Abstract
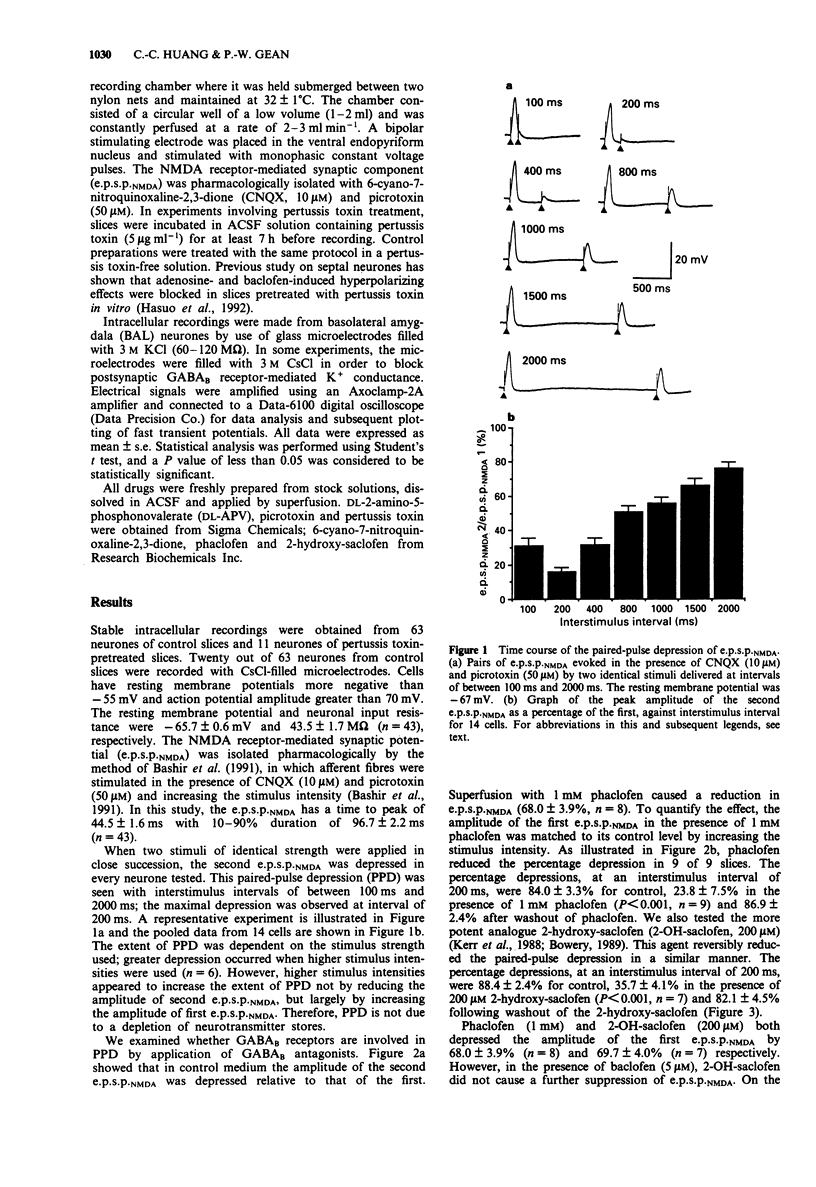
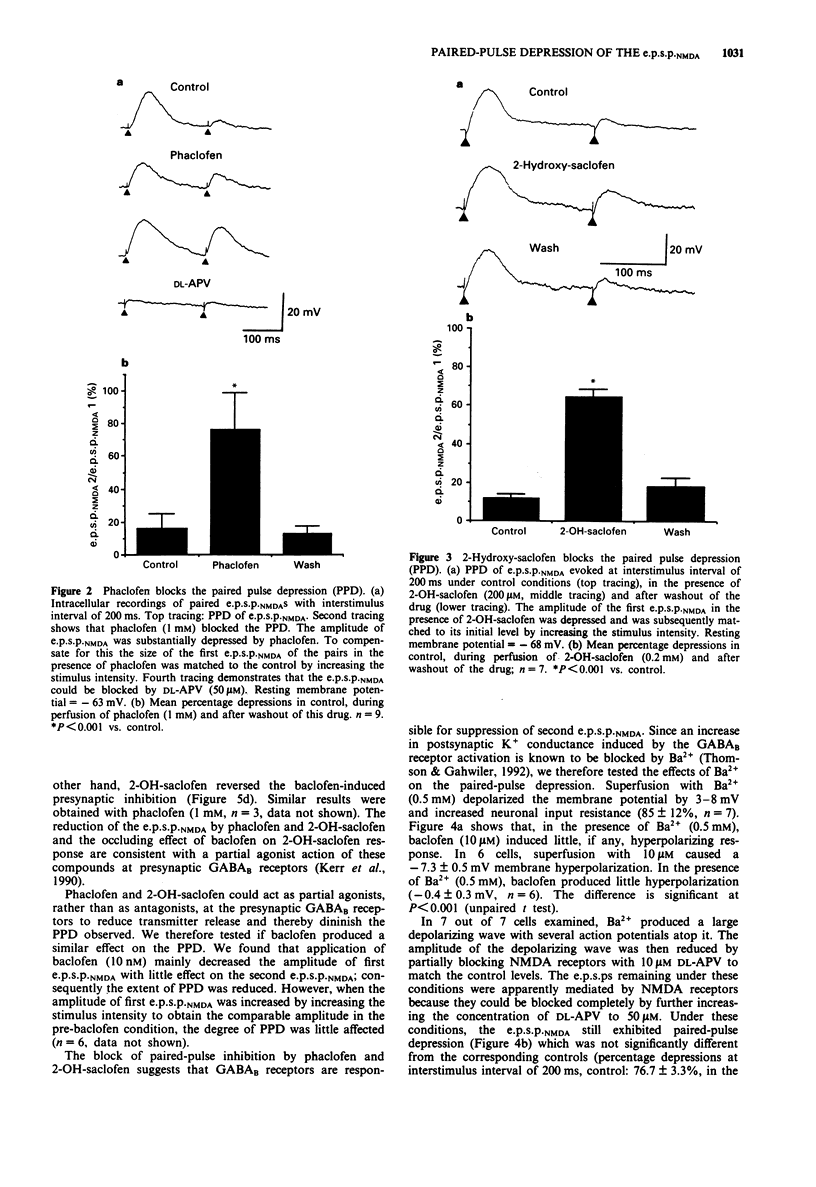
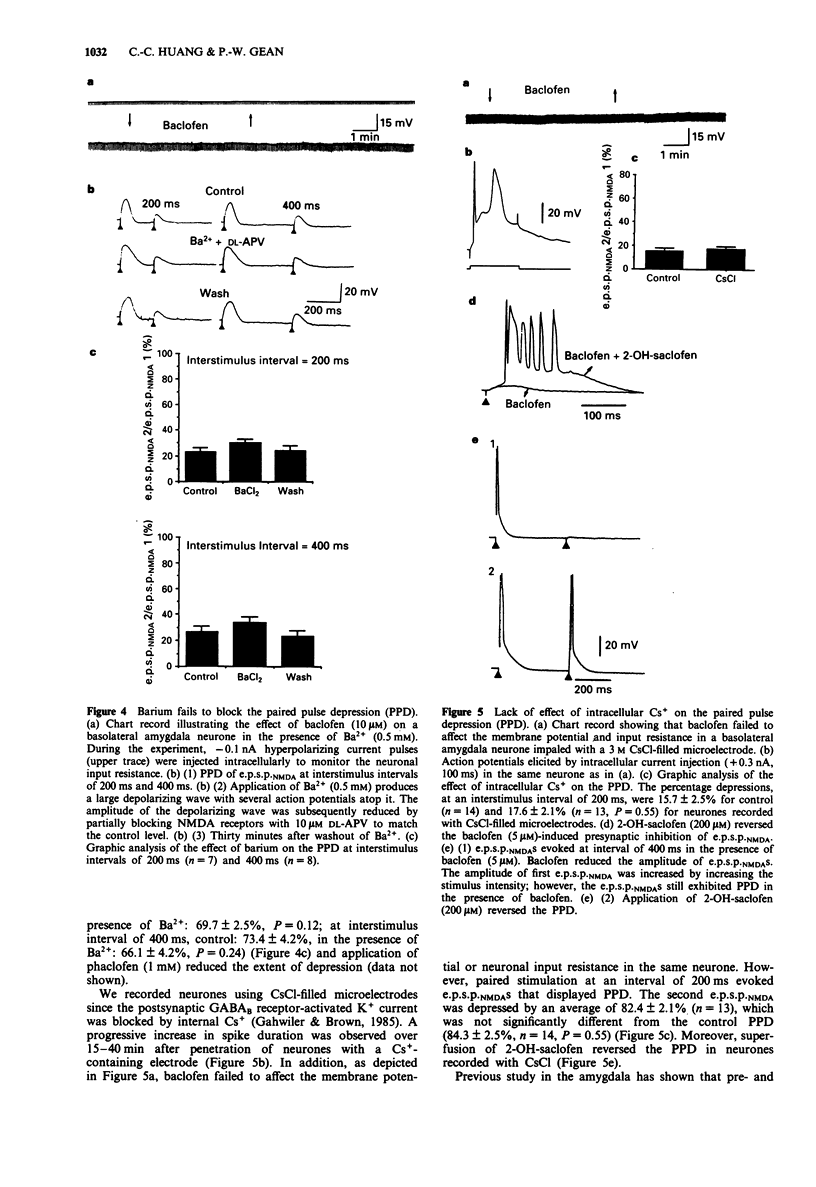
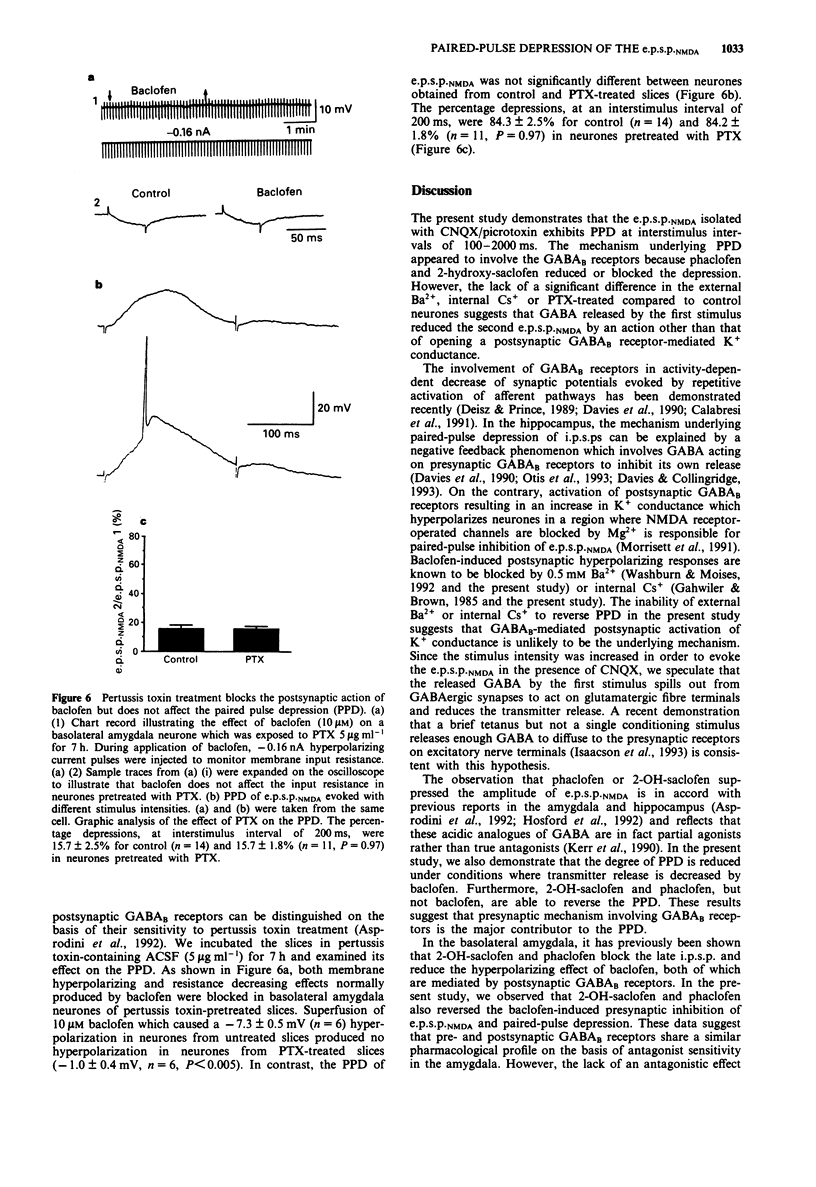
1. An in vitro slice preparation of rat amygdala was used to study the paired-pulse depression of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated synaptic potential e.p.s.p.NMDA. 2. The e.p.s.p.NMDA was isolated pharmacologically by applying a solution containing the non-NMDA receptor antagonist, 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) and the gamma-aminobutyric acidA (GABAA) blocker picrotoxin and increasing the stimulus intensity. 3. When two stimuli of identical strength were applied in close succession, the second e.p.s.p.NMDA was depressed. This paired-pulse depression was seen with interstimulus intervals of between 100 ms and 2000 ms; the maximal depression was observed at interval of 200 ms. 4. Superfusion of phaclofen or 2-hydroxy-saclofen inhibited the paired-pulse depression indicating the involvement of GABAB receptors. 5. Bath applications of Ba2+ or intracellular injection of Cs+ to block post- but not presynaptic GABAB receptors failed to inhibit the paired-pulse depression (PPD). 6. Incubation of slices with pertussis toxin prevented the postsynaptic hyperpolarization induced by baclofen. The PPD of e.p.s.p.NMDA, however, was not affected by pertussis toxin treatment. 7. These results suggest that GABA released by the first stimulus acts on GABAB receptors to suppress the second e.p.s.p.NMDA via mechanisms other than activation of a postsynaptic GABAB receptor-coupled K+ conductance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asprodini E. K., Rainnie D. G., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Epileptogenesis reduces the sensitivity of presynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptors on glutamatergic afferents in the amygdala. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Sep;262(3):1011–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Anticonvulsant-like actions of baclofen in the rat hippocampal slice. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Apr;78(4):701–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashir Z. I., Alford S., Davies S. N., Randall A. D., Collingridge G. L. Long-term potentiation of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):156–158. doi: 10.1038/349156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Aniksztejn L., Bregestovski P. Protein kinase C modulation of NMDA currents: an important link for LTP induction. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Sep;15(9):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90049-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. GABAB receptors and their significance in mammalian pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabresi P., Mercuri N. B., De Murtas M., Bernardi G. Involvement of GABA systems in feedback regulation of glutamate-and GABA-mediated synaptic potentials in rat neostriatum. J Physiol. 1991;440:581–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerne R., Rusin K. I., Randić M. Enhancement of the N-methyl-D-aspartate response in spinal dorsal horn neurons by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Oct 29;161(2):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90275-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Huang L. Y. Sustained potentiation of NMDA receptor-mediated glutamate responses through activation of protein kinase C by a mu opioid. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90270-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Singer W. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jul;11(7):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90011-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. H., Collingridge G. L. The physiological regulation of synaptic inhibition by GABAB autoreceptors in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:245–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. H., Davies S. N., Collingridge G. L. Paired-pulse depression of monosynaptic GABA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic responses in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:513–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisz R. A., Prince D. A. Frequency-dependent depression of inhibition in guinea-pig neocortex in vitro by GABAB receptor feed-back on GABA release. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:513–541. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Scott R. H. Inhibition of calcium currents in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurones by (-)-baclofen. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. Pre- and postsynaptic GABAB receptors in the hippocampus have different pharmacological properties. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gean P. W., Chang F. C., Huang C. C., Lin J. H., Way L. J. Long-term enhancement of EPSP and NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in the amygdala. Brain Res Bull. 1993;31(1-2):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(93)90003-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gean P. W., Chang F. C. Pharmacological characterization of excitatory synaptic potentials in rat basolateral amygdaloid neurons. Synapse. 1992 May;11(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/syn.890110102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gean P. W., Chou S. M., Chang F. C. Epileptiform activity induced by 4-aminopyridine in rat amygdala neurons: the involvement of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 10;184(2-3):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90612-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gean P. W., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Anderson A. C. Spontaneous epileptiform activity and alteration of GABA- and of NMDA-mediated neurotransmission in amygdala neurons kindled in vivo. Brain Res. 1989 Aug 7;494(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gean P. W., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Picrotoxin induced epileptiform activity in amygdaloid neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 14;73(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Brown D. A. GABAB-receptor-activated K+ current in voltage-clamped CA3 pyramidal cells in hippocampal cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1558–1562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasuo H., Shoji S., Gallagher J. P., Akasu T. Adenosine inhibits the synaptic potentials in rat septal nucleus neurons mediated through pre- and postsynaptic A1-adenosine receptors. Neurosci Res. 1992 May;13(4):281–299. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(92)90040-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosford D. A., Clark S., Cao Z., Wilson W. A., Jr, Lin F. H., Morrisett R. A., Huin A. The role of GABAB receptor activation in absence seizures of lethargic (lh/lh) mice. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):398–401. doi: 10.1126/science.1321503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Tsai J. J., Gean P. W. Enhancement of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic potential by isoproterenol is blocked by Rp-adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphothioate. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Oct 29;161(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90295-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson J. S., Solís J. M., Nicoll R. A. Local and diffuse synaptic actions of GABA in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90308-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson G., Kolb C., Hausdorf A., Portet C., Schmutz M., Olpe H. R. GABAB receptors in various in vitro and in vivo models of epilepsy: a study with the GABAB receptor blocker CGP 35348. Neuroscience. 1992;47(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90120-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Johnston G. A., Abbenante J., Prager R. H. 2-Hydroxy-saclofen: an improved antagonist at central and peripheral GABAB receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Sep 23;92(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90748-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gal La Salle G. Unitary responses in the amygdaloid complex following stimulation of various diencephalic structures. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 24;118(3):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90315-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. J. Immunohistochemical identification of gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jan 21;53(2):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B., Garthwaite J. Excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Sep;11(9):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90184-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrisett R. A., Mott D. D., Lewis D. V., Swartzwelder H. S., Wilson W. A. GABAB-receptor-mediated inhibition of the N-methyl-D-aspartate component of synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1991 Jan;11(1):203–209. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-01-00203.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott D. D., Bragdon A. C., Lewis D. V., Wilson W. A. Baclofen has a proepileptic effect in the rat dentate gyrus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jun;249(3):721–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otis T. S., De Koninck Y., Mody I. Characterization of synaptically elicited GABAB responses using patch-clamp recordings in rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1993 Apr;463:391–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfrieger F. W., Gottmann K., Lux H. D. Kinetics of GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of calcium currents and excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons in vitro. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainnie D. G., Asprodini E. K., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Inhibitory transmission in the basolateral amygdala. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Sep;66(3):999–1009. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.3.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainnie D. G., Asprodini E. K., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Kindling-induced long-lasting changes in synaptic transmission in the basolateral amygdala. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Feb;67(2):443–454. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.2.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanziani M., Capogna M., Gähwiler B. H., Thompson S. M. Presynaptic inhibition of miniature excitatory synaptic currents by baclofen and adenosine in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):919–927. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Miller R. J. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ currents and synaptic transmission in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:669–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzwelder H. S., Bragdon A. C., Sutch C. P., Ault B., Wilson W. A. Baclofen suppresses hippocampal epileptiform activity at low concentrations without suppressing synaptic transmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):881–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Yamamoto C. The long-lasting inhibition recorded in vitro from the lateral nucleus of the amygdala. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 16;206(2):474–478. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90550-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Gähwiler B. H. Comparison of the actions of baclofen at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1992;451:329–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P. G., Dekin M. S. GABAb receptors are coupled to a barium-insensitive outward rectifying potassium conductance in premotor respiratory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Jan;69(1):286–289. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.1.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn M. S., Moises H. C. Inhibitory responses of rat basolateral amygdaloid neurons recorded in vitro. Neuroscience. 1992 Oct;50(4):811–830. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90206-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


