Abstract
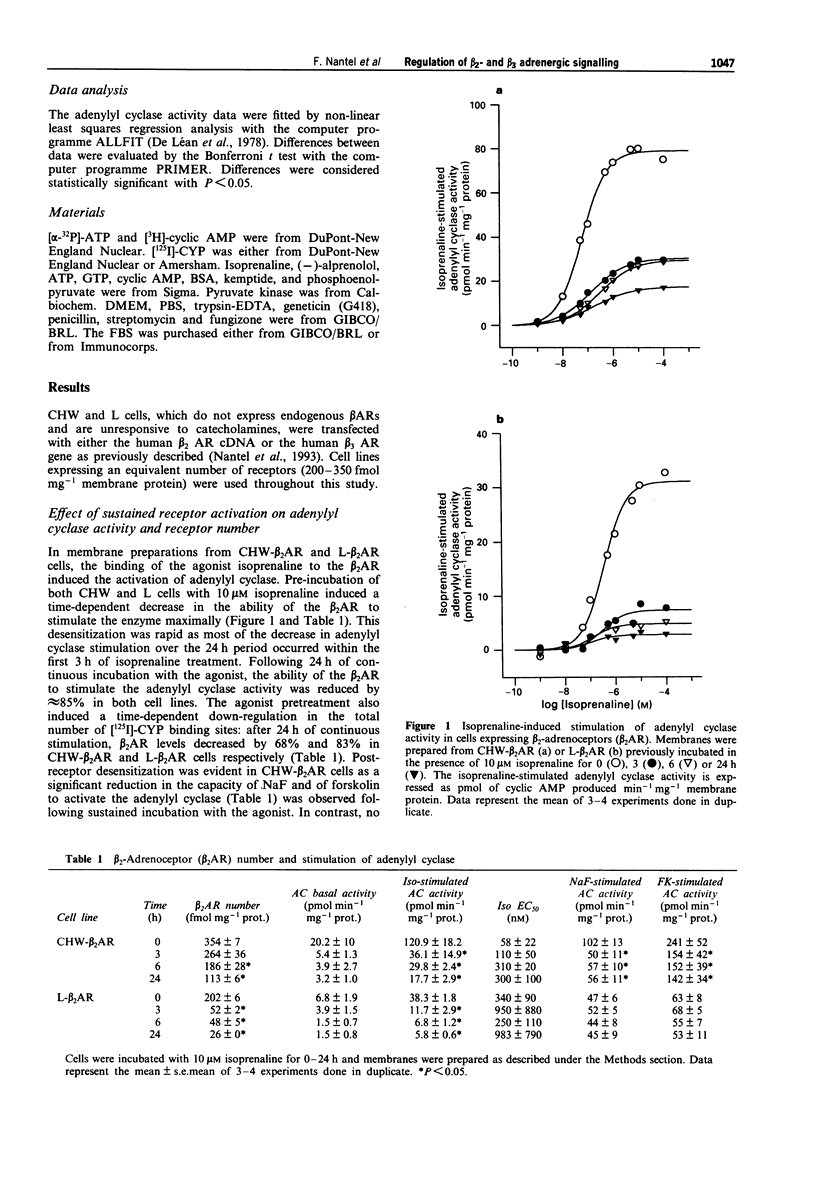
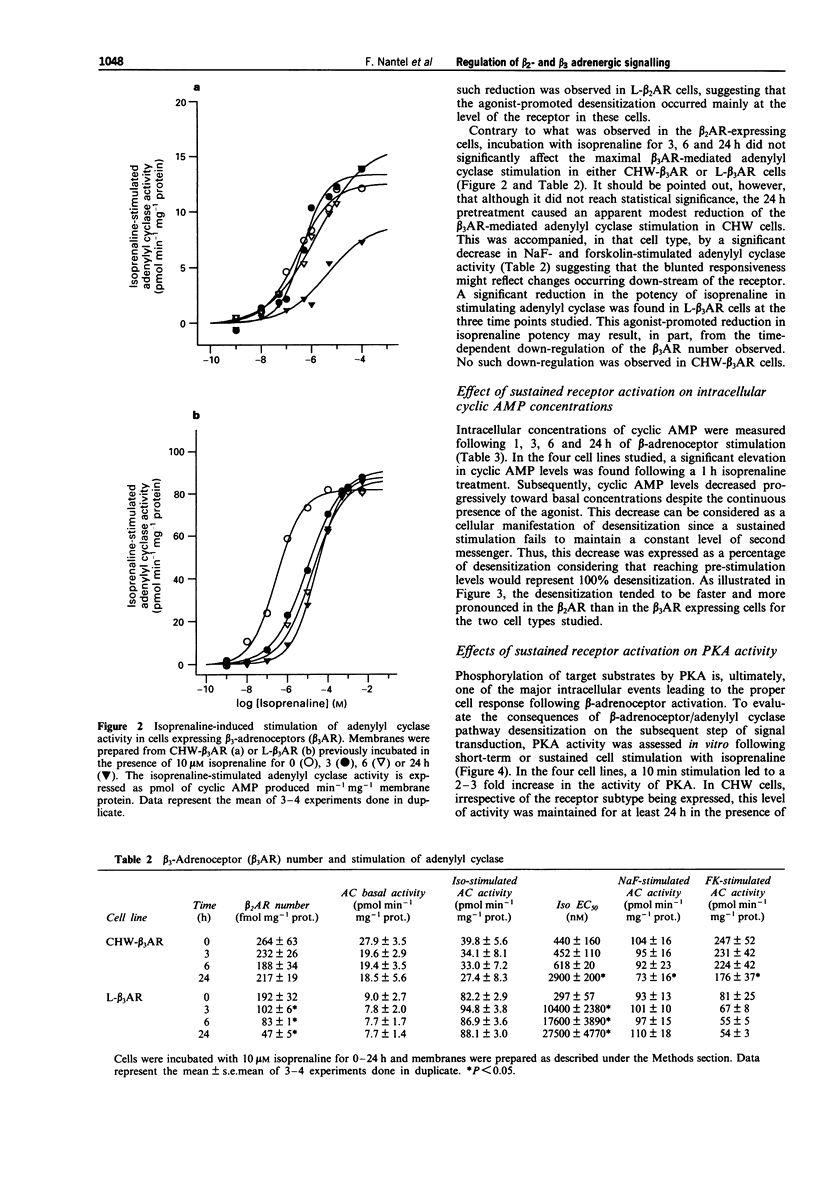
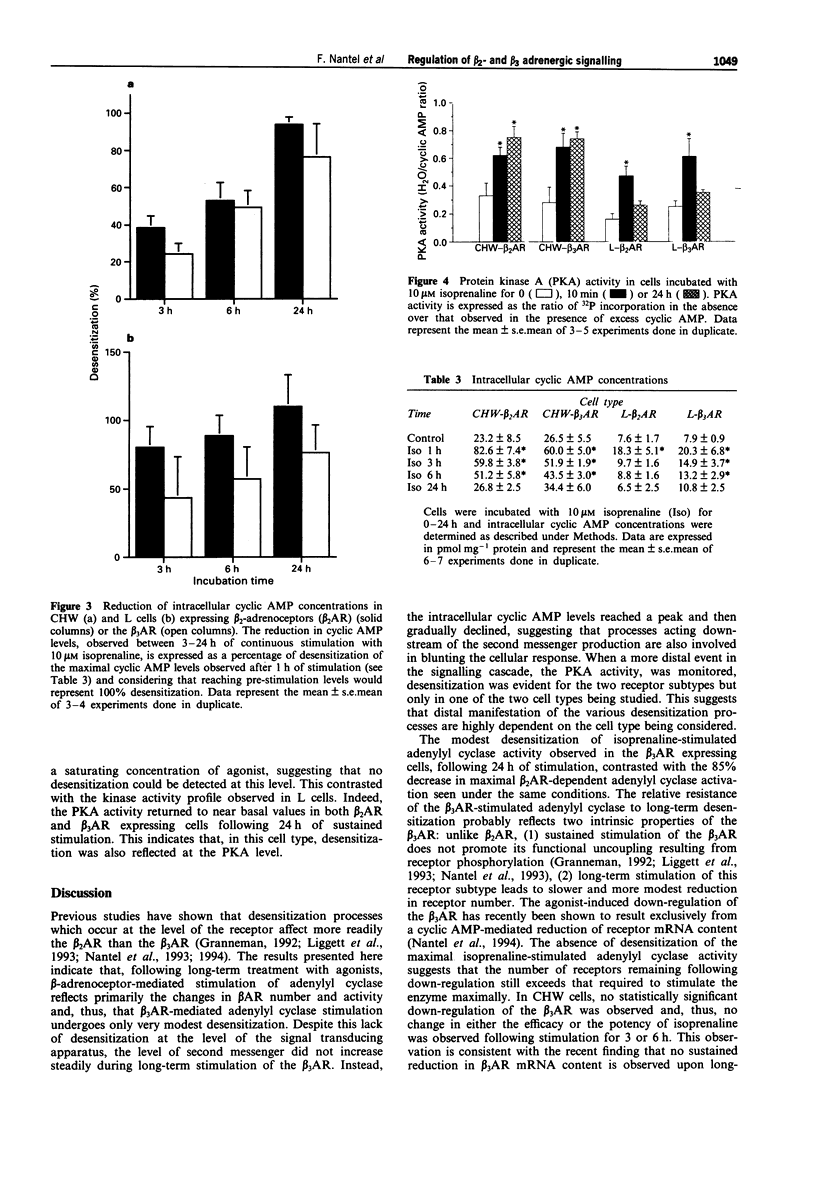
The functional effects of long-term activation of beta-adrenoceptors were investigated by measuring adenylyl cyclase activity, cyclic AMP accumulation and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity in CHW and L cells expressing either human beta 2- or beta 3-adrenoceptors. Pre-incubation of CHW and L cells expressing beta 2-adrenoceptors with 10 microM isoprenaline for 24 h produced a marked reduction in the total receptor number and dramatically reduced the capacity of the receptor to stimulate adenylyl cyclase maximally. In contrast, the ability of beta 3-adrenoceptors number was observed in L but not in CHW cells. Maximal levels of intracellular cyclic AMP concentrations were reached during the first hour of receptor activation with isoprenaline in all four cell lines. In the absence of phosphodiesterase inhibitors, cyclic AMP decreased to basal levels within 24 h of continuous stimulation. This phenomenon occurred more rapidly in cells expressing the beta 2- than the beta 3-adrenoceptors. These results confirm that, at the level of adenylyl cyclase stimulation and cyclic AMP accumulation, the beta 3-adrenoceptor is more resistant than the beta 2-adrenoceptor to long-term desensitization. However, when cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity was considered, a 24 h stimulation of beta 2- and when cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity was considered, a 24 h stimulation of beta 2- and beta 3-adrenoceptor expressing cells led to the desensitization of the kinase in L but not in CHW cells. In conclusion, long-term desensitization may have distinct functional effects on cell signalling depending on the receptor subtype and the cell type considered.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arch J. R., Kaumann A. J. Beta 3 and atypical beta-adrenoceptors. Med Res Rev. 1993 Nov;13(6):663–729. doi: 10.1002/med.2610130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber R., Goka T. J., Butcher R. W. Positively cooperative cAMP phosphodiesterase attenuates cellular cAMP responses. Second Messengers Phosphoproteins. 1992;14(1-2):77–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Bouvier M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adenylyl cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:405–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2797–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Collins S., O'Dowd B. F., Campbell P. T., de Blasi A., Kobilka B. K., MacGregor C., Irons G. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Two distinct pathways for cAMP-mediated down-regulation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Phosphorylation of the receptor and regulation of its mRNA level. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16786–16792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo E. L., Gifford R. W., Jr Current concepts. Pheochromocytoma: diagnosis, localization and management. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 15;311(20):1298–1303. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411153112007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadd G. G., Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. Holoenzymes of cAMP-dependent protein kinase containing the neural form of type I regulatory subunit have an increased sensitivity to cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19502–19506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpéné C., Galitzky J., Collon P., Esclapez F., Dauzats M., Lafontan M. Desensitization of beta-1 and beta-2, but not beta-3, adrenoceptor-mediated lipolytic responses of adipocytes after long-term norepinephrine infusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Apr;265(1):237–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Bouvier M., Bolanowski M. A., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cAMP stimulates transcription of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene in response to short-term agonist exposure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connacher A. A., Jung R. T., Mitchell P. E. Weight loss in obese subjects on a restricted diet given BRL 26830A, a new atypical beta adrenoceptor agonist. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Apr 30;296(6631):1217–1220. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6631.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doss R. C., Perkins J. P., Harden T. K. Recovery of beta-adrenergic receptors following long term exposure of astrocytoma cells to catecholamine. Role of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12281–12286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. D. Beta-adrenergic desensitization reduces the sensitivity of adenylate cyclase for magnesium in permeabilized lymphocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):304–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galant S. P., Duriseti L., Underwood S., Insel P. A. Decreased beta-adrenergic receptors on polymorphonuclear leukocytes after adrenergic therapy. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 26;299(17):933–936. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810262991707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giembycz M. A., Diamond J. Evaluation of kemptide, a synthetic serine-containing heptapeptide, as a phosphate acceptor for the estimation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity in respiratory tissues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 15;39(2):271–283. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90026-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G. Effects of agonist exposure on the coupling of beta 1 and beta 3 adrenergic receptors to adenylyl cyclase in isolated adipocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):638–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Wang H. Y., Malbon C. C. Agonist-induced destabilization of beta-adrenergic receptor mRNA. Attenuation of glucocorticoid-induced up-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19928–19933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Bouvier M., O'Dowd B. F., Irons G. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation sites on two domains of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor are involved in distinct pathways of receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12657–12665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Turning off the signal: desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2881–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homburger V., Pantaloni C., Lucas M., Gozlan H., Bockaert J. Beta adrenergic receptor repopulation of C6 glioma cells after irreversible blockade and down regulation. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Dec;121(3):589–597. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Griffiths S. L., Horton Y. M., Livingstone C., Lobban M., Macdonald F., Morris N., Pryde J., Scotland G., Shakur Y. Regulation of intracellular cyclic AMP concentrations in hepatocytes involves the integrated activation and desensitization of adenylyl cyclase coupled with the action and activation of specific isoforms of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Feb;20(1):140–146. doi: 10.1042/bst0200140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krief S., Lönnqvist F., Raimbault S., Baude B., Van Spronsen A., Arner P., Strosberg A. D., Ricquier D., Emorine L. J. Tissue distribution of beta 3-adrenergic receptor mRNA in man. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):344–349. doi: 10.1172/JCI116191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J. G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80042-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B., Freedman N. J., Schwinn D. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Structural basis for receptor subtype-specific regulation revealed by a chimeric beta 3/beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Multiple pathways of rapid beta 2-adrenergic receptor desensitization. Delineation with specific inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3202–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnqvist F., Krief S., Strosberg A. D., Nyberg S., Emorine L. J., Arner P. Evidence for a functional beta 3-adrenoceptor in man. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):929–936. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLachlan M., Connacher A. A., Jung R. T. Psychological aspects of dietary weight loss and medication with the atypical beta agonist BRL 26830A in obese subjects. Int J Obes. 1991 Jan;15(1):27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor A. M. Autoantibodies to the TSH receptor in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1990 Dec;33(6):683–685. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1990.tb03905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nantel F., Bonin H., Emorine L. J., Zilberfarb V., Strosberg A. D., Bouvier M., Marullo S. The human beta 3-adrenergic receptor is resistant to short term agonist-promoted desensitization. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;43(4):548–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nantel F., Marullo S., Krief S., Strosberg A. D., Bouvier M. Cell-specific down-regulation of the beta 3-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13148–13155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor B. J., Aikman S. L., Barnes P. J. Tolerance to the nonbronchodilator effects of inhaled beta 2-agonists in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1992 Oct 22;327(17):1204–1208. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199210223271704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskén K., Skålhegg B. S., Solberg R., Andersson K. B., Taylor S. S., Lea T., Blomhoff H. K., Jahnsen T., Hansson V. Novel isozymes of cAMP-dependent protein kinase exist in human cells due to formation of RI alpha-RI beta heterodimeric complexes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21276–21283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. F., Holt B. D., Schwinn D. A., Liggett S. B. Long-term agonist exposure induces upregulation of beta 3-adrenergic receptor expression via multiple cAMP response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4490–4494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. S., Lefkowitz R. J., Hausdorff W. P. Beta-adrenergic receptor sequestration. A potential mechanism of receptor resensitization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


