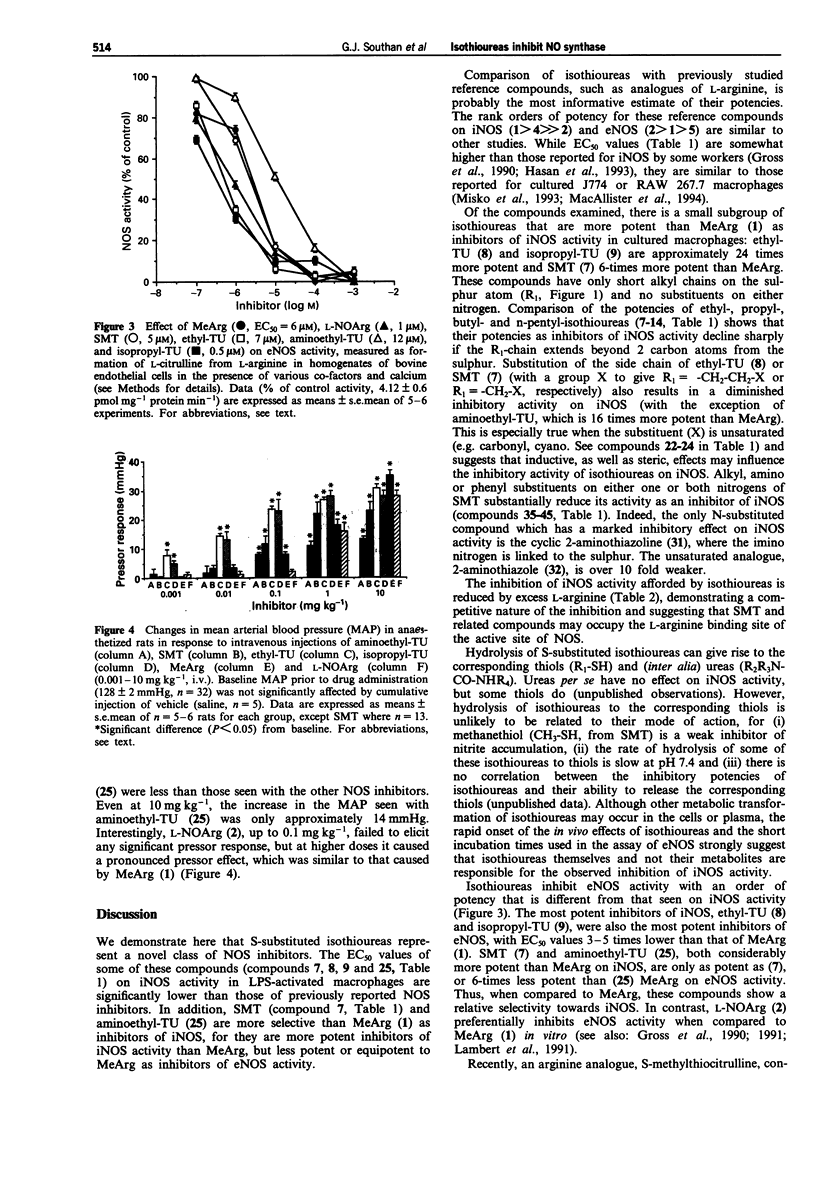
1. The induction of a calcium-independent isoform of nitric oxide (NO) synthase (iNOS) and a subsequent enhanced formation of NO has been implicated in the pathophysiology of a variety of diseases including inflammation and circulatory shock. Here we demonstrate that the S-substituted isothioureas, S-methylisothiourea (SMT), S-(2-aminoethyl)isothiourea (aminoethyl-TU), S-ethylisothiourea (ethyl-TU) and S-isopropylisothiourea (isopropyl-TU) potently inhibit iNOS activity in J774.2 macrophages activated with bacterial endotoxin with EC50 values 8-24 times lower than that of NG-methyl-L-arginine (MeArg) and 200-times lower than that of NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NO2Arg). 2. The inhibition of iNOS activity by these S-substituted isothioureas is dose-dependently prevented by excess of L-arginine suggesting that these isothioureas are competitive inhibitors of iNOS at the L-arginine binding site. 3. Ethyl-TU and isopropyl-TU are 4-6 times more potent than MeArg in inhibiting the constitutive NOS activity in homogenates of bovine aortic endothelial cells (eNOS) and are more potent pressor agents than MeArg in the anaesthetized rat. SMT is equipotent with MeArg, whereas aminoethyl-TU is 6-times less potent in inhibiting eNOS activity in vitro. Both SMT and aminoethyl-TU, however, elicit only weak pressor responses (approximately 15 mmHg at 10 mg kg-1, i.v.) in vivo. 4. A comparison of the potencies of ethyl-, iso-propyl-, n-propyl-, t-butyl- and n-butyl-isothioureas on iNOS activity shows that the inhibitory activity of S-substituted isothioureas declines sharply if the side chain exceeds 2 carbon atoms in length.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babbedge R. C., Bland-Ward P. A., Hart S. L., Moore P. K. Inhibition of rat cerebellar nitric oxide synthase by 7-nitro indazole and related substituted indazoles. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):225–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Advanced glycosylation products quench nitric oxide and mediate defective endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in experimental diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):432–438. doi: 10.1172/JCI115014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calver A., Collier J., Vallance P. Nitric oxide and cardiovascular control. Exp Physiol. 1993 May;78(3):303–326. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1993.sp003687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Tilton R. G., Chang K., Hasan K. S., Ido Y., Wang J. L., Sweetland M. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Williamson J. R., McDaniel M. L. Aminoguanidine, a novel inhibitor of nitric oxide formation, prevents diabetic vascular dysfunction. Diabetes. 1992 Apr;41(4):552–556. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinerman J. L., Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Molecular mechanisms of nitric oxide regulation. Potential relevance to cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 1993 Aug;73(2):217–222. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Kassell N. F., Sasaki T., Nakagomi T., Lehman R. M. Selective hemoglobin inhibition of endothelium-dependent vasodilation of rabbit basilar artery. J Neurosurg. 1986 Mar;64(3):445–452. doi: 10.3171/jns.1986.64.3.0445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Jaffe E. A., Levi R., Kilbourn R. G. Cytokine-activated endothelial cells express an isotype of nitric oxide synthase which is tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent, calmodulin-independent and inhibited by arginine analogs with a rank-order of potency characteristic of activated macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90965-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Stuehr D. J., Aisaka K., Jaffe E. A., Levi R., Griffith O. W. Macrophage and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthesis: cell-type selective inhibition by NG-aminoarginine, NG-nitroarginine and NG-methylarginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91245-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan K., Heesen B. J., Corbett J. A., McDaniel M. L., Chang K., Allison W., Wolffenbuttel B. H., Williamson J. R., Tilton R. G. Inhibition of nitric oxide formation by guanidines. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 2;249(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90667-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Zheng Y. M., Heber-Katz E., Fraser N., Rorke L., Fu Z. F., Hanlon C., Dietzschold B. In vivo expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in experimentally induced neurologic diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3024–3027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert L. E., French J. F., Whitten J. P., Baron B. M., McDonald I. A. Characterization of cell selectivity of two novel inhibitors of nitric oxide synthesis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 May 27;216(1):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90221-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert L. E., Whitten J. P., Baron B. M., Cheng H. C., Doherty N. S., McDonald I. A. Nitric oxide synthesis in the CNS endothelium and macrophages differs in its sensitivity to inhibition by arginine analogues. Life Sci. 1991;48(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90426-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langrehr J. M., Hoffman R. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Simmons R. L. Nitric oxide--a new endogenous immunomodulator. Transplantation. 1993 Jun;55(6):1205–1212. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199306000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Dinerman J. L., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: a physiologic messenger. Ann Intern Med. 1994 Feb 1;120(3):227–237. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-120-3-199402010-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacAllister R. J., Whitley G. S., Vallance P. Effects of guanidino and uremic compounds on nitric oxide pathways. Kidney Int. 1994 Mar;45(3):737–742. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCartney-Francis N., Allen J. B., Mizel D. E., Albina J. E., Xie Q. W., Nathan C. F., Wahl S. M. Suppression of arthritis by an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):749–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Traber L. D., Nelson S., Lentz C. W., Nakazawa H., Herndon D. N., Noda H., Traber D. L. Reversal of hyperdynamic response to continuous endotoxin administration by inhibition of NO synthesis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jul;73(1):324–328. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.1.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Sadowska-Krowicka H., Chotinaruemol S., Kakkis J. L., Clark D. A. Amelioration of chronic ileitis by nitric oxide synthase inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jan;264(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misko T. P., Moore W. M., Kasten T. P., Nickols G. A., Corbett J. A., Tilton R. G., McDaniel M. L., Williamson J. R., Currie M. G. Selective inhibition of the inducible nitric oxide synthase by aminoguanidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 16;233(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90357-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Wallace P., Gaffen Z., Hart S. L., Babbedge R. C. Characterization of the novel nitric oxide synthase inhibitor 7-nitro indazole and related indazoles: antinociceptive and cardiovascular effects. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):219–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., McCracken R., Kaneto H., Vehaskari M., Montani D., Klahr S. Location of an inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA in the normal kidney. Kidney Int. 1994 Apr;45(4):998–1005. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. L., Adams H. R. Selective inhibition of endothelium-dependent vasodilator capacity by Escherichia coli endotoxemia. Circ Res. 1993 Mar;72(3):539–551. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.3.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovic-Racic M., Stadler J., Evans C. H. Nitric oxide and arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Aug;36(8):1036–1044. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Faragó M., Horváth I., Lohinai Z., Kovách A. G. Hemorrhagic hypotension impairs endothelium-dependent relaxations in the renal artery of the cat. Circ Shock. 1992 Mar;36(3):238–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Mitchell J. A., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Nitric oxide-mediated hyporeactivity to noradrenaline precedes the induction of nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin shock. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):786–792. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Southan G. J., Wood E., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Inhibition by spermine of the induction of nitric oxide synthase in J774.2 macrophages: requirement of a serum factor. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;112(2):355–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13078.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Dihydropyridine antagonists and agonists of calcium channels inhibit the induction of nitric oxide synthase by endotoxin in cultured macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 29;196(2):825–830. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C., Szabó C., Mitchell J. A., Vane J. R. Vascular hyporeactivity to vasoconstrictor agents and hemodynamic decompensation in hemorrhagic shock is mediated by nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):267–271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C. The role of the L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway in circulatory shock. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;28:45–79. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60493-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C., Vane J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis reduces the hypotension induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharides in the rat in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 17;182(3):591–595. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90062-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R., Mitchell J. A., Appleton I., Tomlinson A., Bishop-Bailey D., Croxtall J., Willoughby D. A. Inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric-oxide synthase in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. The Croonian Lecture, 1993. The endothelium: maestro of the blood circulation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994 Jan 29;343(1304):225–246. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


