Abstract
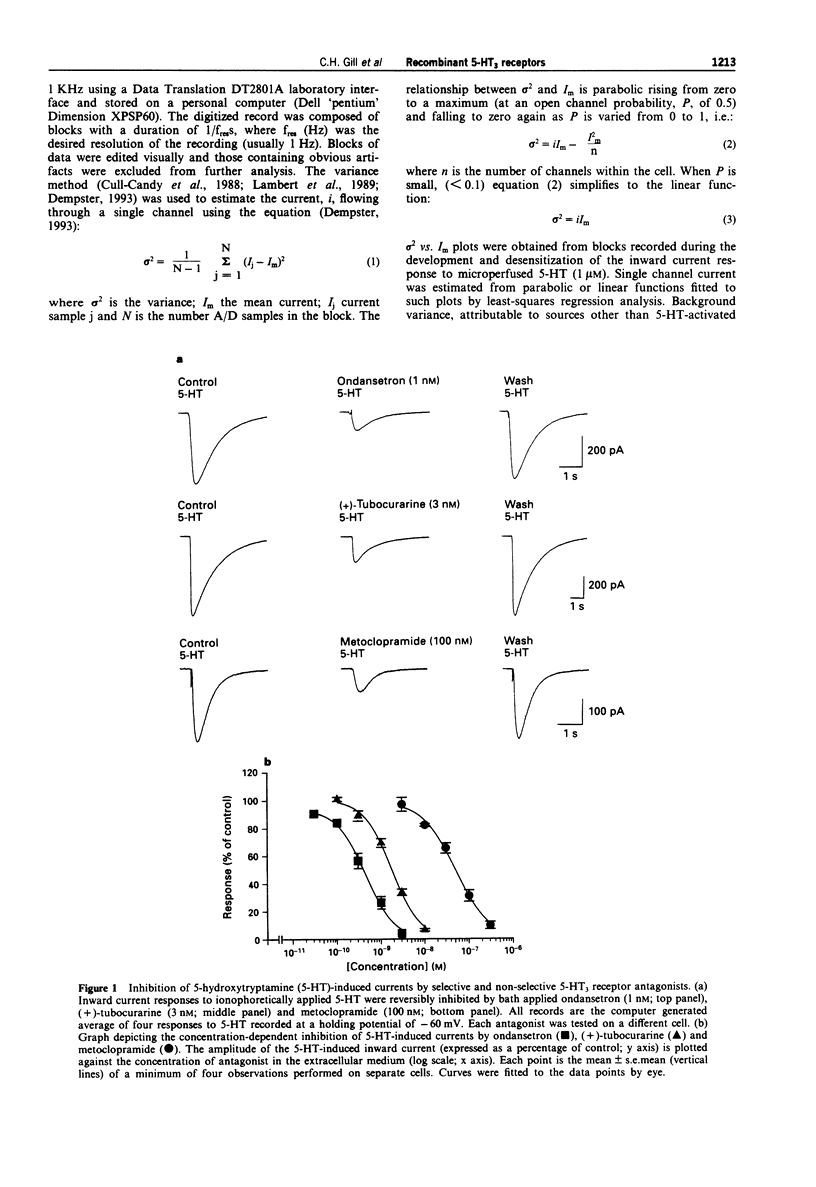
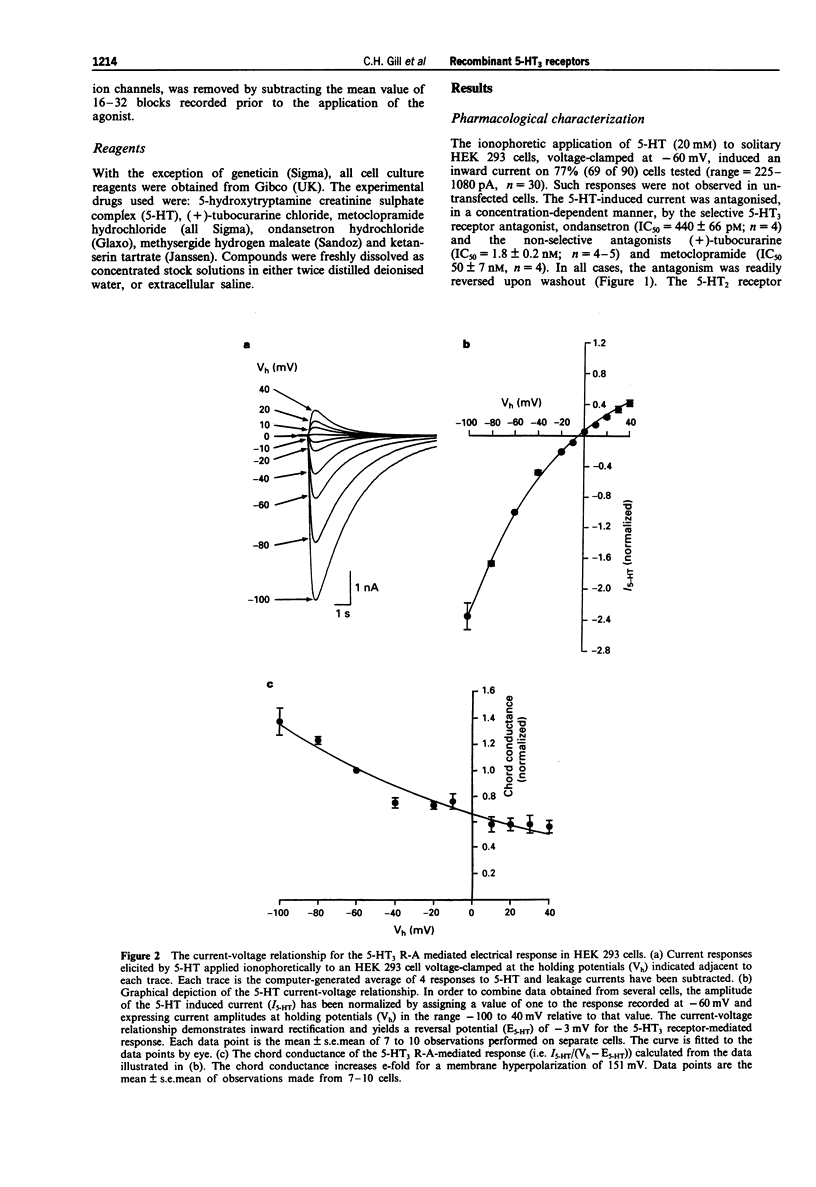
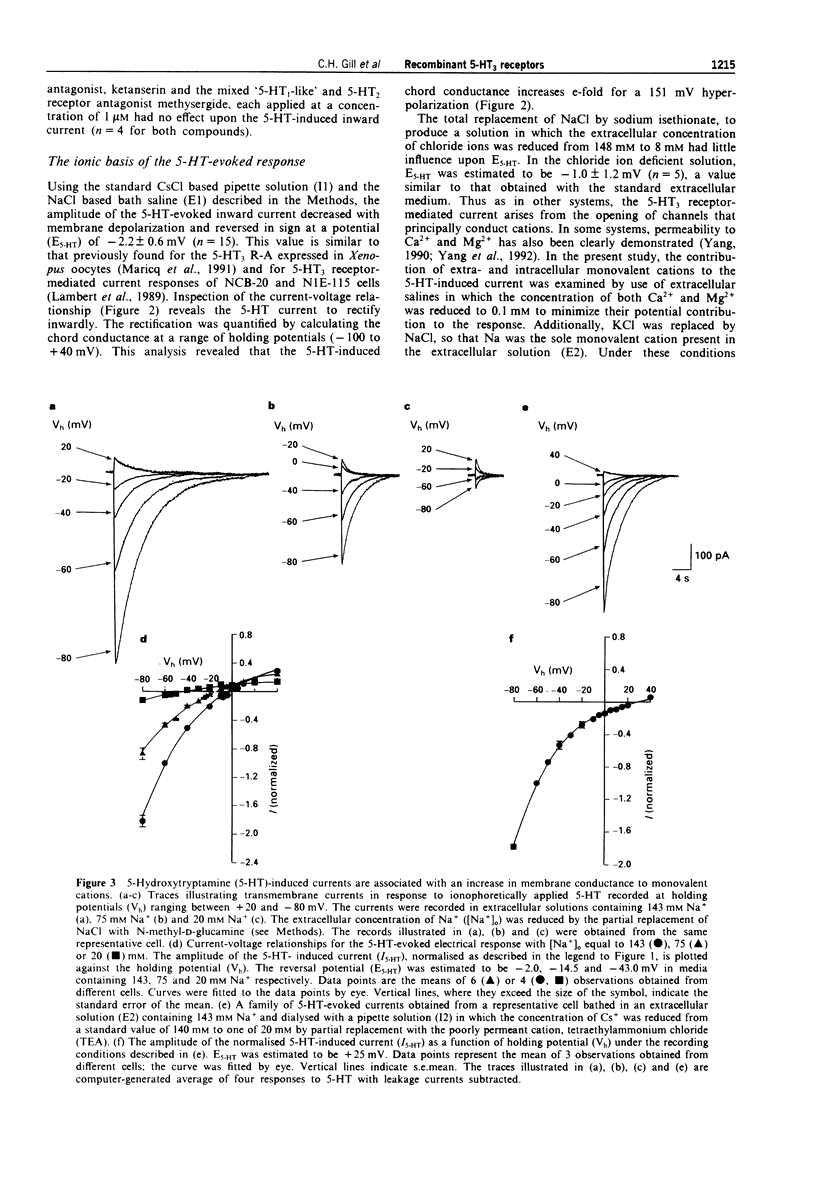
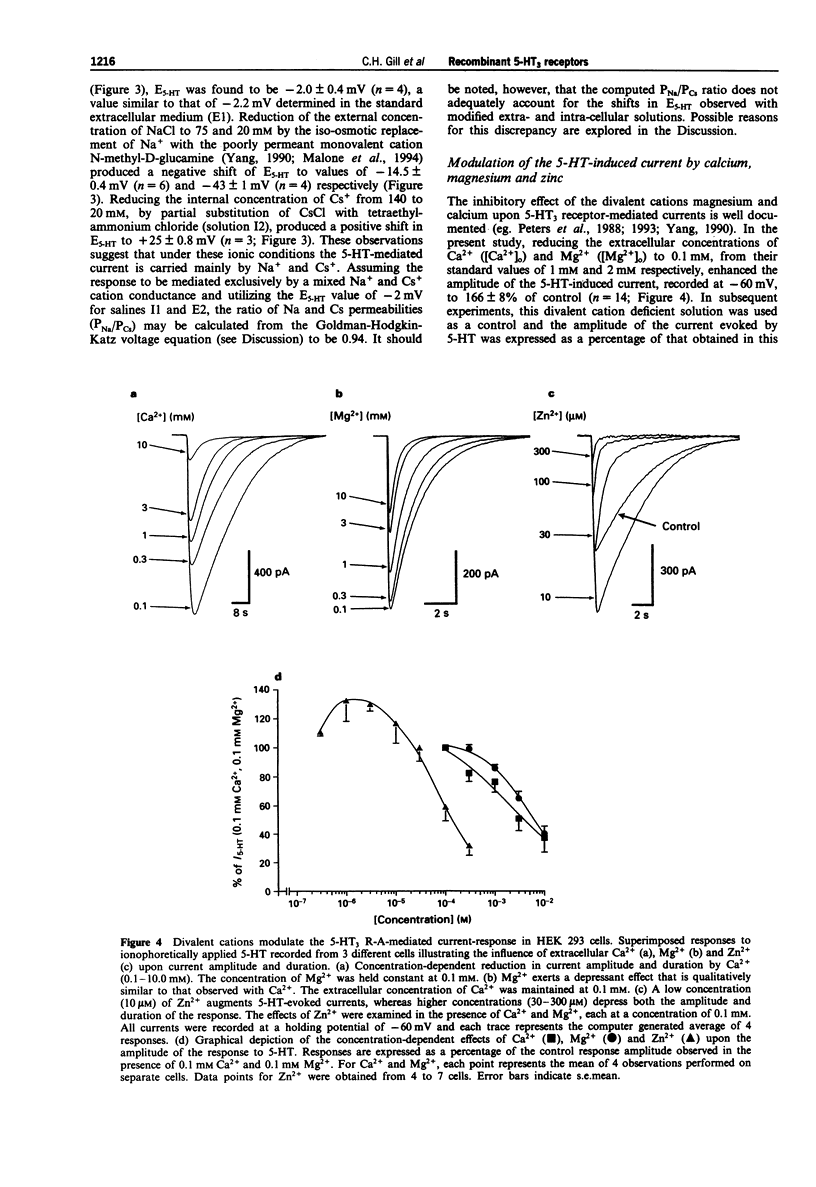
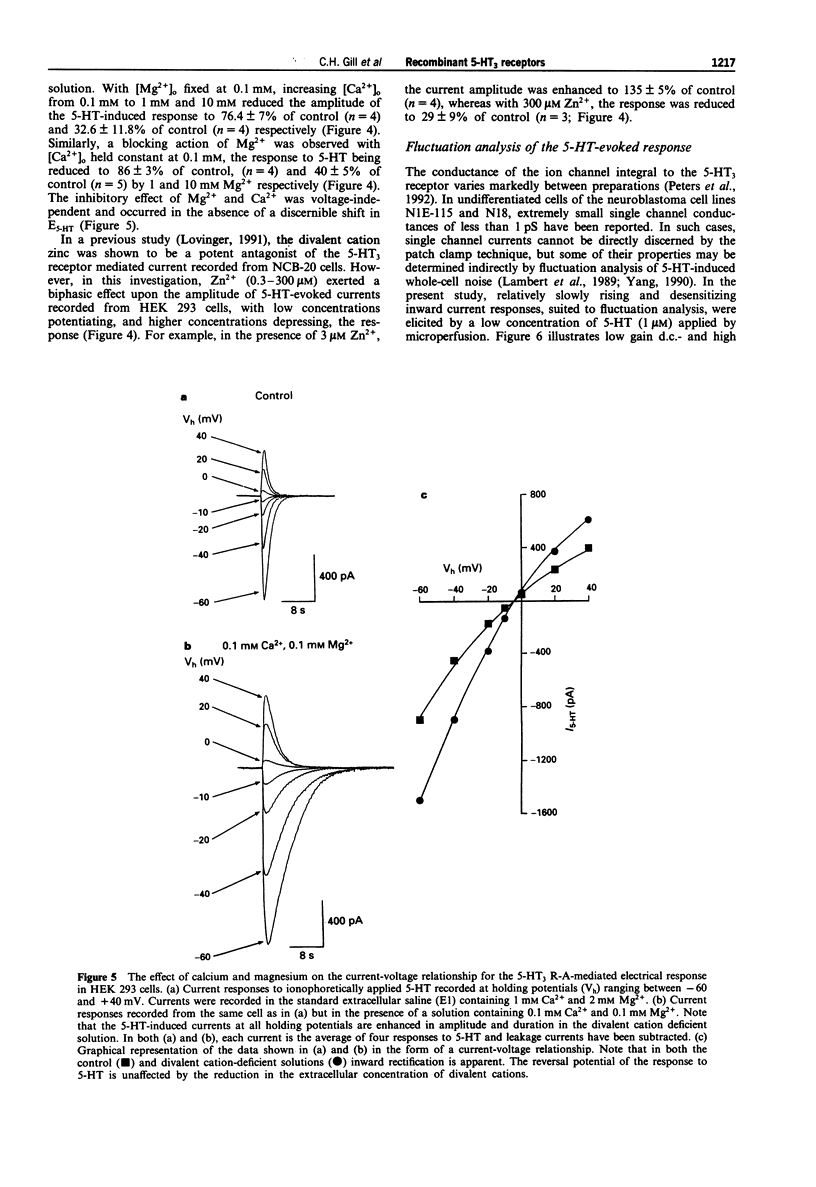
1. The pharmacological and biophysical properties of a recombinant 5-HT3 receptor have been studied by use of patch-clamp techniques applied to HEK 293 cells stably transfected with the murine 5-HT3 R-A cDNA. 2. At a holding potential of -60 mV, 77% of cells investigated responded to ionophoretically applied 5-HT with an inward current. Such currents were unaffected by methysergide (1 microM), or ketanserin (1 microM), but were antagonized in a concentration-dependent and reversible manner by the selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, ondansetron (IC50 = 440 pM) and the non-selective antagonists (+)-tubocurarine (IC50 = 1.8 nM) and metoclopramide (IC50 50 nM). 3. The 5-HT-induced current reversed in sign (E5-HT) at approximately -2mV and exhibited inward rectification. The influence of extra- and intracellular ion substitutions upon E5-HT indicates the 5-HT-evoked current to be mainly mediated by a mixed monovalent cation conductance. 4. Calcium and magnesium (0.1-10 nM) produced a concentration-dependent, voltage-independent, inhibition of the 5-HT-induced response. Zinc (0.3-300 microM) exerted a biphasic effect with low concentrations enhancing, and high concentrations depressing, the 5-HT-evoked current. 5. Fluctuation analysis of inward currents evoked by a low (1 microM) concentration of 5-HT suggests the current to be mediated by the opening of channels with a conductance of 420 fS. 6. The pharmacological and biophysical properties of the 5-HT3 R-A are similar to those previously described for 5-HT3 receptors native to murine neuroblastoma cell lines, with the exception that the function of the recombinant receptor was enhanced by low concentrations of zinc. This observation suggests that the properties of the native receptor are not completely represented by the 5-HT3 R-A subunit alone.
Full text
PDF

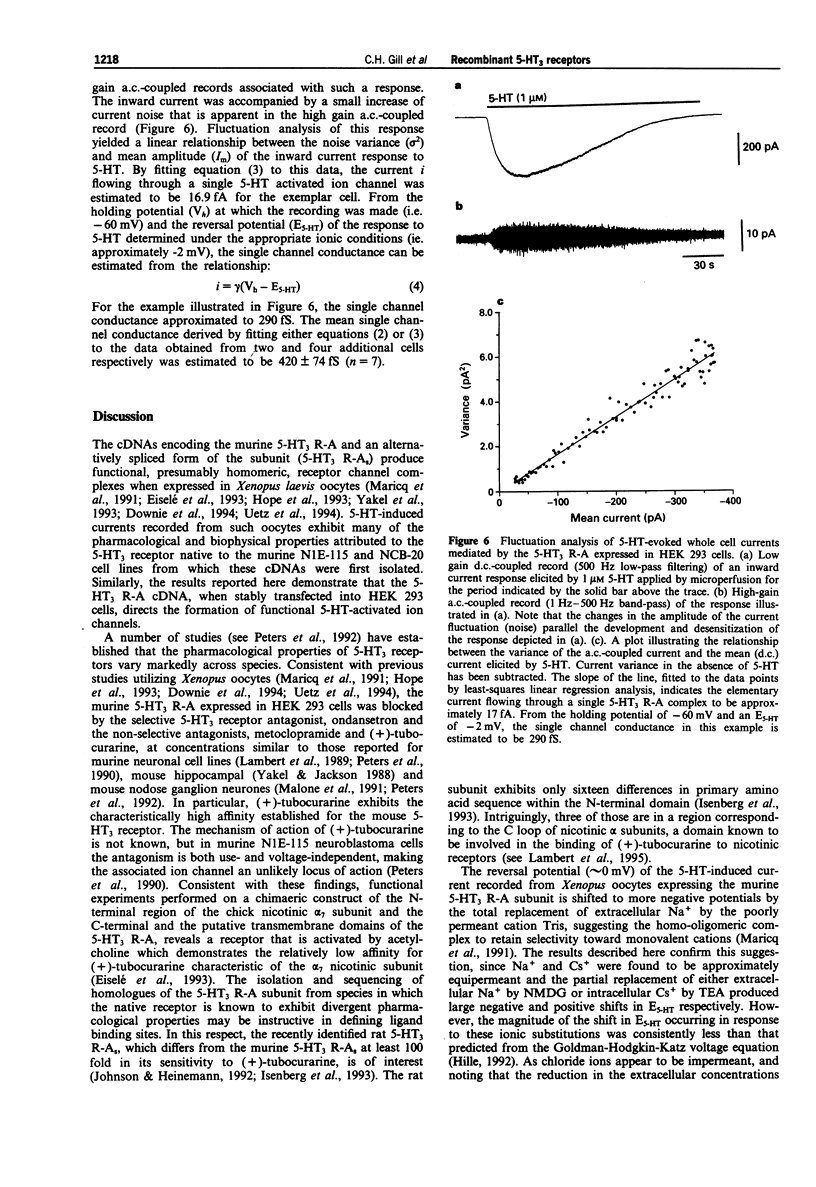



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boess F. G., Martin I. L. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):275–317. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkach V., Surprenant A., North R. A. 5-HT3 receptors are membrane ion channels. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):706–709. doi: 10.1038/339706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie D. L., Hope A. G., Lambert J. J., Peters J. A., Blackburn T. P., Jones B. J. Pharmacological characterization of the apparent splice variants of the murine 5-HT3 R-A subunit expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):473–482. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draguhn A., Verdorn T. A., Ewert M., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional and molecular distinction between recombinant rat GABAA receptor subtypes by Zn2+. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):781–788. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90337-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiselé J. L., Bertrand S., Galzi J. L., Devillers-Thiéry A., Changeux J. P., Bertrand D. Chimaeric nicotinic-serotonergic receptor combines distinct ligand binding and channel specificities. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):479–483. doi: 10.1038/366479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerit M. B., Riad M., Fattaccini C. M., Hamon M. Characteristics of [14C]guanidinium accumulation in NG 108-15 cells exposed to serotonin 5-HT3 receptor ligands and substance P. J Neurochem. 1993 Jun;60(6):2059–2067. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Gibbons S. J. Zn2+: an endogenous modulator of ligand- and voltage-gated ion channels. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Aug;33(8):935–952. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Boulter J., Maron C., Beasley L., Sullivan J., Pecht G., Heinemann S. Zinc potentiates agonist-induced currents at certain splice variants of the NMDA receptor. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):943–954. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90209-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope A. G., Downie D. L., Sutherland L., Lambert J. J., Peters J. A., Burchell B. Cloning and functional expression of an apparent splice variant of the murine 5-HT3 receptor A subunit. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Apr 15;245(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90128-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg K. E., Ukhun I. A., Holstad S. G., Jafri S., Uchida U., Zorumski C. F., Yang J. Partial cDNA cloning and NGF regulation of a rat 5-HT3 receptor subunit. Neuroreport. 1993 Nov 18;5(2):121–124. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199311180-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Surprenant A. Single channel properties of the 5-HT3 subtype of serotonin receptor in primary cultures of rodent hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Jun 20;174(2):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A. Structure of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;3(3):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90121-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawa K. Distribution and functional properties of 5-HT3 receptors in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus: a patch-clamp study. J Neurophysiol. 1994 May;71(5):1935–1947. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.5.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooyman A. R., Zwart R., Vijverberg H. P. Tetraethylammonium ions block 5-HT3 receptor-mediated ion current at the agonist recognition site and prevent desensitization in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 15;246(3):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90038-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. J., Peters J. A., Hales T. G., Dempster J. The properties of 5-HT3 receptors in clonal cell lines studied by patch-clamp techniques. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):27–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11920.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Peoples R. W., Li Z., Weight F. F. Zn2+ potentiates excitatory action of ATP on mammalian neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8264–8267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M. Inhibition of 5-HT3 receptor-mediated ion current by divalent metal cations in NCB-20 neuroblastoma cells. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Oct;66(4):1329–1337. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.4.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone H. M., Peters J. A., Lambert J. J. Physiological and pharmacological properties of 5-HT3 receptors--a patch clamp-study. Neuropeptides. 1991 Jul;19 (Suppl):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq A. V., Peterson A. S., Brake A. J., Myers R. M., Julius D. Primary structure and functional expression of the 5HT3 receptor, a serotonin-gated ion channel. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1718042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Hales T. G., Lambert J. J. Divalent cations modulate 5-HT3 receptor-induced currents in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 14;151(3):491–495. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90550-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Lambert J. J., Cottrell G. A. An electrophysiological investigation of the characteristics and function of GABAA receptors on bovine adrenomedullary chromaffin cells. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Oct;415(1):95–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00373146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Malone H. M., Lambert J. J. An electrophysiological investigation of the properties of 5-HT3 receptors of rabbit nodose ganglion neurones in culture. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):665–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Malone H. M., Lambert J. J. Antagonism of 5-HT3 receptor mediated currents in murine N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells by (+)-tubocurarine. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Mar 2;110(1-2):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90796-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Malone H. M., Lambert J. J. Recent advances in the electrophysiological characterization of 5-HT3 receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Oct;13(10):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90119-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassendren F. A., Lory P., Pin J. P., Nargeot J. Zinc has opposite effects on NMDA and non-NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90199-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B., Bevan S. Properties of 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor-gated currents in adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):272–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H. The TiPS/TINS lecture: the molecular biology of mammalian glutamate receptor channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Aug;14(8):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90047-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. GABAA receptors: ligand-gated Cl- ion channels modulated by multiple drug-binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Dec;13(12):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90142-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart T. G., Xie X., Krishek B. J. Modulation of inhibitory and excitatory amino acid receptor ion channels by zinc. Prog Neurobiol. 1994 Feb;42(3):393–441. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(94)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uetz P., Abdelatty F., Villarroel A., Rappold G., Weiss B., Koenen M. Organisation of the murine 5-HT3 receptor gene and assignment to human chromosome 11. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 21;339(3):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Burnett D. M., Leidenheimer N. J., Burt D. R., Wang J. B., Kofuji P., Dunwiddie T. V., Harris R. A., Sikela J. M. Ethanol sensitivity of the GABAA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes requires 8 amino acids contained in the gamma 2L subunit. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakel J. L., Jackson M. B. 5-HT3 receptors mediate rapid responses in cultured hippocampus and a clonal cell line. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakel J. L., Lagrutta A., Adelman J. P., North R. A. Single amino acid substitution affects desensitization of the 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5030–5033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakel J. L., Shao X. M., Jackson M. B. The selectivity of the channel coupled to the 5-HT3 receptor. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 12;533(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91793-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. Ion permeation through 5-hydroxytryptamine-gated channels in neuroblastoma N18 cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Dec;96(6):1177–1198. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.6.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Mathie A., Hille B. 5-HT3 receptor channels in dissociated rat superior cervical ganglion neurons. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:237–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X., Zhang L., Durand G. M., Bennett M. V., Zukin R. S. Mutagenesis rescues spermine and Zn2+ potentiation of recombinant NMDA receptors. Neuron. 1994 Apr;12(4):811–818. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hooft J. A., Kooyman A. R., Verkerk A., van Kleef R. G., Vijverberg H. P. Single 5-HT3 receptor-gated ion channel events resolved in N1E-115 mouse neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 28;199(1):227–233. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


