Abstract
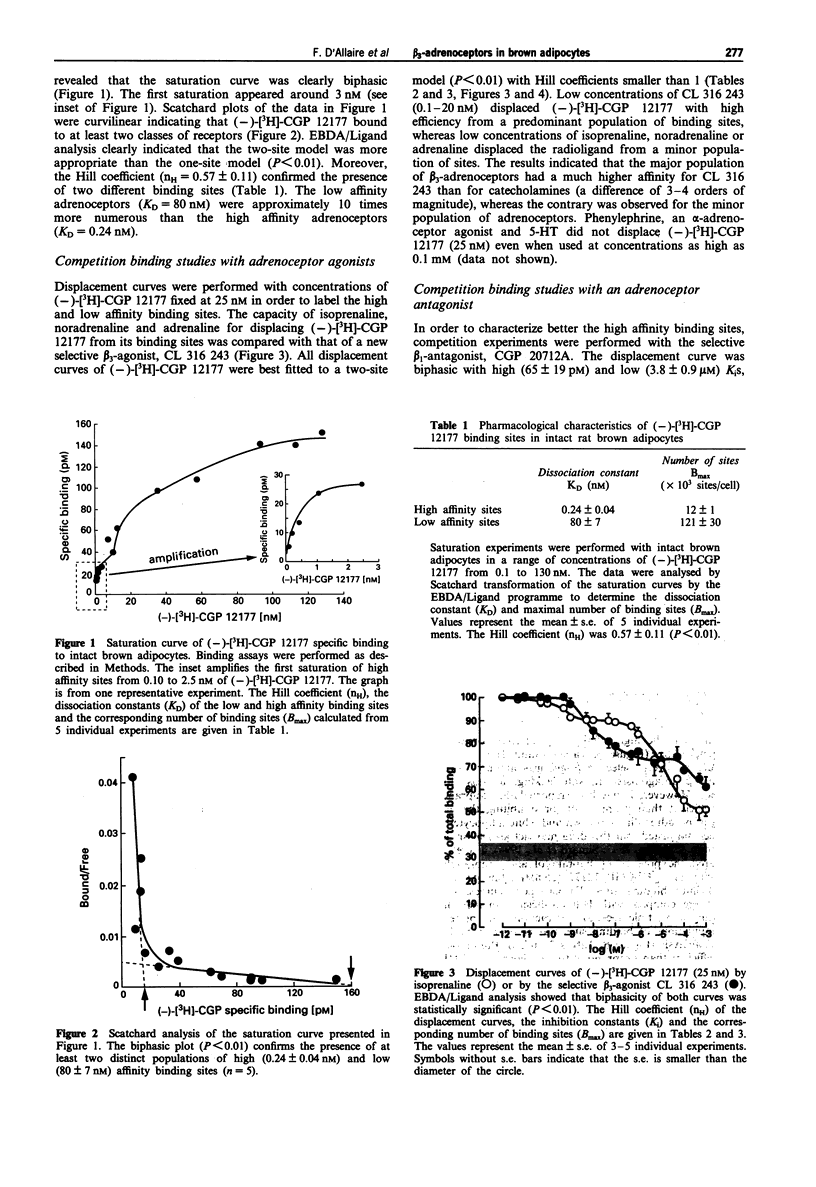
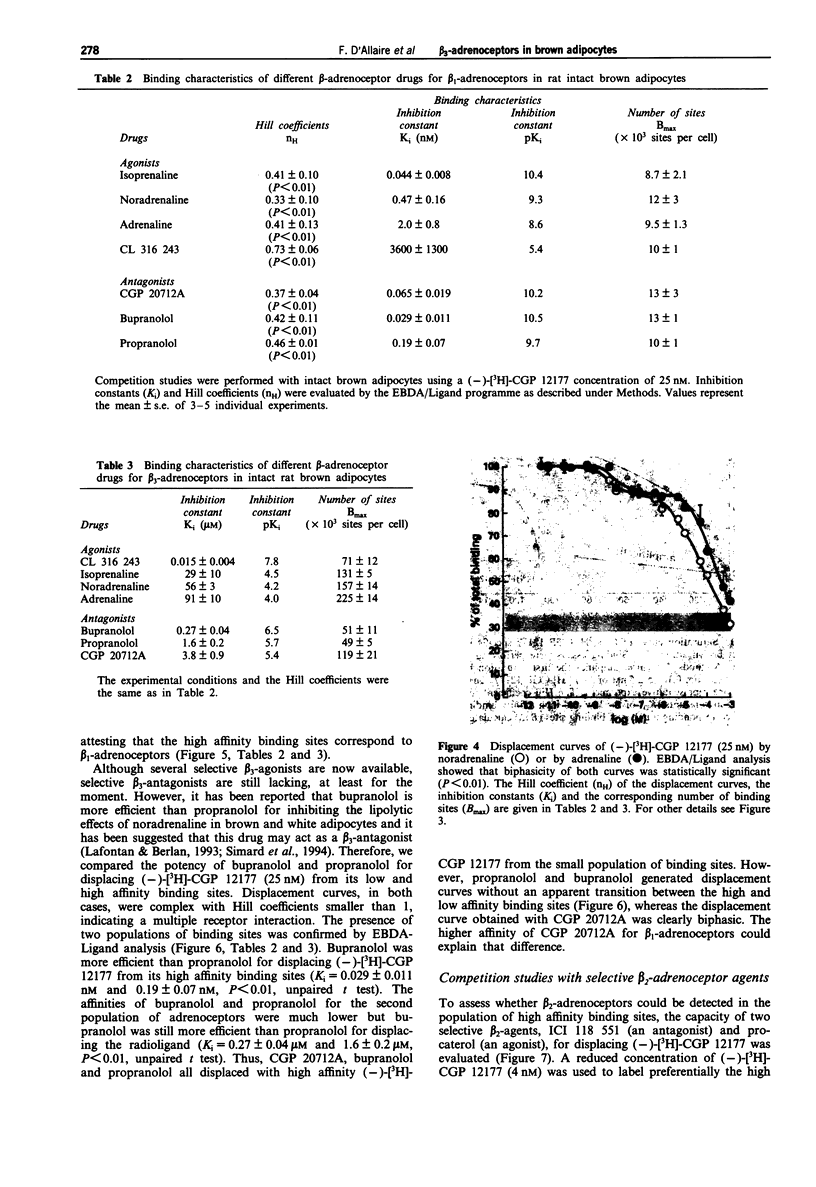
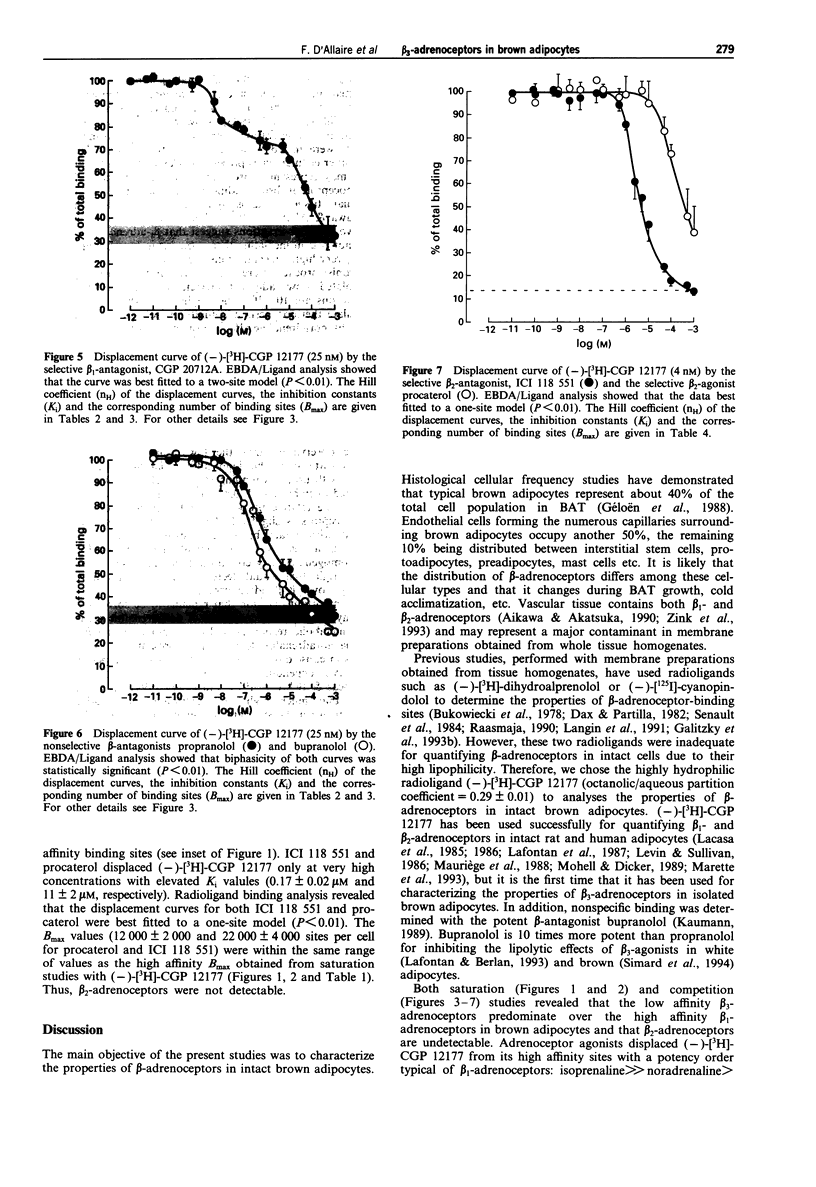
1. The binding properties of beta 1-, beta 2- and beta 3-adrenoceptors were determined in isolated brown adipocytes of the rat rather than in membrane preparations from tissue homogenates, because typical brown adipocytes represent only about 40% of the various cells present in brown adipose tissue. Binding characteristics were assessed with the hydrophilic beta-adrenoceptor radioligand, (-)-[3H]-CGP 12177. The potent beta-antagonist, bupranolol (100 microM) was used to determine nonspecific binding. Characterization was essentially performed by saturation and competition studies. 2. The saturation curve of (-)-[3H]-CGP 12177 was clearly biphasic (Hill coefficient, nH = 0.57 +/- 0.11, P < 0.01) indicating the presence of two different beta-adrenoceptor populations of high (KD = 0.24 +/- 0.04 nM) and low (KD = 80 +/- 7 nM) affinity. The low affinity sites were more numerous (Bmax = 121,000 +/- 30,000 sites/cell) than the high affinity sites (Bmax = 12,000 +/- 1,000 sites/cell). 3. (-)-[3H]-CGP 12177 (25 nM) was displaced by adrenaline (Ad), noradrenaline (NA), isoprenaline (Iso), phenylephrine (Phe) and by the new beta 3 agonist, CL 316,243 (CL) in a biphasic pattern. The order of potency for (-)-[3H]-CGP 12177 displacement from the small population of high affinity sites (Iso >> NA > Ad >> CL >> Phe was in agreement with a beta 1/beta 2-classification. In contrast, the potencies of the same agonists for displacing the radioligand from the low affinity binding sites (CL >> Iso > NA > Ad >> Phe) revealed the presence of a distinct population of adrenoceptors obeying a beta 3-classification.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa J., Akatsuka N. Vascular smooth muscle relaxation by endothelium-dependent beta 1-adrenergic action. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1990;97(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(90)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Ainsworth A. T., Cawthorne M. A., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Thody V. E., Wilson C., Wilson S. Atypical beta-adrenoceptor on brown adipocytes as target for anti-obesity drugs. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):163–165. doi: 10.1038/309163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R. The brown adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor. Proc Nutr Soc. 1989 Jul;48(2):215–223. doi: 10.1079/pns19890032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. D., Dutia M. D., Johnson B. D., Wissner A., Burns M. G., Largis E. E., Dolan J. A., Claus T. H. Disodium (R,R)-5-[2-[[2-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]-amino] propyl]-1,3-benzodioxole-2,2-dicarboxylate (CL 316,243). A potent beta-adrenergic agonist virtually specific for beta 3 receptors. A promising antidiabetic and antiobesity agent. J Med Chem. 1992 Aug 7;35(16):3081–3084. doi: 10.1021/jm00094a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L. J., Folléa N., Lupien J., Paradis A. Metabolic relationships between lipolysis and respiration in rat brown adipocytes. The role of long chain fatty acids as regulators of mitochondrial respiration and feedback inhibitors of lipolysis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12840–12848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L. J., Géloën A., Collet A. J. Proliferation and differentiation of brown adipocytes from interstitial cells during cold acclimation. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):C880–C887. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.6.C880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L., Follea N., Vallieres J., Leblanc J. Beta-Adrenergic receptors in brown-adipose tissue. Characterization and alterations during acclimation of rats to cold. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L., Folléa N., Paradis A., Collet A. Stereospecific stimulation of brown adipocyte respiration by catecholamines via beta 1-adrenoreceptors. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):E552–E563. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.6.E552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpéné C., Ambid L., Lafontan M. Predominance of beta 3-adrenergic component in catecholamine activation of lipolysis in garden dormouse adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 2):R896–R904. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.3.R896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpéné C., Galitzky J., Collon P., Esclapez F., Dauzats M., Lafontan M. Desensitization of beta-1 and beta-2, but not beta-3, adrenoceptor-mediated lipolytic responses of adipocytes after long-term norepinephrine infusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Apr;265(1):237–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottle M. K., Cottle W. H., Pérusse F., Bukowiecki L. J. An improved glyoxylic acid technique for the histochemical localization of catecholamines in brown adipose tissue. Histochem J. 1985 Dec;17(12):1279–1288. doi: 10.1007/BF01002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dax E. M., Partilla J. S. Adrenergic ligand liposolubility in membranes. Direct assessment in a beta-adrenergic binding system. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;22(1):5–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depocas F., Behrens W. A., Foster D. O. Noradrenaline-induced calorigenesis in warm- and in cold-acclimated rats: the interrelation of dose of noradrenaline, its concentration in arterial plasma, and calorigenic response. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Apr;56(2):168–174. doi: 10.1139/y78-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depocas F., Behrens W. A. Levels of noradrenaline in plasma during thermogenesis induced by cold-exposure or by noradrenaline infusion in warm- and in cold-acclimated rats. Experientia Suppl. 1978;32:135–146. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-5559-4_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Emorine L. J., Lasnier F., Blin N., Baude B., Nahmias C., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J. Atypical beta-adrenergic receptor in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Pharmacological and molecular relationship with the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20329–20336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galitzky J., Reverte M., Carpene C., Lafontan M., Berlan M. Beta 3-adrenoceptors in dog adipose tissue: studies on their involvement in the lipomobilizing effect of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):358–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galitzky J., Reverte M., Portillo M., Carpéné C., Lafontan M., Berlan M. Coexistence of beta 1-, beta 2-, and beta 3-adrenoceptors in dog fat cells and their differential activation by catecholamines. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):E403–E412. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.264.3.E403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goglia F., Géloën A., Lanni A., Minaire Y., Bukowiecki L. J. Morphometric-stereologic analysis of brown adipocyte differentiation in adult mice. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C1018–C1023. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G. Effects of agonist exposure on the coupling of beta 1 and beta 3 adrenergic receptors to adenylyl cyclase in isolated adipocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):638–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N. Differential adrenergic regulation of beta 1- and beta 3-adrenoreceptor messenger ribonucleic acids in adipose tissues. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):109–114. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1309320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G. Norepinephrine and BRL 37344 stimulate adenylate cyclase by different receptors in rat brown adipose tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Aug;254(2):508–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Géloën A., Collet A. J., Guay G., Bukowiecki L. J. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of brown adipocyte proliferation. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):C175–C182. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.1.C175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Géloën A., Collet A. J., Guay G., Bukowiecki L. J. In vivo differentiation of brown adipocytes in adult mice: an electron microscopic study. Am J Anat. 1990 Aug;188(4):366–372. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001880404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumann A. J. Is there a third heart beta-adrenoceptor? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Aug;10(8):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacasa D., Agli B., Giudicelli Y. Direct assessment of beta-adrenergic receptors in intact rat adipocytes by binding of [3H]CGP 12177. Evidence for agonist high-affinity binding complex and for beta 1 and beta 2 receptor subtypes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):339–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacasa D., Mauriège P., Lafontan M., Berlan M., Giudicelli Y. A reliable assay for beta-adrenoceptors in intact isolated human fat cells with a hydrophilic radioligand, [3H]CGP-12177. J Lipid Res. 1986 Apr;27(4):368–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafontan M., Berlan M. Fat cell adrenergic receptors and the control of white and brown fat cell function. J Lipid Res. 1993 Jul;34(7):1057–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Portillo M. P., Saulnier-Blache J. S., Lafontan M. Coexistence of three beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in white fat cells of various mammalian species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. E., Sullivan A. C. Beta-1 receptor is the predominant beta-adrenoreceptor on rat brown adipose tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):681–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. Beta-adrenergic receptors and their mode of coupling to adenylate cyclase. Physiol Rev. 1986 Jul;66(3):819–854. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.3.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Pérusse F., Bukowiecki L. J. Chronic norepinephrine infusion stimulates glucose uptake in white and brown adipose tissues. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 2):R914–R920. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.3.R914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marette A., Mauriège P., Després J. P., Tulp O. L., Bukowiecki L. J. Norepinephrine- and insulin-resistant glucose transport in brown adipocytes from diabetic SHR/N-cp rats. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):R577–R583. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.265.3.R577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauriège P., De Pergola G., Berlan M., Lafontan M. Human fat cell beta-adrenergic receptors: beta-agonist-dependent lipolytic responses and characterization of beta-adrenergic binding sites on human fat cell membranes with highly selective beta 1-antagonists. J Lipid Res. 1988 May;29(5):587–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohell N., Dicker A. The beta-adrenergic radioligand [3H]CGP-12177, generally classified as an antagonist, is a thermogenic agonist in brown adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):401–405. doi: 10.1042/bj2610401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohell N., Nedergaard J. Comparison of the pharmacological profiles of adrenergic drugs (including BRL-agonists) at [3H]prazosin and [3H]CGP-12177 binding sites in brown adipose tissue. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1989;94(1):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(89)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzzin P., Revelli J. P., Fraser C. M., Giacobino J. P. Radioligand binding studies of the atypical beta 3-adrenergic receptor in rat brown adipose tissue using [3H]CGP 12177. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 24;298(2-3):162–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80046-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raasmaja A. Alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic receptors in brown adipose tissue and the adrenergic regulation of thyroxine 5'-deiodinase. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1990;590:1–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revelli J. P., Pescini R., Muzzin P., Seydoux J., Fitzgerald M. G., Fraser C. M., Giacobino J. P. Changes in beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor mRNA levels in brown adipose tissue and heart of hypothyroid rats. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):625–629. doi: 10.1042/bj2770625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J., Sudera D. K. Beta-adrenoreceptors in rat brown adipose tissue: proportions of beta 1- and beta 2-subtypes. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 1):E397–E402. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.4.E397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senault C., Le Comte V., Portet R. Characteristics of beta-adrenergic receptors in isolated cells and in crude membranes of brown adipose tissue. Biochimie. 1984 Jul-Aug;66(7-8):573–578. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(84)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence M. N., Moore N. G., Pegg G. G., Lindsay D. B. Ligand binding properties of putative beta 3-adrenoceptors compared in brown adipose tissue and in skeletal muscle membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1157–1163. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard P. M., Atgié C., Mauriège P., D'Allaire F., Bukowiecki L. J. Comparison of the lipolytic effects of norepinephrine and BRL 37344 in rat brown and white adipocytes. Obes Res. 1994 Sep;2(5):424–431. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1994.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin M., Simons P., Jaeggi K., Wigger N. CGP-12177. A hydrophilic beta-adrenergic receptor radioligand reveals high affinity binding of agonists to intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3496–3502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuuchi Y., Yamashita S., Tei S. S. Pharmacological studies of OPC-2009, a newly synthesized selective beta adrenoceptor stimulant, in the broncho-motor and cardiovascular system of the anesthetized dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):326–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink S., Rösen P., Sackmann B., Lemoine H. Regulation of endothelial permeability by beta-adrenoceptor agonists: contribution of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 13;1178(3):286–298. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


