Abstract
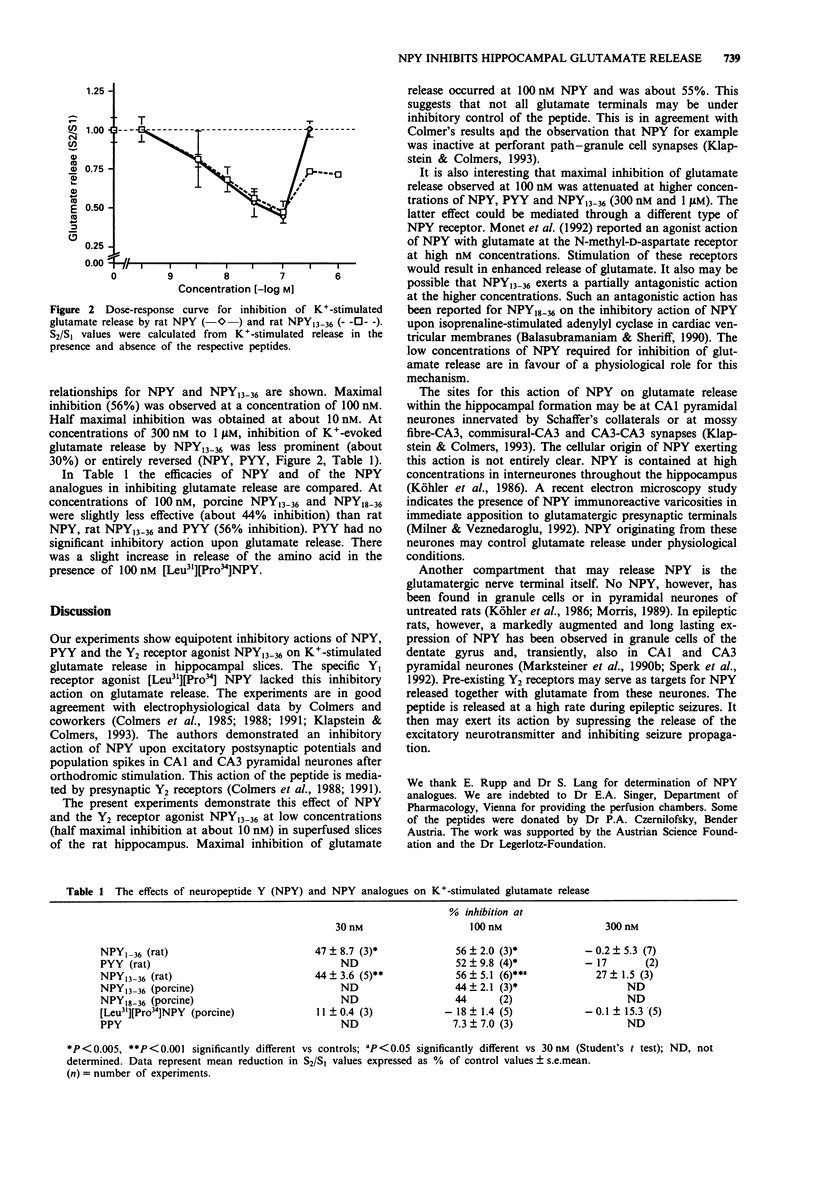
1. We investigated the effects of neuropeptide Y (NPY), peptide YY (PYY), NPY13-36, NPY18-36, [Leu31][Pro34]NPY and of pancreatic polypeptide Y (PPY) on calcium-dependent, potassium-stimulated glutamate release in superfused rat hippocampal slices. 2. NPY, PYY and the Y2 receptor agonist NPY13-36 equipotently inhibited the release of glutamate. The half-maximal response was observed at about 10 nM in a dose-dependent manner (3 to 100 nM). Maximal inhibition of 50 to 60% was obtained at 100 nM. At higher concentrations of the peptides (300 nM and 1 microM) this inhibition was partially or entirely reversed. Porcine NPY13-36 and NPY18-36 inhibited glutamate release by about 44% at 100 nM. 3. The specific Y1 receptor agonist, [Leu31][Pro34]NPY, caused an insignificant increase in glutamate release at 100 to 300 nM concentrations. PPY had no effect on potassium-evoked glutamate release in hippocampal slices at concentrations of 30 nM to 1 microM. 4. The experiments support previous electrophysiological data. They suggest a potent inhibitory action of NPY through NPY-Y2 receptors on the release of the excitatory amino acid glutamate in rat hippocampus. Especially under conditions of increased NPY synthesis, such as in epilepsy, this mechanism may be of pathophysiological relevance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aicher S. A., Springston M., Berger S. B., Reis D. J., Wahlestedt C. Receptor-selective analogs demonstrate NPY/PYY receptor heterogeneity in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Sep 2;130(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90220-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen Y. S., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):877–879. doi: 10.1126/science.6136091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramaniam A., Sheriff S. Neuropeptide Y (18-36) is a competitive antagonist of neuropeptide Y in rat cardiac ventricular membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14724–14727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellmann R., Widmann R., Olenik C., Meyer D. K., Maas D., Marksteiner J., Sperk G. Enhanced rate of expression and biosynthesis of neuropeptide Y after kainic acid-induced seizures. J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke S. P., Nadler J. V. Regulation of glutamate and aspartate release from slices of the hippocampal CA1 area: effects of adenosine and baclofen. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1541–1551. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chronwall B. M., DiMaggio D. A., Massari V. J., Pickel V. M., Ruggiero D. A., O'Donohue T. L. The anatomy of neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1985 Aug;15(4):1159–1181. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmers W. F., Klapstein G. J., Fournier A., St-Pierre S., Treherne K. A. Presynaptic inhibition by neuropeptide Y in rat hippocampal slice in vitro is mediated by a Y2 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):41–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmers W. F., Lukowiak K., Pittman Q. J. Neuropeptide Y action in the rat hippocampal slice: site and mechanism of presynaptic inhibition. J Neurosci. 1988 Oct;8(10):3827–3837. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-10-03827.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmers W. F., Lukowiak K., Pittman Q. J. Neuropeptide Y reduces orthodromically evoked population spike in rat hippocampal CA1 by a possibly presynaptic mechanism. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90880-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danho W., Triscari J., Vincent G., Nakajima T., Taylor J., Kaiser E. T. Synthesis and biological evaluation of pNPY fragments. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1988 Dec;32(6):496–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1988.tb01380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont Y., Fournier A., St-Pierre S., Quirion R. Comparative characterization and autoradiographic distribution of neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes in the rat brain. J Neurosci. 1993 Jan;13(1):73–86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-01-00073.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flood J. F., Morley J. E. Dissociation of the effects of neuropeptide Y on feeding and memory: evidence for pre- and postsynaptic mediation. Peptides. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):963–966. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhlendorff J., Gether U., Aakerlund L., Langeland-Johansen N., Thøgersen H., Melberg S. G., Olsen U. B., Thastrup O., Schwartz T. W. [Leu31, Pro34]neuropeptide Y: a specific Y1 receptor agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):182–186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlert D. R., Gackenheimer S. L., Schober D. A. [Leu31-Pro34] neuropeptide Y identifies a subtype of 125I-labeled peptide YY binding sites in the rat brain. Neurochem Int. 1992 Jul;21(1):45–67. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(92)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundemar L., Wahlestedt C., Reis D. J. Neuropeptide Y acts at an atypical receptor to evoke cardiovascular depression and to inhibit glutamate responsiveness in the brainstem. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Aug;258(2):633–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Hermann A., Greene R. W., Chan-Palay V. Action and location of neuropeptide tyrosine (Y) on hippocampal neurons of the rat in slice preparations. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Mar 8;257(2):208–215. doi: 10.1002/cne.902570207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig M., Murison R. Intracerebroventricular neuropeptide Y suppresses open field and home cage activity in the rat. Regul Pept. 1987 Nov;19(3-4):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(87)90278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig M., Wahlestedt C., Widerlöv E. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-induced suppression of activity in the rat: evidence for NPY receptor heterogeneity and for interaction with alpha-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 22;157(2-3):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90384-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapstein G. J., Colmers W. F. On the sites of presynaptic inhibition by neuropeptide Y in rat hippocampus in vitro. Hippocampus. 1993 Jan;3(1):103–111. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450030111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Eriksson L., Davies S., Chan-Palay V. Neuropeptide Y innervation of the hippocampal region in the rat and monkey brain. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Feb 15;244(3):384–400. doi: 10.1002/cne.902440310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marksteiner J., Ortler M., Bellmann R., Sperk G. Neuropeptide Y biosynthesis is markedly induced in mossy fibers during temporal lobe epilepsy of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1990 May 4;112(2-3):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90193-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marksteiner J., Sperk G. Concomitant increase of somatostatin, neuropeptide Y and glutamate decarboxylase in the frontal cortex of rats with decreased seizure threshold. Neuroscience. 1988 Aug;26(2):379–385. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marksteiner J., Sperk G., Maas D. Differential increases in brain levels of neuropeptide Y and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide after kainic acid-induced seizures in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Jan-Feb;339(1-2):173–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00165140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marksteiner Josef, Lassmann Hans, Saria Alois, Humpel Christian, Meyer Dieter K., Sperk Günther. Neuropeptide Levels after Pentylenetetrazol Kindling in the Rat. Eur J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;2(1):98–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel J. C., Fournier A., St Pierre S., Quirion R. Quantitative autoradiographic distribution of [125I]Bolton-Hunter neuropeptide Y receptor binding sites in rat brain. Comparison with [125I]peptide YY receptor sites. Neuroscience. 1990;36(1):255–283. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90367-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner T. A., Veznedaroglu E. Ultrastructural localization of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in the rat hippocampal formation. Hippocampus. 1992 Apr;2(2):107–125. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450020204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Debonnel G., Fournier A., de Montigny C. Neuropeptide Y potentiates the N-methyl-D-aspartate response in the CA3 dorsal hippocampus. II. Involvement of a subtype of sigma receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Dec;263(3):1219–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J. Neuronal localisation of neuropeptide Y gene expression in rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Dec 15;290(3):358–368. doi: 10.1002/cne.902900305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer E. A. Transmitter release from brain slices elicited by single pulses: a powerful method to study presynaptic mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):274–276. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperk G., Marksteiner J., Gruber B., Bellmann R., Mahata M., Ortler M. Functional changes in neuropeptide Y- and somatostatin-containing neurons induced by limbic seizures in the rat. Neuroscience. 1992 Oct;50(4):831–846. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90207-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley B. G., Leibowitz S. F. Neuropeptide Y injected in the paraventricular hypothalamus: a powerful stimulant of feeding behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3940–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenfors C., Theodorsson E., Mathé A. A. Effect of repeated electroconvulsive treatment on regional concentrations of tachykinins, neurotensin, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, neuropeptide Y, and galanin in rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Nov;24(3):445–450. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth P. T., Bindokas V. P., Bleakman D., Colmers W. F., Miller R. J. Mechanism of presynaptic inhibition by neuropeptide Y at sympathetic nerve terminals. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):635–639. doi: 10.1038/364635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C., Pich E. M., Koob G. F., Yee F., Heilig M. Modulation of anxiety and neuropeptide Y-Y1 receptors by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):528–531. doi: 10.1126/science.8380941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C., Yanaihara N., Håkanson R. Evidence for different pre-and post-junctional receptors for neuropeptide Y and related peptides. Regul Pept. 1986 Feb;13(3-4):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(86)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. W., Miller R. J. 125I-neuropeptide Y and 125I-peptide YY bind to multiple receptor sites in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):779–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Quidt M. E., Emson P. C. Distribution of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system--II. Immunohistochemical analysis. Neuroscience. 1986 Jul;18(3):545–618. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


