Abstract
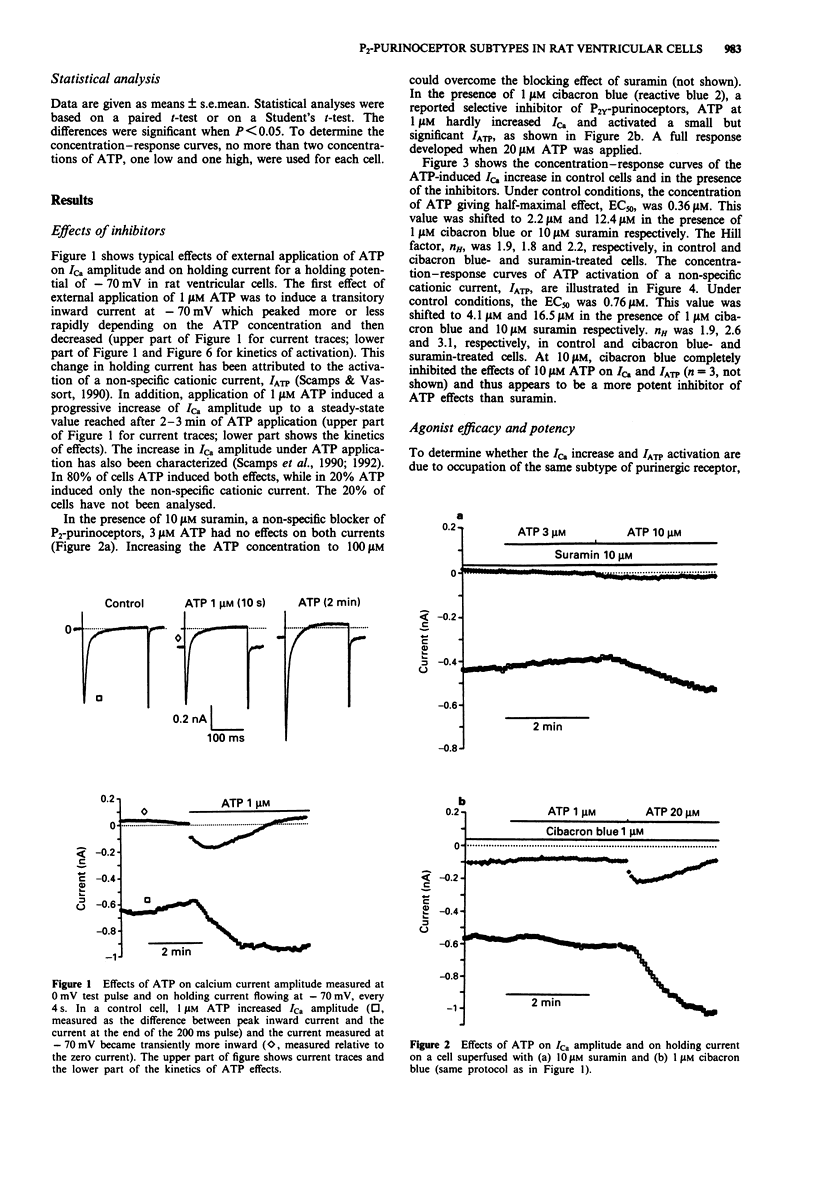
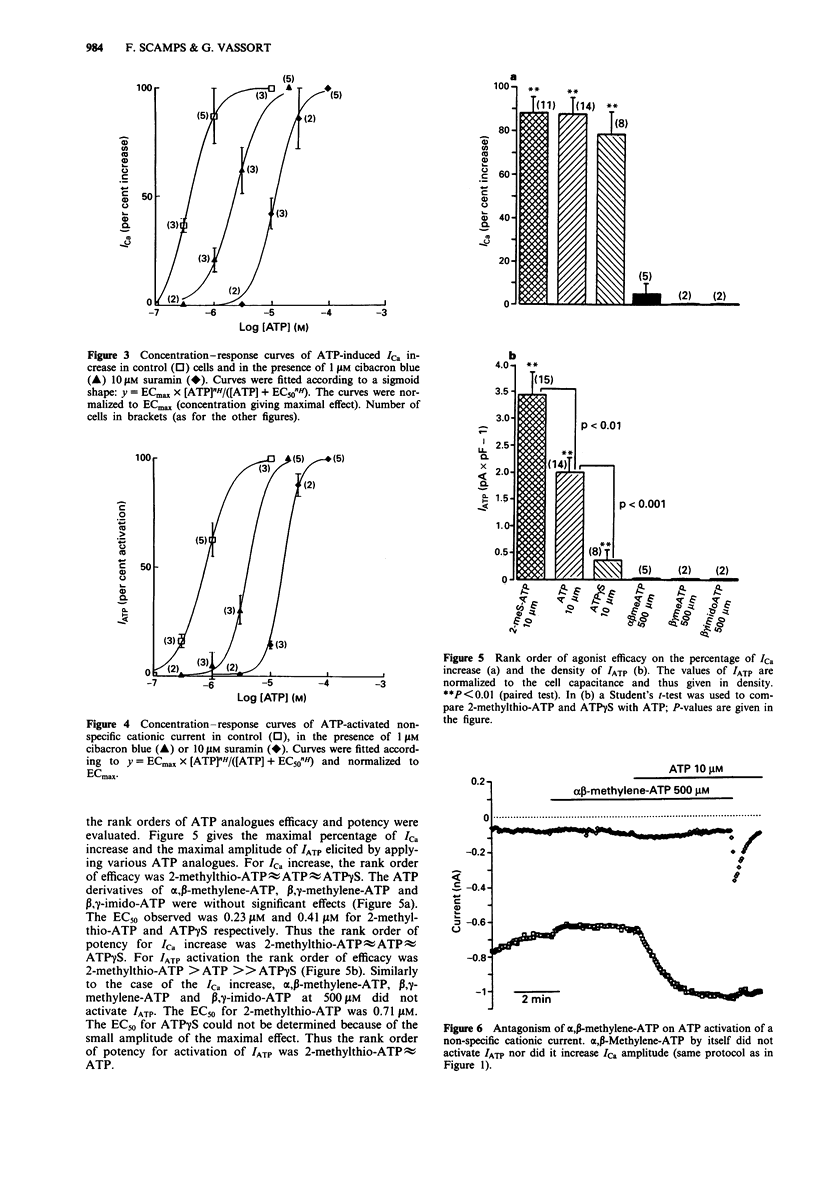
1. The pharmacological profile of the ATP-induced increase in ICa amplitude and of ATP activation of a non-specific cationic current, IATP, was investigated in rat ventricular cells. 2. The EC50 values for ICa increase and IATP activation were 0.36 microM and 0.76 microM respectively. Suramin (10 microM) and cibacron blue (1 microM) competitively antagonized both effects of ATP. 3. The rank order of efficacy and potency of ATP analogues in increasing ICa amplitude was 2-methylthio-ATP approximately ATP approximately ATP gamma S. The derivatives alpha,beta-methylene-ATP, beta,gamma-methylene-ATP and beta,gamma-imido-ATP up to 500 microM had no significant effects. 4. The rank order of efficacy of ATP analogues in activating a non-specific cationic current, IATP, was 2-methylthio-ATP > ATP >> ATP gamma S. The rank order of potency was 2-methylthio-ATP approximately ATP. The EC50 of ATP gamma S could not be determined owing to its very low efficacy. 5. The ATP analogues alpha,beta-methylene-ATP, beta,gamma-methylene-ATP and beta,gamma-imido-ATP at 500 microM did not activate IATP but acted as antagonists of activation of IATP by ATP. 6. The results suggest that the increase in ICa amplitude induced by external ATP is due to activation of P2Y-purinoceptors. 7. The mechanism of IATP activation remains to be determined before the receptor subtype involved can be deduced.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez J. L., Vassort G. Properties of the low threshold Ca current in single frog atrial cardiomyocytes. A comparison with the high threshold Ca current. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(3):519–545. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Burnstock G., Webb T. E. G protein-coupled receptors for ATP and other nucleotides: a new receptor family. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Mar;15(3):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björnsson O. G., Monck J. R., Williamson J. R. Identification of P2Y purinoceptors associated with voltage-activated cation channels in cardiac ventricular myocytes of the rat. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):395–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Simon J., Burnstock G., Barnard E. A. Solubilization and molecular size determination of the P2x purinoceptor from rat vas deferens. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17581–17587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie A., Sharma V. K., Sheu S. S. Mechanism of extracellular ATP-induced increase of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in isolated rat ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:369–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danziger R. S., Raffaeli S., Moreno-Sanchez R., Sakai M., Capogrossi M. C., Spurgeon H. A., Hansford R. G., Lakatta E. G. Extracellular ATP has a potent effect to enhance cytosolic calcium and contractility in single ventricular myocytes. Cell Calcium. 1988 Aug;9(4):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(88)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Young M. B., Scarpa A. Extracellular ATP induces Ca2+ transients in cardiac myocytes which are potentiated by norepinephrine. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80508-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., el-Moatassim C. Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):C577–C606. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Gibb A. J. ATP--a fast neurotransmitter. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 28;325(1-2):86–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81419-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Bean B. P. Dual control by ATP and acetylcholine of inwardly rectifying K+ channels in bovine atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Mar;415(6):651–657. doi: 10.1007/BF02584001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Bean B. P. Two ATP-activated conductances in bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jan;91(1):1–27. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandía L., García A. G., Morad M. ATP modulation of calcium channels in chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:55–72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano Y., Abe S., Sawanobori T., Hiraoka M. External ATP-induced changes in [Ca2+]i and membrane currents in mammalian atrial myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 1):C673–C680. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.4.C673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Nörenberg W. Neuronal ATP receptors and their mechanism of action. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Feb;14(2):50–54. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90030-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legssyer A., Poggioli J., Renard D., Vassort G. ATP and other adenine compounds increase mechanical activity and inositol trisphosphate production in rat heart. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:185–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantelli L., Amerini S., Filippi S., Ledda F. Blockade of adenosine receptors unmasks a stimulatory effect of ATP on cardiac contractility. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1268–1271. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura H., Ehara T. Activation of chloride current by purinergic stimulation in guinea pig heart cells. Circ Res. 1992 Apr;70(4):851–855. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.4.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucéat M., Clément O., Scamps F., Vassort G. Extracellular ATP-induced acidification leads to cytosolic calcium transient rise in single rat cardiac myocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/bj2740055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucéat M., Clément O., Vassort G. Extracellular MgATP activates the Cl-/HCO3- exchanger in single rat cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:241–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu Y., Campbell D. L., Strauss H. C. Modulation of L-type Ca2+ current by extracellular ATP in ferret isolated right ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:295–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu Y., Himmel H. M., Campbell D. L., Strauss H. C. Effects of extracellular ATP on ICa, [Ca2+]i, and contraction in isolated ferret ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):C702–C708. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scamps F., Legssyer A., Mayoux E., Vassort G. The mechanism of positive inotropy induced by adenosine triphosphate in rat heart. Circ Res. 1990 Oct;67(4):1007–1016. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.4.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scamps F., Rybin V., Puceat M., Tkachuk V., Vassort G. A Gs protein couples P2-purinergic stimulation to cardiac Ca channels without cyclic AMP production. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Oct;100(4):675–701. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scamps F., Vassort G. Mechanism of extracellular ATP-induced depolarization in rat isolated ventricular cardiomyocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Nov;417(3):309–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00370997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J. S., Christie A., Levy M. N., Scarpa A. Modulation by extracellular ATP of two distinct currents in rat myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 1):C1411–C1417. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.6.C1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


