Abstract
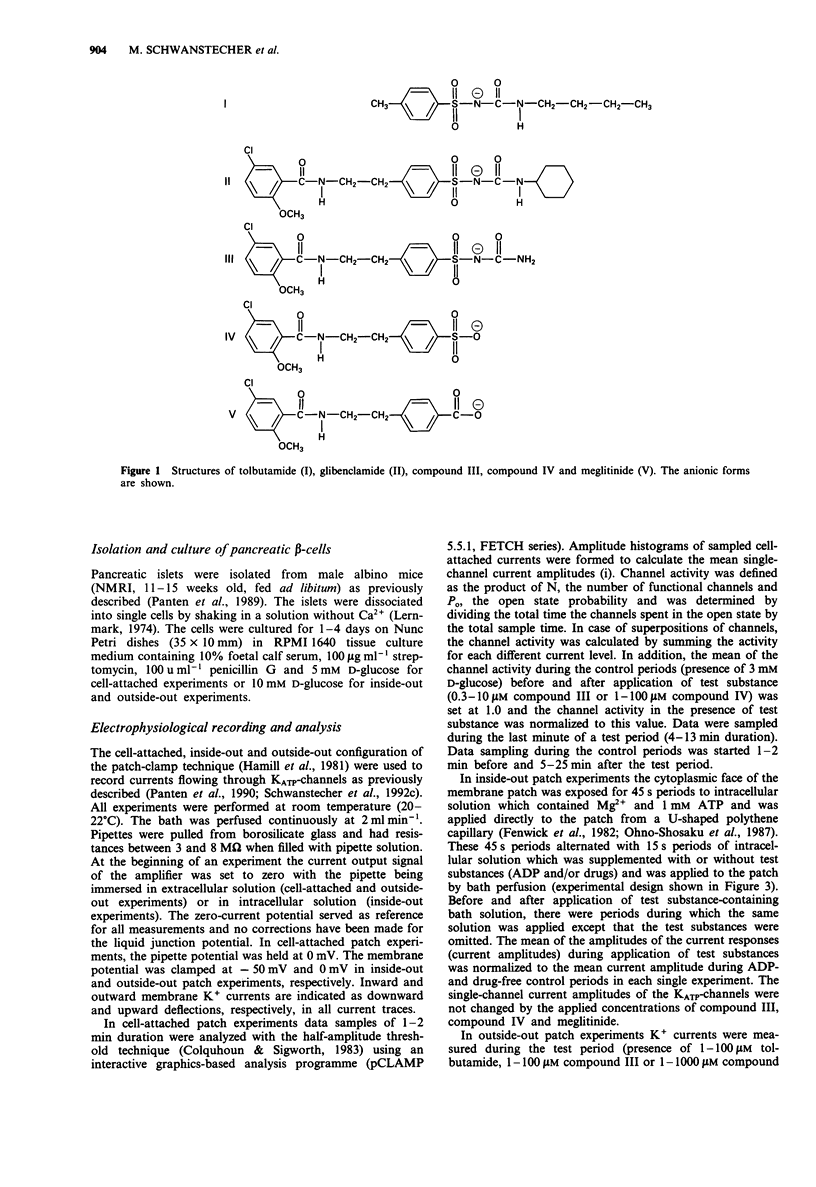
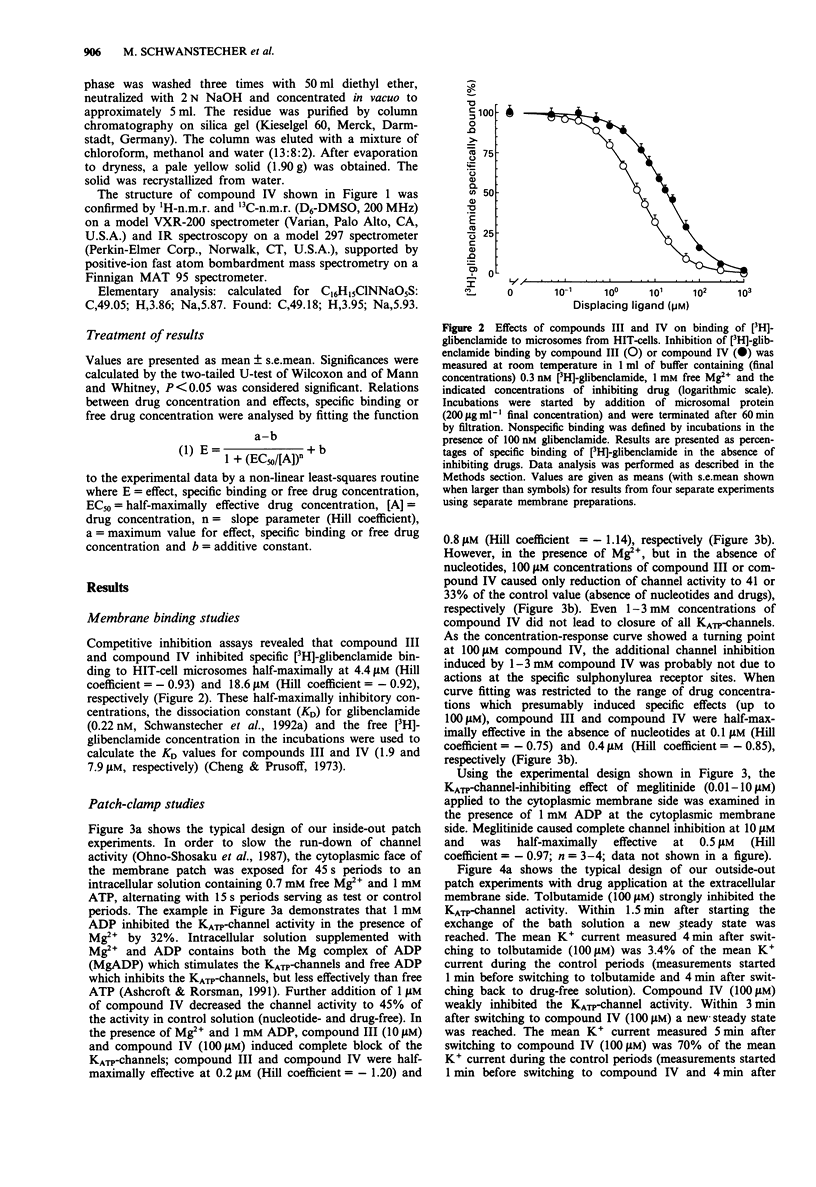
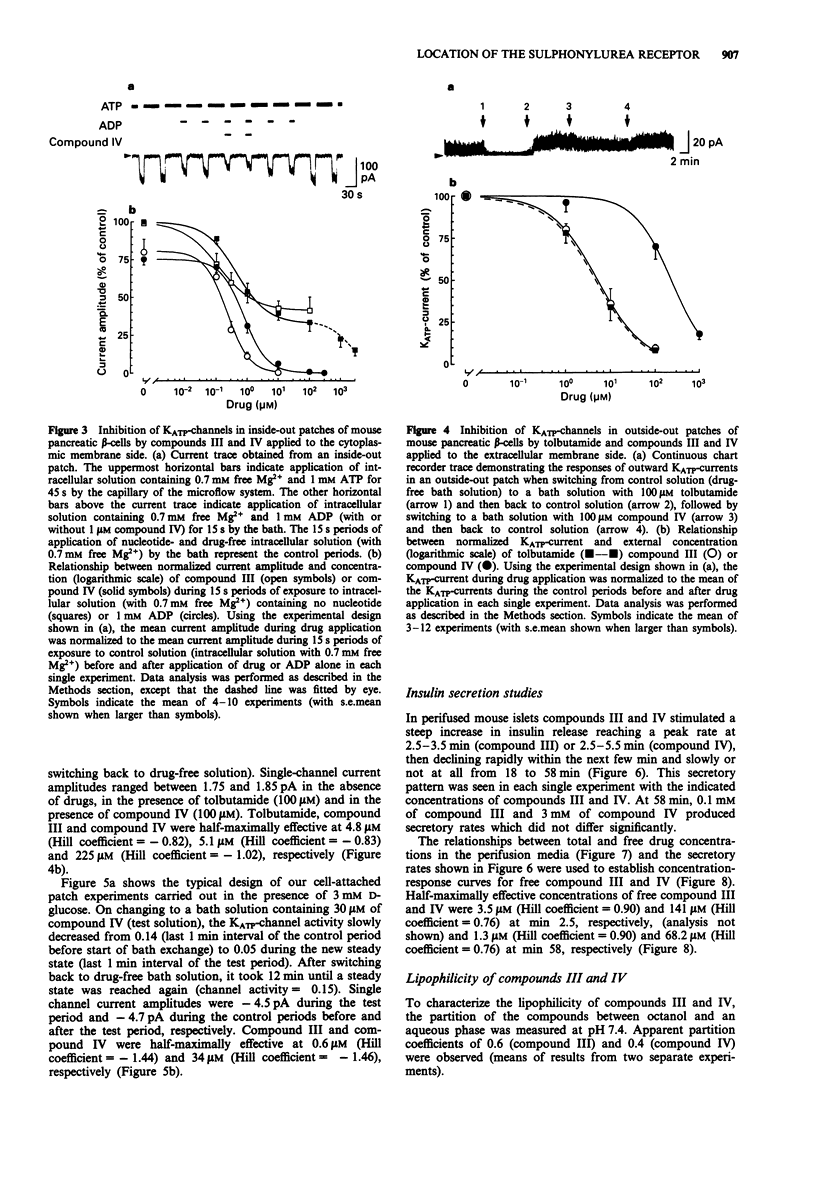
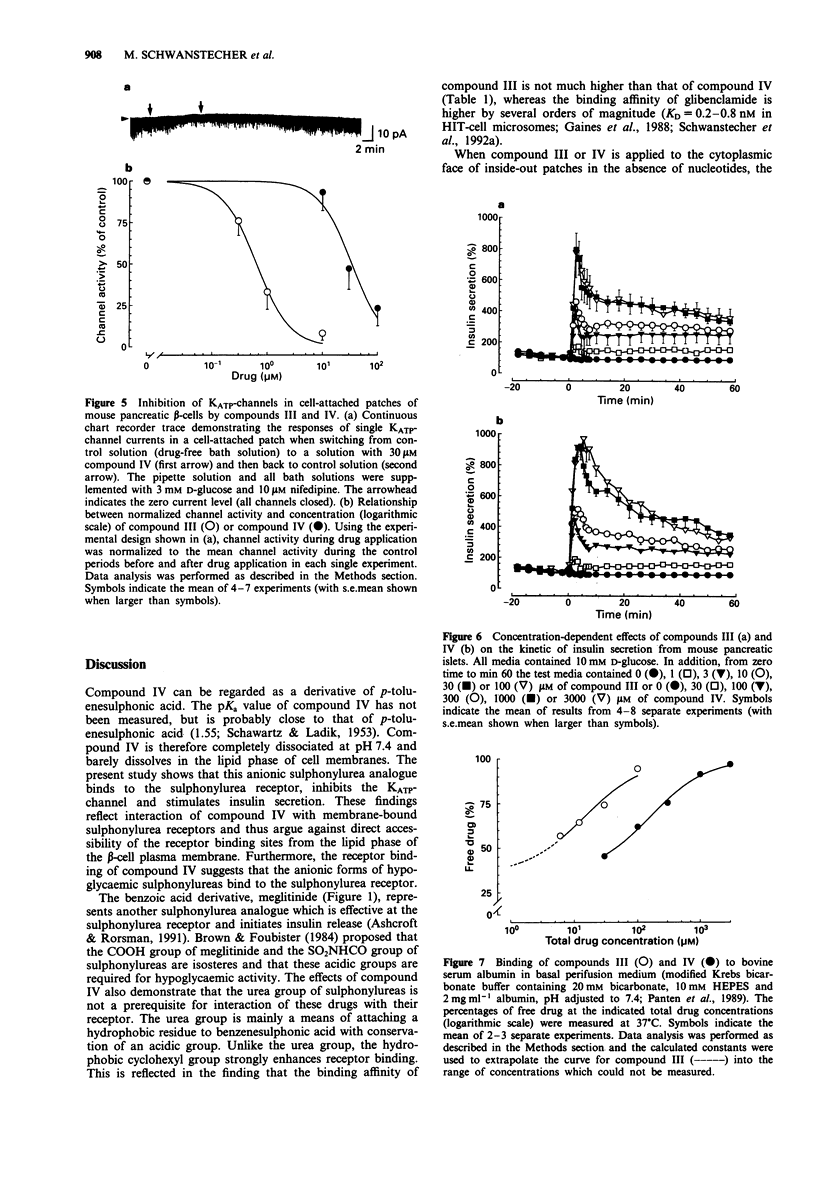
1. In insulin-secreting cells the location of the sulphonylurea receptor was examined by use of a sulphonylurea derivative representing the glibenclamide molecule devoid of its cyclohexy moiety (compound III) and a benzenesulphonic acid derivative representing the glibenclamide molecule devoid of its cyclohexylurea moiety (compound IV). At pH 7.4 compound IV is only present in charged form. 2. Lipid solubility declined in the order tolbutamide > compound III > compound IV. 3. The dissociation constant (KD) for binding of compound IV to the sulphonylurea receptor in HIT-cells (pancreatic beta-cell line) was similar to the KD value for tolbutamide and fourfold higher than the KD value for compound III. 4. In mouse pancreatic beta-cells, drug concentrations inhibiting adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive K+ channels (KATP-channels) half-maximally (EC50) were determined by use of the patch-clamp technique. When the drugs were applied to the extracellular side of outside-out or the intracellular side of inside-out membrane patches, the ratio of extracellular to intracellular EC50 values was 281 for compound IV, 25.5 for compound III and 1.2 for tolbutamide. 5. In mouse pancreatic beta-cells, measurement of KATP-channel activity in cell-attached patches and recording of insulin release displayed much higher EC50 values for compound IV than inside-out patch experiments. A corresponding, but less pronounced difference in EC50 values was observed for compound III, whereas the EC50 values for tolbutamide did not differ significantly. 6. It is concluded that the sulphonylurea receptor is located at the cytoplasmic face of the beta-cell plasma membrane. Receptor activation is induced by the anionic forms of sulphonylureas and their analogues.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(2):87–143. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. The sulfonylurea receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 15;1175(1):45–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90008-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. R., Foubister A. J. Receptor binding sites of hypoglycemic sulfonylureas and related [(acylamino)alkyl]benzoic acids. J Med Chem. 1984 Jan;27(1):79–81. doi: 10.1021/jm00367a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Potassium selective ion channels in insulin-secreting cells: physiology, pharmacology and their role in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90012-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Weston A. H. The pharmacology of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:597–637. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines K. L., Hamilton S., Boyd A. E., 3rd Characterization of the sulfonylurea receptor on beta cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2589–2592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisen K., Hitzel V., Okomonopoulos R., Pünter J., Weyer R., Summ H. D. Inhibition of 3H-glibenclamide binding to sulfonylurea receptors by oral antidiabetics. Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(4):707–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. The preparation of, and studies on, free cell suspensions from mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1974 Oct;10(5):431–438. doi: 10.1007/BF01221634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Burckhardt G. Membrane transport of anions across epithelia of mammalian small intestine and kidney proximal tubule. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1983;96:1–51. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Shosaku T., Zünkler B. J., Trube G. Dual effects of ATP on K+ currents of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Feb;408(2):133–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00581342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Burgfeld J., Goerke F., Rennicke M., Schwanstecher M., Wallasch A., Zünkler B. J., Lenzen S. Control of insulin secretion by sulfonylureas, meglitinide and diazoxide in relation to their binding to the sulfonylurea receptor in pancreatic islets. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 15;38(8):1217–1229. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90327-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Heipel C., Rosenberger F., Scheffer K., Zünkler B. J., Schwanstecher C. Tolbutamide-sensitivity of the adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;342(5):566–574. doi: 10.1007/BF00169047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Schwanstecher M., Schwanstecher C. Pancreatic and extrapancreatic sulfonylurea receptors. Horm Metab Res. 1992 Dec;24(12):549–554. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Pusch M., Neher E. Washout phenomena in dialyzed mast cells allow discrimination of different steps in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biosci Rep. 1987 Apr;7(4):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF01121453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petzinger E., Fückel D. Evidence for a saturable, energy-dependent and carrier-mediated uptake of oral antidiabetics into rat hepatocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 31;213(3):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90627-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher C., Dickel C., Ebers I., Lins S., Zünkler B. J., Panten U. Diazoxide-sensitivity of the adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):87–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher C., Dickel C., Panten U. Interaction of tolbutamide and cytosolic nucleotides in controlling the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in mouse beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):302–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher M., Behrends S., Brandt C., Panten U. The binding properties of the solubilized sulfonylurea receptor from a pancreatic B-cell line are modulated by the Mg(++)-complex of ATP. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Aug;262(2):495–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher M., Brandt C., Behrends S., Schaupp U., Panten U. Effect of MgATP on pinacidil-induced displacement of glibenclamide from the sulphonylurea receptor in a pancreatic beta-cell line and rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;106(2):295–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Ashford M. L., Cook D. L., Hales C. N. The sulphonylurea receptor may be an ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Lancet. 1985 Aug 31;2(8453):474–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Kozlowski R. Z., Carrington C. A., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Effects of sulphonylureas and diazoxide on insulin secretion and nucleotide-sensitive channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):83–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Rorsman P., Ohno-Shosaku T. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00657506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zünkler B. J., Lenzen S., Männer K., Panten U., Trube G. Concentration-dependent effects of tolbutamide, meglitinide, glipizide, glibenclamide and diazoxide on ATP-regulated K+ currents in pancreatic B-cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;337(2):225–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00169252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zünkler B. J., Lins S., Ohno-Shosaku T., Trube G., Panten U. Cytosolic ADP enhances the sensitivity to tolbutamide of ATP-dependent K+ channels from pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 7;239(2):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80925-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zünkler B. J., Trube G., Panten U. How do sulfonylureas approach their receptor in the B-cell plasma membrane? Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;340(3):328–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00168518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


