Abstract
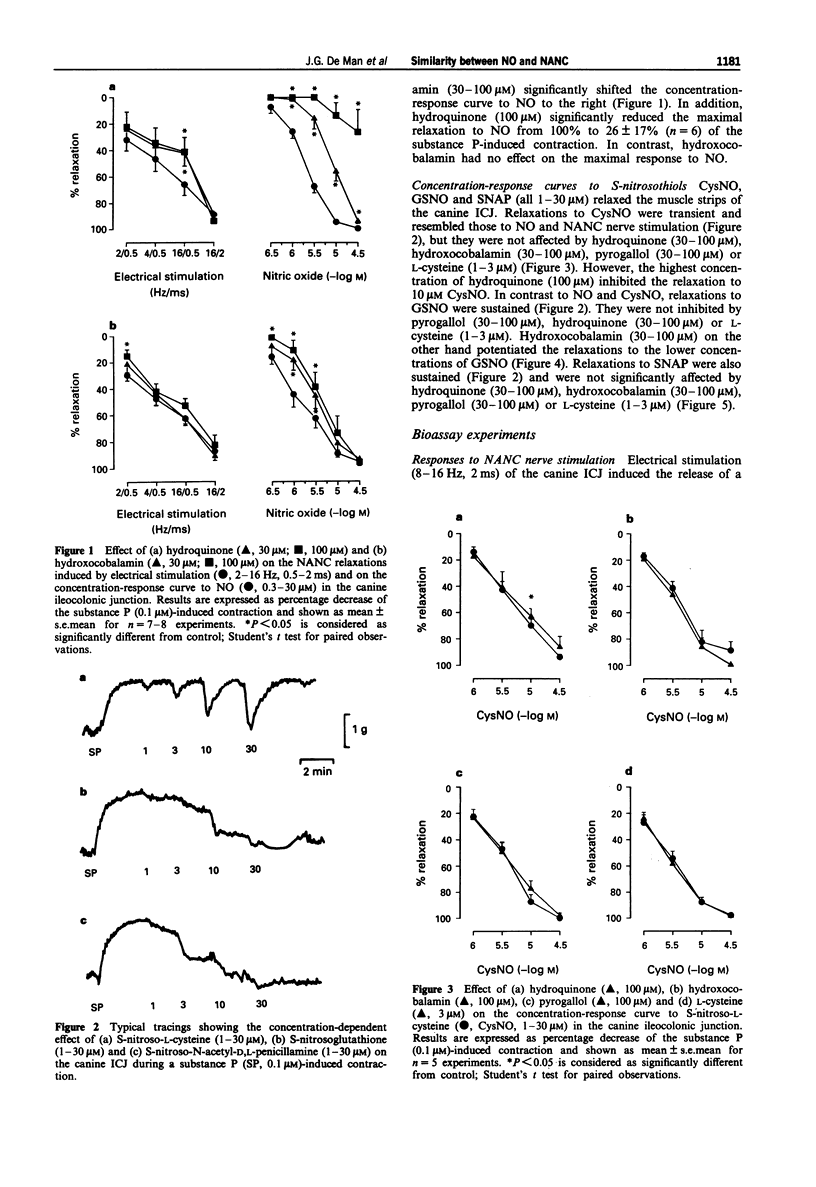
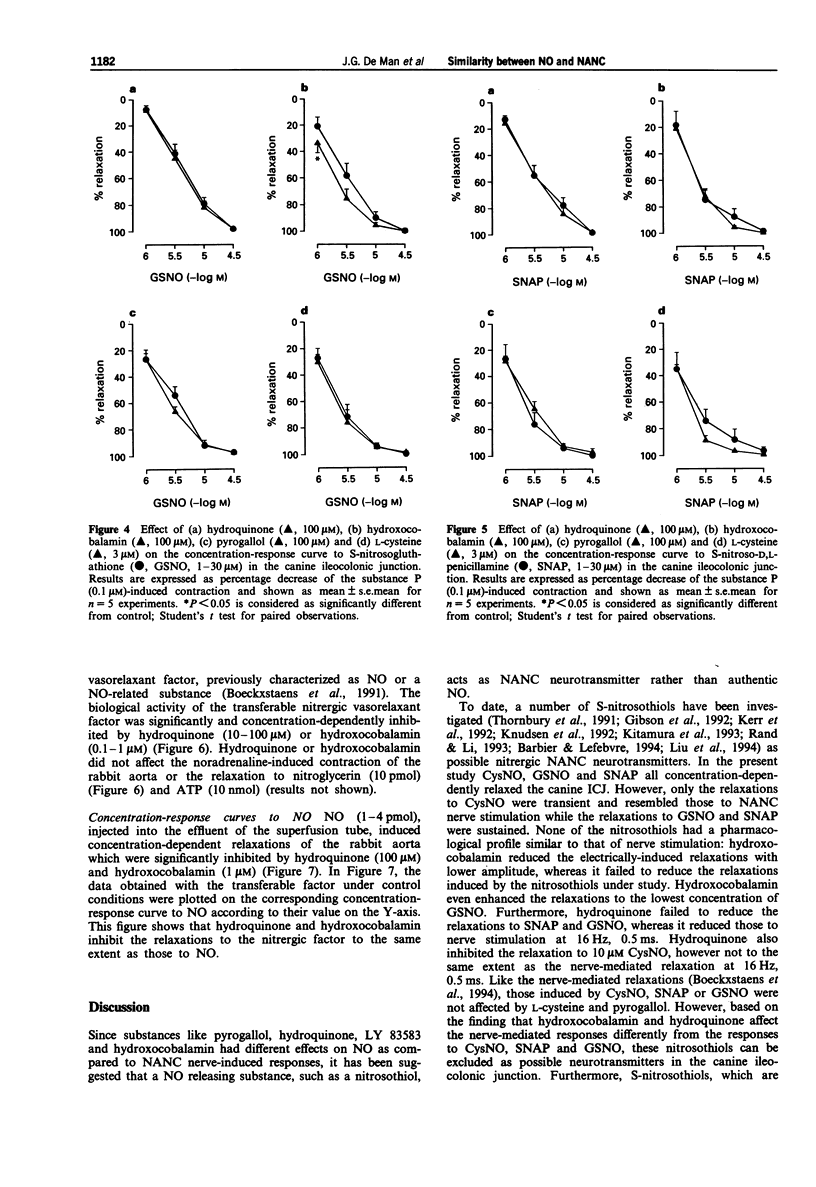
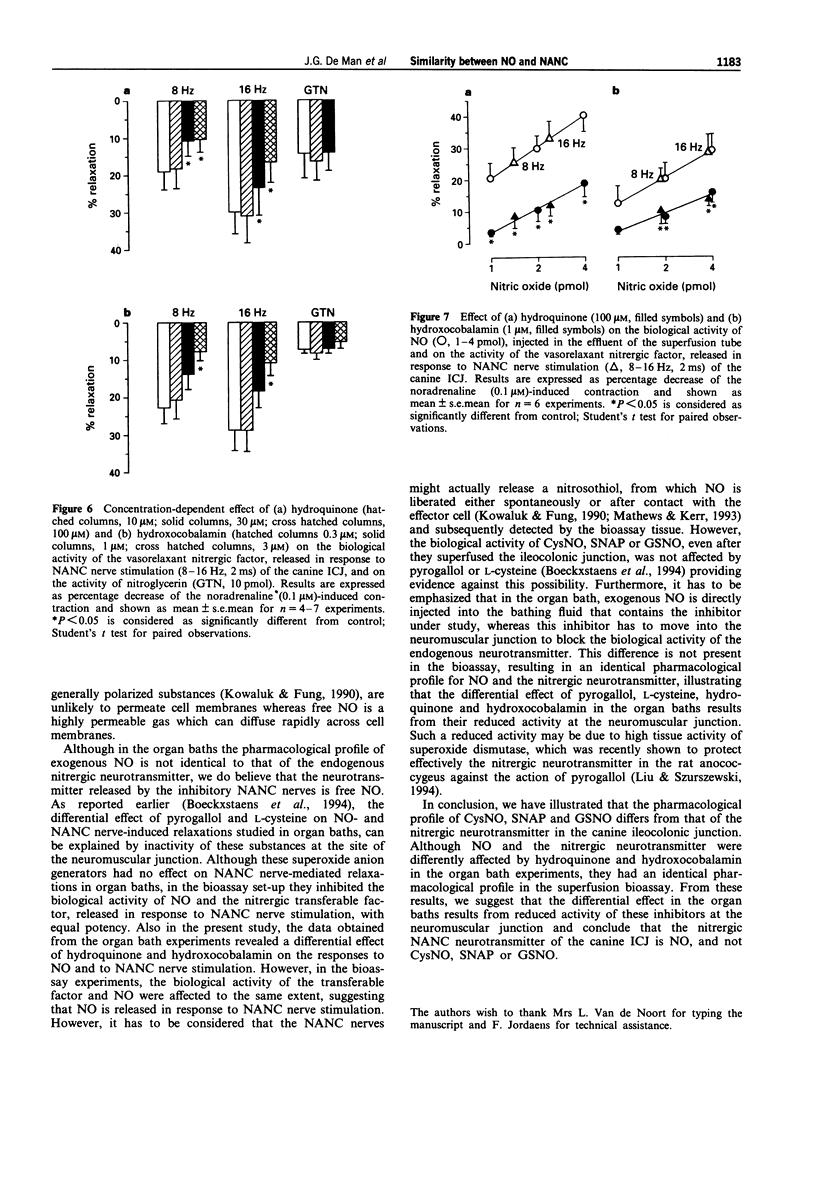
1. In organ bath experiments, hydroquinone (30-100 microM) and hydroxocobalamin (30-100 microM) concentration-dependently inhibited the relaxations induced by NO (0.3-30 microM) but not those by nitroglycerin (GTN, 1 microM) in the canine ileocolonic junction (ICJ). Hydroxocobalamin reduced the relaxation to low frequency (2 Hz) stimulation of the non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic (NANC) nerves, whereas hydroquinone only reduced the NANC nerve-mediated relaxations to electrical stimulation at 16 Hz, 0.5 ms. 2. Relaxations to S-nitroso-L-cysteine (CysNO, 1-30 microM), or S-nitroso-N-acetyl-D,L-penicillamine (SNAP, 1-30 microM) were not inhibited by hydroquinone (30-100 microM), hydroxocobalamin (30-100 microM), pyrogallol (30-100 microM) or L-cysteine (1-3 microM). Hydroquinone (100 microM) only reduced the relaxation to 10 microM CysNO. Hydroxocobalamin, but not hydroquinone, pyrogallol or L-cysteine, potentiated the relaxations to the lowest concentration (1 microM) of S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO, 1-30 microM). 3. In the superfusion bioassay, hydroquinone (100 microM) and hydroxocobalamin (1 microM) concentration-dependently inhibited the biological activity of authentic NO (1-4 pmol) to the same extent as that of the transferable nitrergic factor, released from the canine ICJ in response to NANC nerve stimulation (8-16 Hz, 2 ms). Responses to GTN (10 pmol) or adenosine 5'-triphosphate (10 nmol) were not affected. 4. In conclusion, the nitrosothiols CysNO, SNAP and GSNO relax the canine ileocolonic junction, but these relaxations, pharmacologically, behave differently from the NANC nerve-mediated relaxations.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbier A. J., Lefebvre R. A. Influence of S-nitrosothiols and nitrate tolerance in the rat gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1280–1286. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., De Man J. G., De Winter B. Y., Herman A. G., Pelckmans P. A. Pharmacological similarity between nitric oxide and the nitrergic neurotransmitter in the canine ileocolonic junction. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct 13;264(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90640-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bult H., De Man J. G., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation mediated by nitric oxide in the canine ileocolonic junction. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94132-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Ruytjens I. F., Bult H., De Man J. G., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Bioassay of nitric oxide released upon stimulation of non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nerves in the canine ileocolonic junction. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1085–1091. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12304.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bult H., Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Jordaens F. H., Van Maercke Y. M., Herman A. G. Nitric oxide as an inhibitory non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmitter. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):346–347. doi: 10.1038/345346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., te Poel M., Zamora R., Deussen A., Moncada S. Understanding the controversy over the identity of EDRF. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):62–65. doi: 10.1038/368062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A., Babbedge R., Brave S. R., Hart S. L., Hobbs A. J., Tucker J. F., Wallace P., Moore P. K. An investigation of some S-nitrosothiols, and of hydroxy-arginine, on the mouse anococcygeus. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):715–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Sheng H. The effects of pyrogallol and hydroquinone on the response to NANC nerve stimulation in the rat anococcygeus and the bovine retractor penis muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):194–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14677.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. J., Tucker J. F., Gibson A. Differentiation by hydroquinone of relaxations induced by exogenous and endogenous nitrates in non-vascular smooth muscle: role of superoxide anions. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):645–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lippton H., Edwards J. C., Baricos W. H., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J., Gruetter C. A. Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by organic nitrates, nitrites, nitroprusside and nitric oxide: evidence for the involvement of S-nitrosothiols as active intermediates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelm M., Feelisch M., Spahr R., Piper H. M., Noack E., Schrader J. Quantitative and kinetic characterization of nitric oxide and EDRF released from cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):236–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90675-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr S. W., Buchanan L. V., Bunting S., Mathews W. R. Evidence that S-nitrosothiols are responsible for the smooth muscle relaxing activity of the bovine retractor penis inhibitory factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Lian Q., Carl A., Kuriyama H. S-nitrosocysteine, but not sodium nitroprusside, produces apamin-sensitive hyperpolarization in rat gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;109(2):415–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen M. A., Svane D., Tøttrup A. Action profiles of nitric oxide, S-nitroso-L-cysteine, SNP, and NANC responses in opossum lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):G840–G846. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.5.G840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowaluk E. A., Fung H. L. Spontaneous liberation of nitric oxide cannot account for in vitro vascular relaxation by S-nitrosothiols. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Dec;255(3):1256–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Gillespie J. S., Martin W. Non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxation of the bovine retractor penis muscle: role of S-nitrosothiols. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1287–1295. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14885.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews W. R., Kerr S. W. Biological activity of S-nitrosothiols: the role of nitric oxide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Dec;267(3):1529–1537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Minor R. L., Jr, Guerra R., Jr, Bates J. N., Harrison D. G. Vasorelaxant properties of the endothelium-derived relaxing factor more closely resemble S-nitrosocysteine than nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):161–163. doi: 10.1038/345161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelckmans P. A., Boeckxstaens G. E., Van Maercke Y. M., Herman A. G., Verbeuren T. J. Acetylcholine is an indirect inhibitory transmitter in the canine ileocolonic junction. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 7;170(3):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90544-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajanayagam M. A., Li C. G., Rand M. J. Differential effects of hydroxocobalamin on NO-mediated relaxations in rat aorta and anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand M. J., Li C. G. Differential effects of hydroxocobalamin on relaxations induced by nitrosothiols in rat aorta and anococcygeus muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 14;241(2-3):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Ward S. M. Nitric oxide as a mediator of nonadrenergic noncholinergic neurotransmission. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):G379–G392. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.3.G379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. E., Szurszewski J. H. Role of nitric oxide in gastrointestinal and hepatic function and disease. Gastroenterology. 1992 Dec;103(6):1928–1949. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91454-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornbury K. D., Ward S. M., Dalziel H. H., Carl A., Westfall D. P., Sanders K. M. Nitric oxide and nitrosocysteine mimic nonadrenergic, noncholinergic hyperpolarization in canine proximal colon. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 1):G553–G557. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.3.G553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


