Abstract
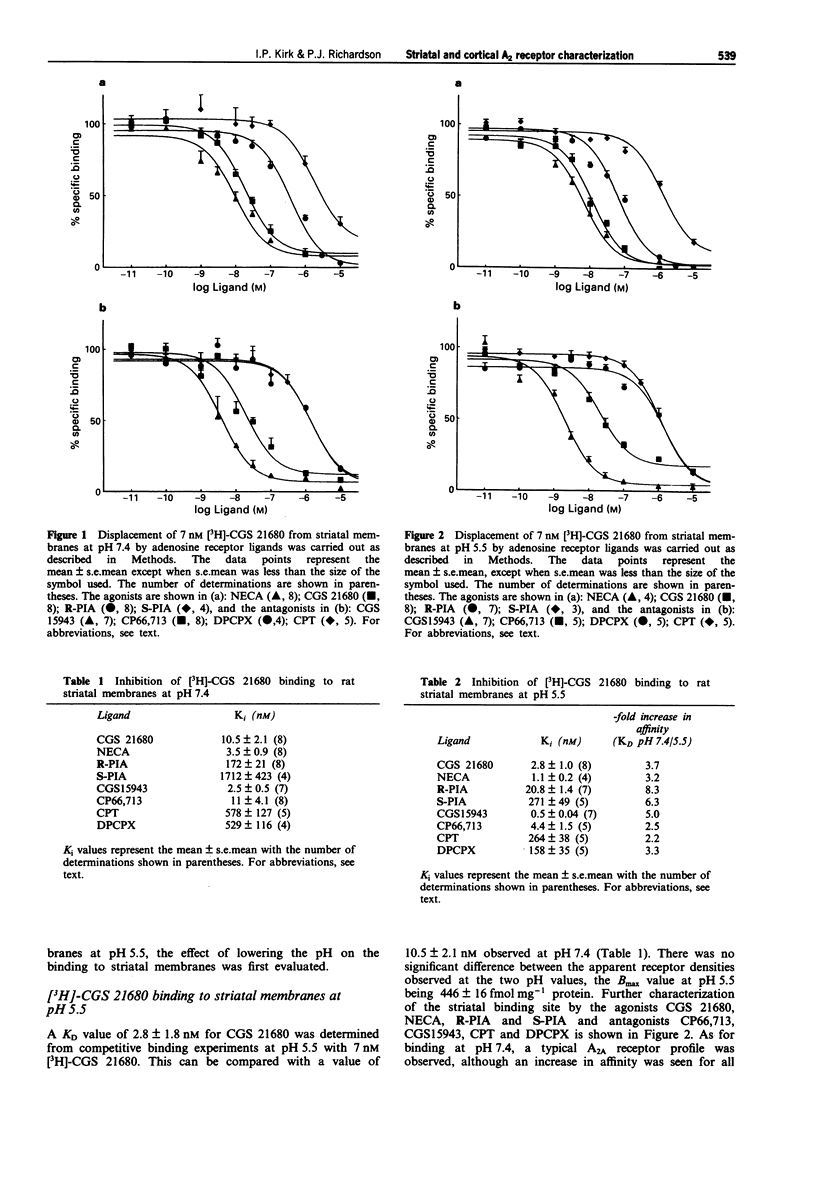
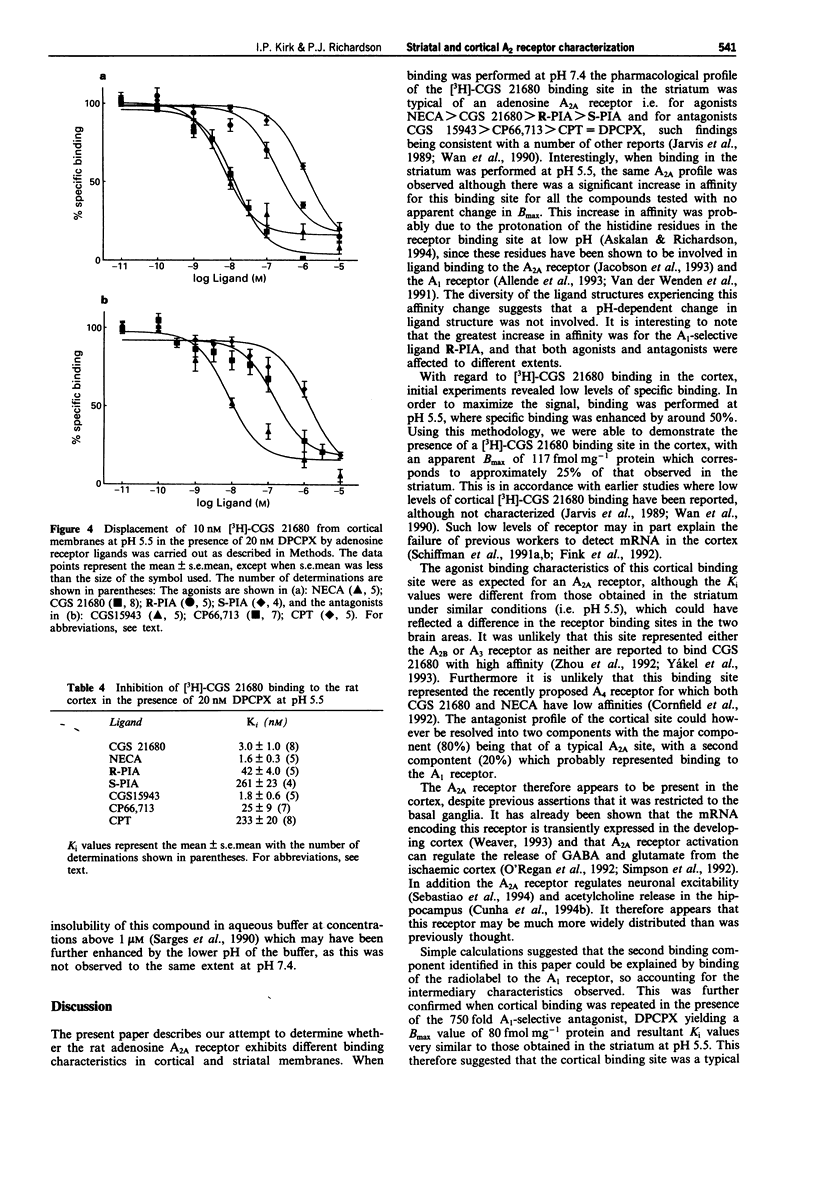
1. The putative high affinity binding site for the adenosine A2A receptor agonist 2-p-(2-carboxyethyl)phenethyl-amino-5'-N- ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (CGS 21680) in the rat cerebral cortex was characterized by use of a number of selective A1 and A2 adenosine receptor ligands, and compared to the characteristics of the more abundant striatal A2A receptor. 2. The binding of [3H]-CGS 21680 to cortical membranes was performed at pH 5.5, in order to increase the amount of specific binding. 3. Reduction of the pH from 7.4 to 5.5 increased the apparent affinity of the striatal binding side for both agonists and antagonists. The relative order of potencies of both groups of ligands were the same at both pH values, and were consistent with binding to the A2A receptor. There was no observable change in the Bmax, the values being 415 and 446 fmol mg-1 protein at pH 5.5 and 7.4 respectively. 4. The cortical binding site yielded a Bmax value of 117 fmol mg-1 protein. The relative order of potencies of the adenosine receptor ligands observed at this binding site were not the same as those observed in the striatum, exhibiting a profile with both A1 and A2 characteristics. 5. Further characterization of this cortical binding site in the presence of the A1 selective antagonist 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine (DPCPX) revealed a more typical A2A profile. This indicated that under the conditions used there were two components of [3H]-CGS 21680 binding, approximately 20% of the A1 receptor and 80% to the A2A receptor.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

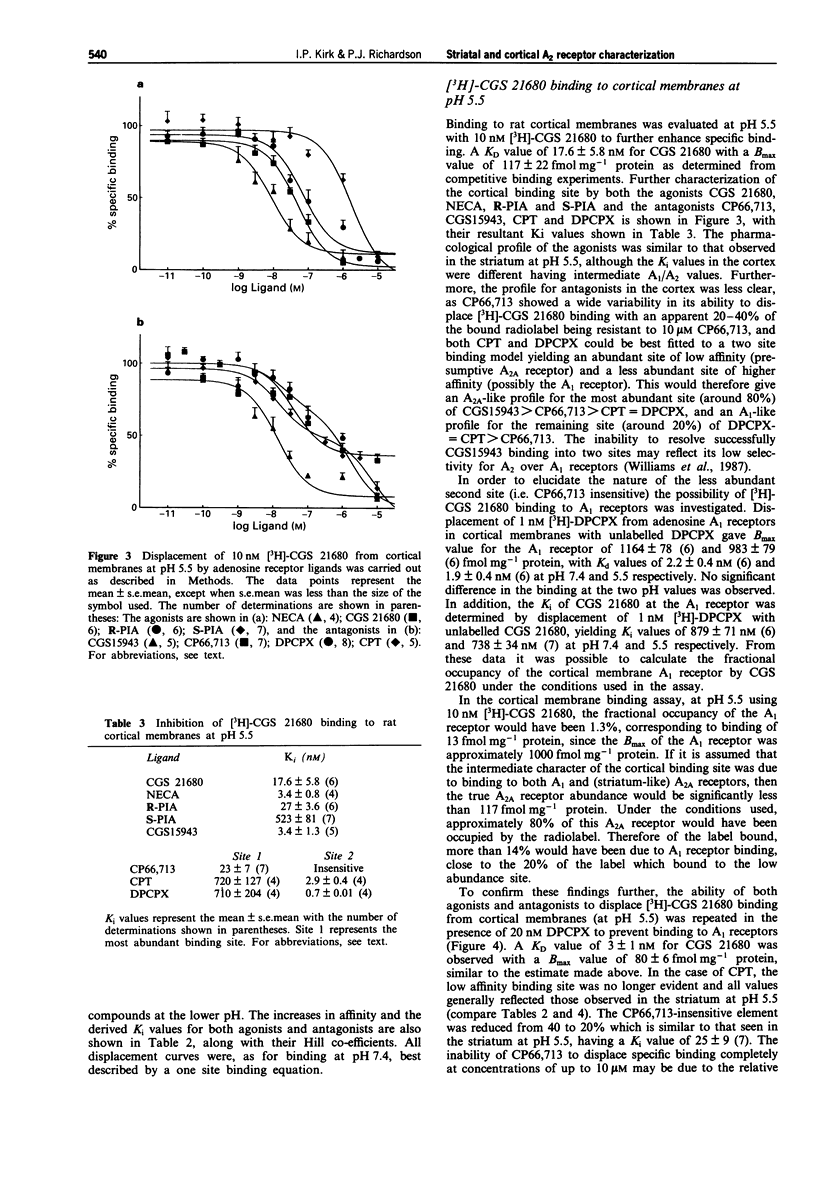


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allende G., Casadó V., Mallol J., Franco R., Lluis C., Canela E. I. Role of histidine residues in agonist and antagonist binding sites of A1 adenosine receptor. J Neurochem. 1993 Apr;60(4):1525–1533. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. J., James S., Reddington M., Richardson P. J. Both A1 and A2a purine receptors regulate striatal acetylcholine release. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lu G. H., Pugsley T. A. Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornfield L. J., Hu S., Hurt S. D., Sills M. A. [3H]2-phenylaminoadenosine ([3H]CV 1808) labels a novel adenosine receptor in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Nov;263(2):552–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha R. A., Milusheva E., Vizi E. S., Ribeiro J. A., Sebastião A. M. Excitatory and inhibitory effects of A1 and A2A adenosine receptor activation on the electrically evoked [3H]acetylcholine release from different areas of the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1994 Jul;63(1):207–214. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63010207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBlasi A., O'Reilly K., Motulsky H. J. Calculating receptor number from binding experiments using same compound as radioligand and competitor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jun;10(6):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. S., Weaver D. R., Rivkees S. A., Peterfreund R. A., Pollack A. E., Adler E. M., Reppert S. M. Molecular cloning of the rat A2 adenosine receptor: selective co-expression with D2 dopamine receptors in rat striatum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Jul;14(3):186–195. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Dunwiddie T. V. How does adenosine inhibit transmitter release? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Apr;9(4):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S., Xuereb J. H., Askalan R., Richardson P. J. Adenosine receptors in post-mortem human brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;105(1):238–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Schulz R., Hutchison A. J., Do U. H., Sills M. A., Williams M. [3H]CGS 21680, a selective A2 adenosine receptor agonist directly labels A2 receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Williams M. Direct autoradiographic localization of adenosine A2 receptors in the rat brain using the A2-selective agonist, [3H]CGS 21680. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 13;168(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90571-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B., Georgiev V., Parkinson F. E., Fredholm B. B. The binding of the adenosine A2 receptor selective agonist [3H]CGS 21680 to rat cortex differs from its binding to rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct 15;247(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90066-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk I. P., Richardson P. J. Adenosine A2a receptor-mediated modulation of striatal [3H]GABA and [3H]acetylcholine release. J Neurochem. 1994 Mar;62(3):960–966. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62030960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick K. A., Richardson P. J. Adenosine receptor-mediated modulation of acetylcholine release from rat striatal synaptosomes. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):949–954. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13905.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield R. D., Suzuki F., Zahniser N. R. Adenosine A2a receptor modulation of electrically evoked endogenous GABA release from slices of rat globus pallidus. J Neurochem. 1993 Jun;60(6):2334–2337. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanoff C., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. The A2 adenosine receptor: guanine nucleotide modulation of agonist binding is enhanced by proteolysis. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;39(2):130–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Regan M. H., Simpson R. E., Perkins L. M., Phillis J. W. Adenosine receptor agonists inhibit the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) from the ischemic rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1992 Jun 5;582(1):22–26. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90312-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarges R., Howard H. R., Browne R. G., Lebel L. A., Seymour P. A., Koe B. K. 4-Amino[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalines. A novel class of potent adenosine receptor antagonists and potential rapid-onset antidepressants. J Med Chem. 1990 Aug;33(8):2240–2254. doi: 10.1021/jm00170a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann S. N., Jacobs O., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Striatal restricted adenosine A2 receptor (RDC8) is expressed by enkephalin but not by substance P neurons: an in situ hybridization histochemistry study. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):1062–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann S. N., Libert F., Vassart G., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Distribution of adenosine A2 receptor mRNA in the human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Sep 16;130(2):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada J., Suzuki F., Nonaka H., Ishii A., Ichikawa S. (E)-1,3-dialkyl-7-methyl-8-(3,4,5-trimethoxystyryl)xanthines: potent and selective adenosine A2 antagonists. J Med Chem. 1992 Jun 12;35(12):2342–2345. doi: 10.1021/jm00090a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. E., O'Regan M. H., Perkins L. M., Phillis J. W. Excitatory transmitter amino acid release from the ischemic rat cerebral cortex: effects of adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1683–1690. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukena D., Poeschla E., Hüttemann E., Schwabe U. Effects of N-ethylmaleimide on adenosine receptors of rat fat cells and human platelets. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;327(3):247–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00502457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan W., Sutherland G. R., Geiger J. D. Binding of the adenosine A2 receptor ligand [3H]CGS 21680 to human and rat brain: evidence for multiple affinity sites. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1763–1771. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. R. A2a adenosine receptor gene expression in developing rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993 Dec;20(4):313–327. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(93)90058-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Francis J., Ghai G., Braunwalder A., Psychoyos S., Stone G. A., Cash W. D. Biochemical characterization of the triazoloquinazoline, CGS 15943, a novel, non-xanthine adenosine antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):415–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakel J. L., Warren R. A., Reppert S. M., North R. A. Functional expression of adenosine A2b receptor in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;43(2):277–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Li C., Olah M. E., Johnson R. A., Stiles G. L., Civelli O. Molecular cloning and characterization of an adenosine receptor: the A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7432–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


