Abstract
1. The possible existence of atypical beta-adrenoceptors in vascular smooth muscle of the rat common carotid artery was examined in this study. 2. Isoprenaline produced concentration-dependent relaxation of noradrenaline (10(-7) M) precontracted ring segments of the carotid artery. The relaxation was not affected by endothelial denudation. 3. Propranolol (10(-8) M-3 x 10(-7) M) shifted the isoprenaline curve to the right without suppressing the maximum response. However, the slope (0.74) of the Schild plot was significantly (P < 0.05) less than 1. 4. Salbutamol (beta 2), CGP 12177 and BRL 37344 (beta 3) also concentration-dependently relaxed noradrenaline precontracted artery segments. These relaxations were not affected by propranolol (10(-7) M). Pretreatment of the artery segments with BRL 37344 did not desensitize the tissue to the relaxant effect of isoprenaline, CGP 12177 and salbutamol. 5. It is concluded that atypical beta-adrenoceptors exist in vascular smooth muscle of the common carotid artery.
Full text
PDF
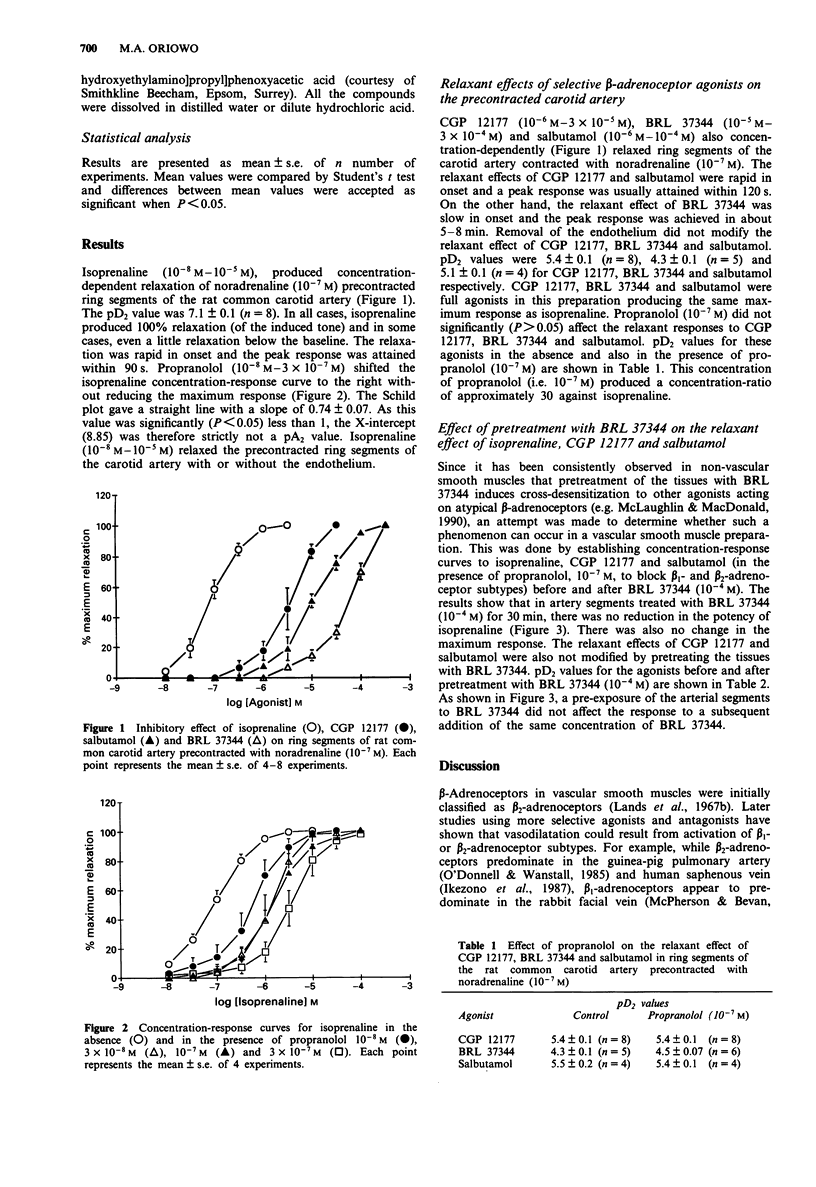
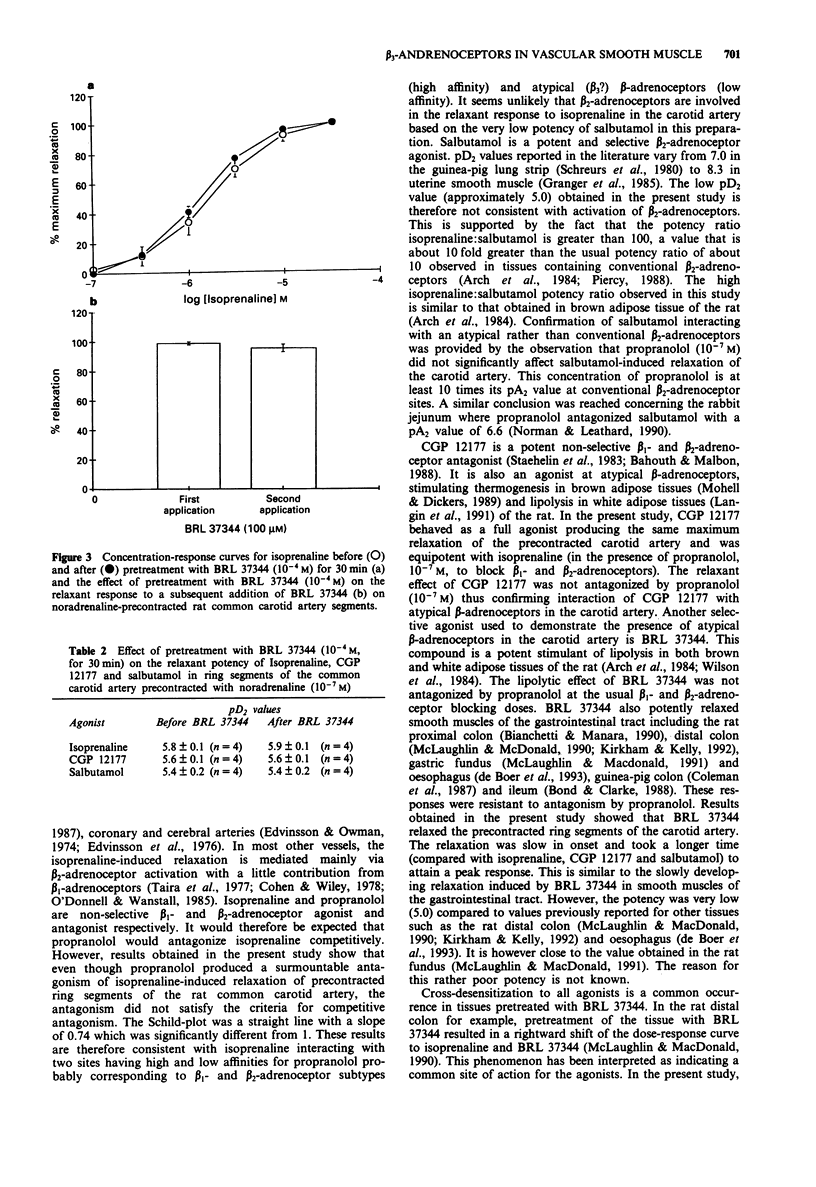

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R. The brown adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor. Proc Nutr Soc. 1989 Jul;48(2):215–223. doi: 10.1079/pns19890032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahouth S. W., Malbon C. C. Subclassification of beta-adrenergic receptors of rat fat cells: a re-evaluation. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;34(3):318–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetti A., Manara L. In vitro inhibition of intestinal motility by phenylethanolaminotetralines: evidence of atypical beta-adrenoceptors in rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):831–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Clarke D. E. Agonist and antagonist characterization of a putative adrenoceptor with distinct pharmacological properties from the alpha- and beta-subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):723–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. J., Bertholet A. Effects of pindolol on vascular smooth muscle. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(1):117–119. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wiley K. S. Rat jugular vein relaxes to norepinephrine, phenylephrine and histamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 May;205(2):400–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggrell S. A. Relaxant and beta 2-adrenoceptor blocking activities of (+/- )-, (+)- and (-)-pindolol on the rat isolated aorta. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;42(6):444–446. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1990.tb06590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Owman C. Pharmacological characterization of adrenergic alpha and beta receptors mediating the vasomotor responses of cerebral arteries in vitro. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):835–849. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Owman C., Sjöberg N. O. Autonomic nerves, mast cells, and amine receptors in human brain vessels. A histochemical and pharmacological study. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 22;115(3):377–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger S. E., Hollingsworth M., Weston A. H. A comparison of several calcium antagonists on uterine, vascular and cardiac muscles from the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 May;85(1):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. W., Marshall I. Novel signal transduction pathway mediating endothelium-dependent beta-adrenoceptor vasorelaxation in rat thoracic aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):684–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezono K., Zerkowski H. R., Beckeringh J. J., Michel M. C., Brodde O. E. Beta-2 adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation of the isolated human saphenous vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Apr;241(1):294–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Luduena F. P., Buzzo H. J. Differentiation of receptors responsive to isoproterenol. Life Sci. 1967 Nov 1;6(21):2241–2249. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Portillo M. P., Saulnier-Blache J. S., Lafontan M. Coexistence of three beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in white fat cells of various mammalian species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Characterization of catecholamine-mediated relaxations in rat isolated gastric fundus: evidence for an atypical beta-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1351–1356. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Evidence for the existence of 'atypical' beta-adrenoceptors (beta 3-adrenoceptors) mediating relaxation in the rat distal colon in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):569–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Bevan J. A. Specialization in beta-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptor distribution in veins of the rabbit face: relationship to myogenic tone and sympathetic nerve innervation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jan;240(1):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohell N., Dicker A. The beta-adrenergic radioligand [3H]CGP-12177, generally classified as an antagonist, is a thermogenic agonist in brown adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):401–405. doi: 10.1042/bj2610401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman B. J., Leathard H. L. Evidence that an atypical beta-adrenoceptor mediates the inhibition of spontaneous rhythmical contractions of rabbit isolated jejunum induced by ritodrine and salbutamol. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):27–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12083.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Wanstall J. C. Responses to the beta 2-selective agonist procaterol of vascular and atrial preparations with different functional beta-adrenoceptor populations. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):227–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piercy V. Method for assessing the activity of drugs at beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in the same animal. J Pharmacol Methods. 1988 Sep;20(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(88)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreurs A. J., Terpstra G. K., Raaijmakers J. A., Nijkamp F. P. Effects of vaccination with Haemophilus influenzae on adrenoceptor function of tracheal and parenchymal strips. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Dec;215(3):691–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin M., Simons P., Jaeggi K., Wigger N. CGP-12177. A hydrophilic beta-adrenergic receptor radioligand reveals high affinity binding of agonists to intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3496–3502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira N., Yabuuchi Y., Yamashita S. Profile of beta-adrenoceptors in femoral, superior mesenteric and renal vascular beds of dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Apr;59(4):577–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Wilson S., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Arch J. R. The rat lipolytic beta-adrenoceptor: studies using novel beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 May 4;100(3-4):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer R. E., Brouwer F., Zaagsma J. The beta-adrenoceptors mediating relaxation of rat oesophageal muscularis mucosae are predominantly of the beta 3-, but also of the beta 2-subtype. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):442–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


