Abstract
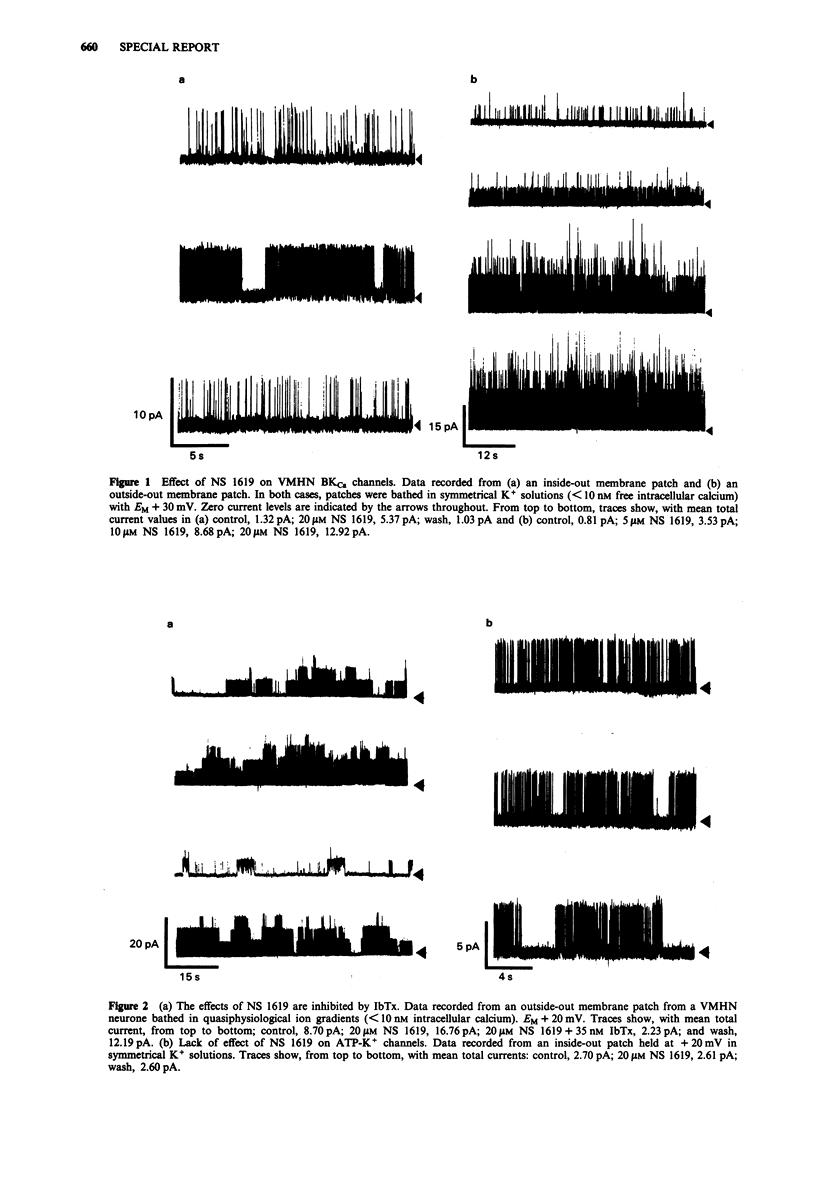
NS 1619 activates the large-conductance Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channel (BKCa) in membrane patches isolated from rat ventromedial hypothalamic neurones. The activation is concentration dependent, with a maximal effect at less than 30 microM, reversible and can be inhibited by application of iberiotoxin to the extracellular membrane. NS 1619 does not activate ATP-K+ channels present in the same neurones.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amoroso S., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Glucose, sulfonylureas, and neurotransmitter release: role of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):852–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2305257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashford M. L., Boden P. R., Treherne J. M. Glucose-induced excitation of hypothalamic neurones is mediated by ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jan;415(4):479–483. doi: 10.1007/BF00373626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candia S., Garcia M. L., Latorre R. Mode of action of iberiotoxin, a potent blocker of the large conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):583–590. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81630-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Weston A. H. The pharmacology of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:597–637. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfo G., Gottesmann C., Bidard J. N., Lazdunski M. K+ channels openers prevent epilepsy induced by the bee venom peptide MCD. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 17;159(3):329–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., Amoroso S., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. K+ channel openers activate brain sulfonylurea-sensitive K+ channels and block neurosecretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3489–3492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers A. J., Boden P. R., Ashford M. L. Lack of effect of potassium channel openers on ATP-modulated potassium channels recorded from rat ventromedial hypothalamic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1068–1074. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


