Abstract
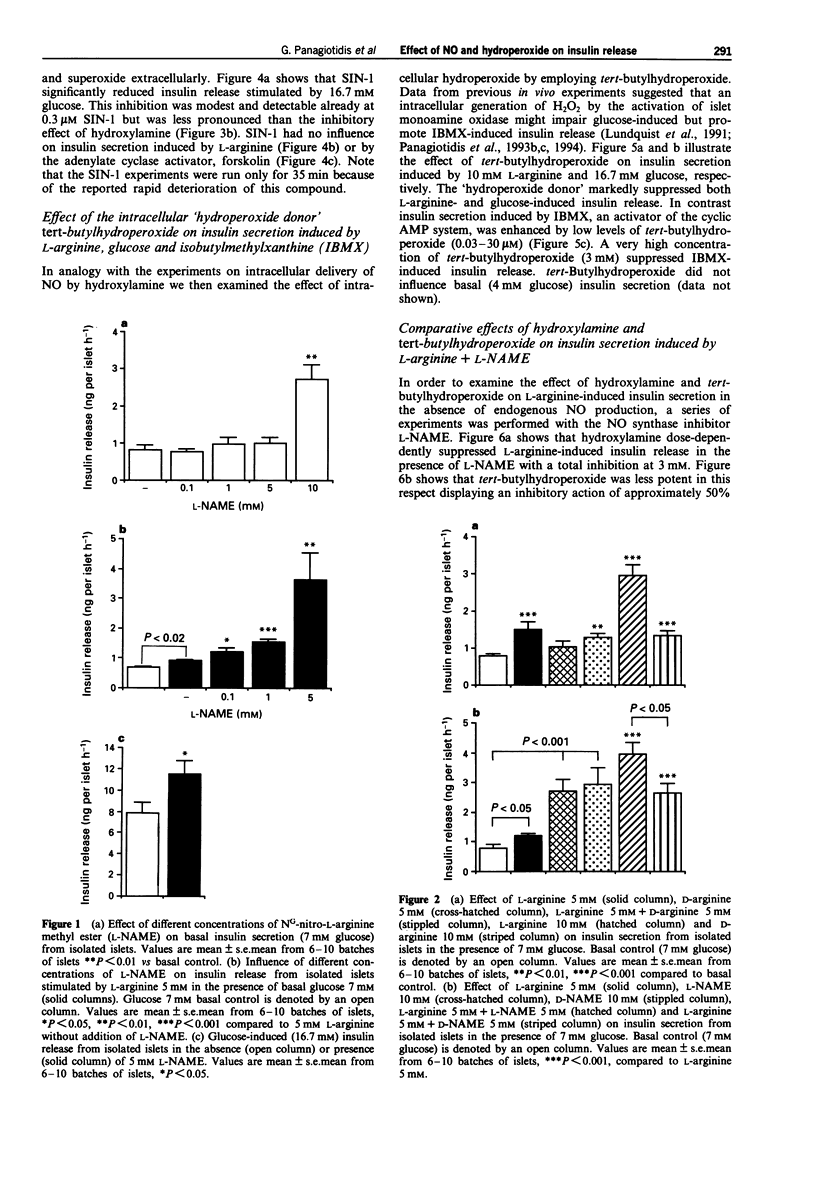
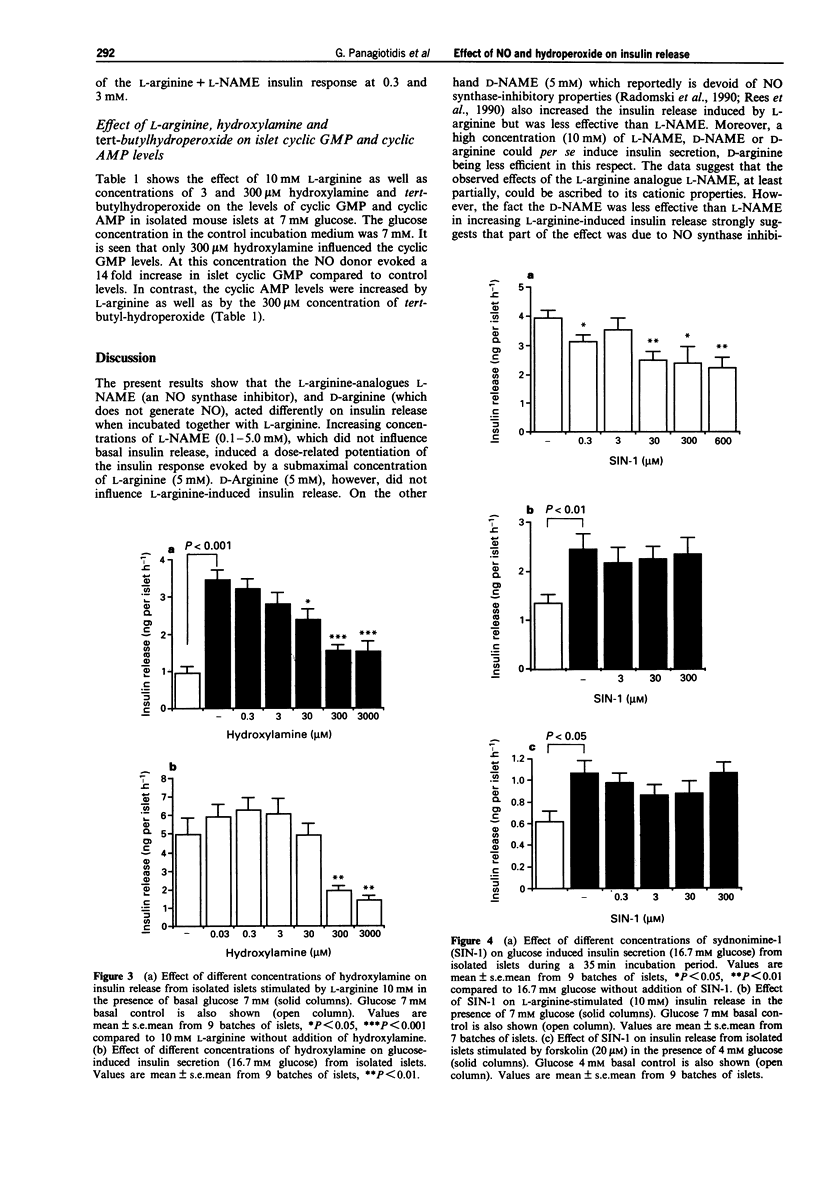
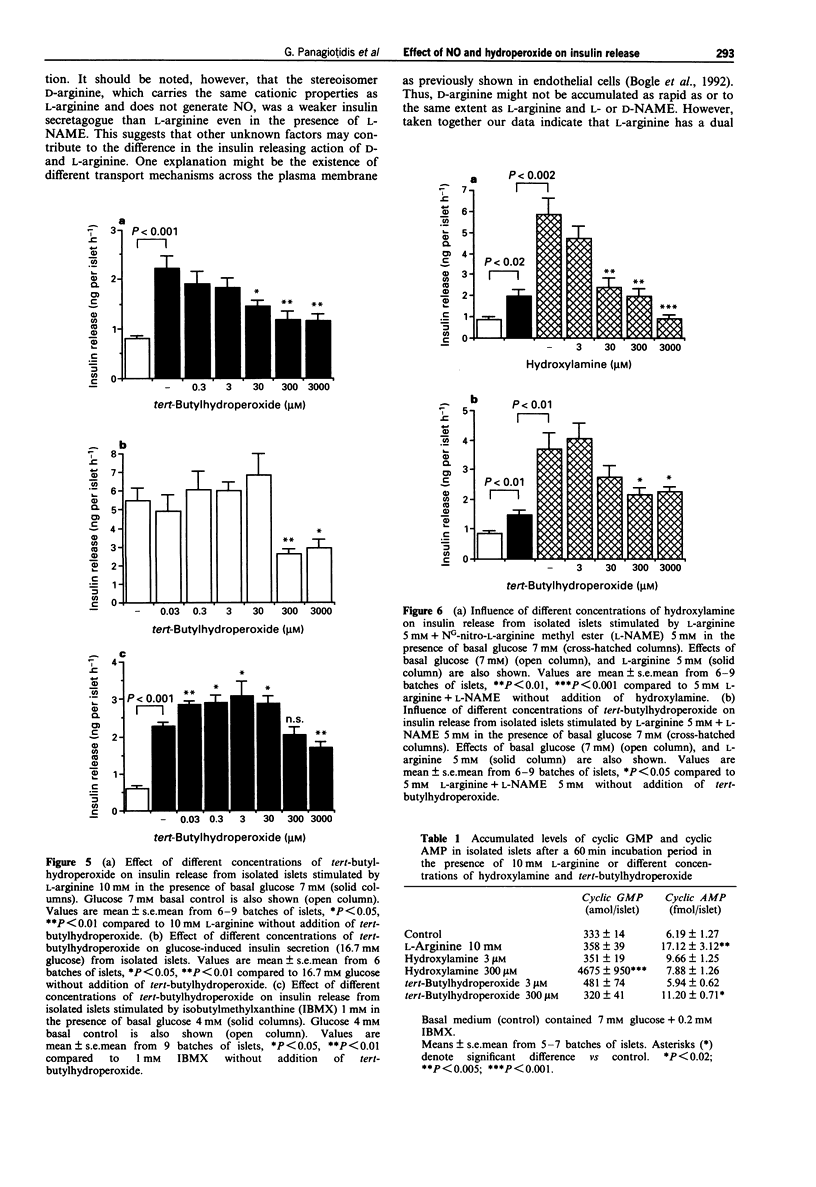
1. Recent studies have suggested that the generation of nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by islet NO synthase and monoamine oxidase, respectively, may have a regulatory influence on insulin secretory processes. We have investigated the pattern of insulin release from isolated islets of Langerhans in the presence of various pharmacological agents known to perturb the intracellular levels of NO and the oxidation state of SH-groups. 2. The NO synthase inhibitor, NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) dose-dependently increased L-arginine-induced insulin release. D-Arginine did not influence L-arginine-induced insulin secretion. However, D-NAME which reportedly has no inhibitory action on NO synthase, modestly increased L-arginine-induced insulin release, but was less effective than L-NAME. High concentrations (10 mM) of D-arginine as well as L-NAME and D-NAME could enhance basal insulin release. 3. The intracellular NO donor, hydroxylamine, dose-dependently inhibited insulin secretion induced by L-arginine and L-arginine+L-NAME. 4. Glucose-induced insulin release was increased by NO synthase inhibition (L-NAME) and inhibited by the intracellular NO donor, hydroxylamine. Sydnonimine-1 (SIN-1), an extracellular donor of NO and superoxide, induced a modest suppression of glucose-stimulated insulin release. SIN-1 did not influence insulin secretion induced by L-arginine or the adenylate cyclase activator, forskolin. 5. The intracellular 'hydroperoxide donor' tert-butylhydroperoxide in the concentration range of 0.03-3 mM inhibited insulin release stimulated by the nutrient secretagogues glucose and L-arginine. Low concentrations (0.03-30 microM) of tert-butylhydroperoxide, however enhanced insulin secretion induced by the phosphodiesterase inhibitor isobutylmethylxanthine (IBMX).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammon H. P., Mark M. Thiols and pancreatic beta-cell function: a review. Cell Biochem Funct. 1985 Jul;3(3):157–171. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290030302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogle R. G., Moncada S., Pearson J. D., Mann G. E. Identification of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase that do not interact with the endothelial cell L-arginine transporter. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):768–770. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Wang J. L., Misko T. P., Zhao W., Hickey W. F., McDaniel M. L. Nitric oxide mediates IL-1 beta-induced islet dysfunction and destruction: prevention by dexamethasone. Autoimmunity. 1993;15(2):145–153. doi: 10.3109/08916939309043889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. cis-Unsaturated fatty acids induce the fusion of chromaffin granules aggregated by synexin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):247–256. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMaster E. G., Raij L., Archer S. L., Weir E. K. Hydroxylamine is a vasorelaxant and a possible intermediate in the oxidative conversion of L-arginine to nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):527–533. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin B. Intracellular calcium, insulin secretion, and action. Am J Med. 1988 Nov 28;85(5A):44–58. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Schmidt H. H., Pollock J. S., Sheng H., Mitchell J. A., Warner T. D., Nakane M., Murad F. Isoforms of nitric oxide synthase. Characterization and purification from different cell types. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 24;42(10):1849–1857. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90581-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Charles M. A., Grodsky G. M. Characterization of the effects of arginine and glucose on glucagon and insulin release from the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):833–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI107823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh M., Maki T., Kiyoizumi T., Satomi S., Monaco A. P. An improved method for isolation of mouse pancreatic islets. Transplantation. 1985 Oct;40(4):437–438. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198510000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Darley-Usmar V. M., Wilson M. T., Moncada S. Production of hydroxyl radicals from the simultaneous generation of superoxide and nitric oxide. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):419–424. doi: 10.1042/bj2810419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson L., Sandler S. The nitric oxide synthase II inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine stimulates pancreatic islet insulin release in vitro, but not in the perfused pancreas. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):3081–3085. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-3081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. M., Persaud S. J., Bjaaland T., Pearson J. D., Howell S. L. Nitric oxide is not involved in the initiation of insulin secretion from rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1992 Nov;35(11):1020–1027. doi: 10.1007/BF02221676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G., Modica M. E., Cavanaugh C. T. L-arginine stimulates cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation in rat islets of Langerhans and RINm5F insulinoma cells: evidence for L-arginine:nitric oxide synthase. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3043–3052. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist I., Panagiotidis G., Stenström A. Effect of L-dopa administration on islet monoamine oxidase activity and glucose-induced insulin release in the mouse. Pancreas. 1991 Sep;6(5):522–527. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199109000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotidis G., Alm P., Lundquist I. Inhibition of islet nitric oxide synthase increases arginine-induced insulin release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 15;229(2-3):277–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90568-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotidis G., Lindström P., Stenström A., Lundquist I. Glucose modulation of islet monoamine oxidase activity in lean and obese hyperglycemic mice. Metabolism. 1993 Nov;42(11):1398–1404. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(93)90189-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotidis G., Stenström A., Lundquist I. Effects of adrenergic and cholinergic stimulation on islet monoamine oxidase activity and insulin secretion in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 23;233(2-3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90063-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotidis G., Stenström A., Lundquist I. Influence of beta 2-adrenoceptor stimulation and glucose on islet monoamine oxidase activity and insulin secretory response in the mouse. Pancreas. 1993 May;8(3):368–374. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199305000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Characterization of the L-arginine:nitric oxide pathway in human platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):325–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salehi A., Lundquist I. Ca2+ deficiency, selective alpha-glucosidehydrolase inhibition, and insulin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):E1–E9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.265.1.E1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Warner T. D., Ishii K., Sheng H., Murad F. Insulin secretion from pancreatic B cells caused by L-arginine-derived nitrogen oxides. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):721–723. doi: 10.1126/science.1371193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J. S., Simon D. I., Osborne J. A., Mullins M. E., Jaraki O., Michel T., Singel D. J., Loscalzo J. S-nitrosylation of proteins with nitric oxide: synthesis and characterization of biologically active compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara E., Tamarit-Rodriguez J. Does cyclic guanosine monophosphate mediate noradrenaline-induced inhibition of islet insulin secretion stimulated by glucose and palmitate? Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):243–248. doi: 10.1042/bj2780243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R. Nitric oxide and arginine-evoked insulin secretion. Science. 1992 Nov 20;258(5086):1376–1378. doi: 10.1126/science.1455235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh N., Eizirik D. L., Bendtzen K., Sandler S. Interleukin-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production in isolated rat pancreatic islets requires gene transcription and may lead to inhibition of the Krebs cycle enzyme aconitase. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3167–3173. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


