Abstract
1. Experiments were designed to analyse the requirement of myoendothelial junctions by bradykinin-induced endothelium-dependent relaxations resistant to NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG) and indomethacin porcine coronary arteries. 2. Rings of porcine coronary arteries were contracted with the thromboxane receptor agonist, U46619 and relaxations to bradykinin recorded isometrically. All experiments were performed in the presence of indomethacin. Nitric oxide (NO)-mediated effects were blocked by the NO synthase inhibitor L-NOARG (250 microM) and myoendothelial contacts inhibited by treatment with hypertonic solution containing D-mannitol or sucrose (each 180 mM) or the gap junctional uncoupling agent 1-heptanol (2 mM). High [K+] solutions (40 mM) were used to probe a possible contribution of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF). 3. In the presence of endothelium, bradykinin induced concentration-dependent relaxations with a mean EC50 of 3.2 nM and a maximum response of 95 +/- 1% of papaverine-induced relaxation (control curve). 4. In the absence of endothelium, bradykinin failed to induce relaxations. Addition of cultured porcine aortic endothelial cells to the organ bath resulted in some relaxation and restored in part the relaxant effect of bradykinin. This endothelial cell-mediated relaxant effect was completely abolished in the presence of 250 microM L-NOARG. 5. Bradykinin-induced relaxations in endothelium-preserved rings were only slightly suppressed by L-NOARG (86% of control). In vessels partially depolarized by high extracellular [K+] (40 mM) relaxation was reduced to 72% of control. In the presence of L-NOARG, bradykinin failed to relax partially depolarized vessels.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

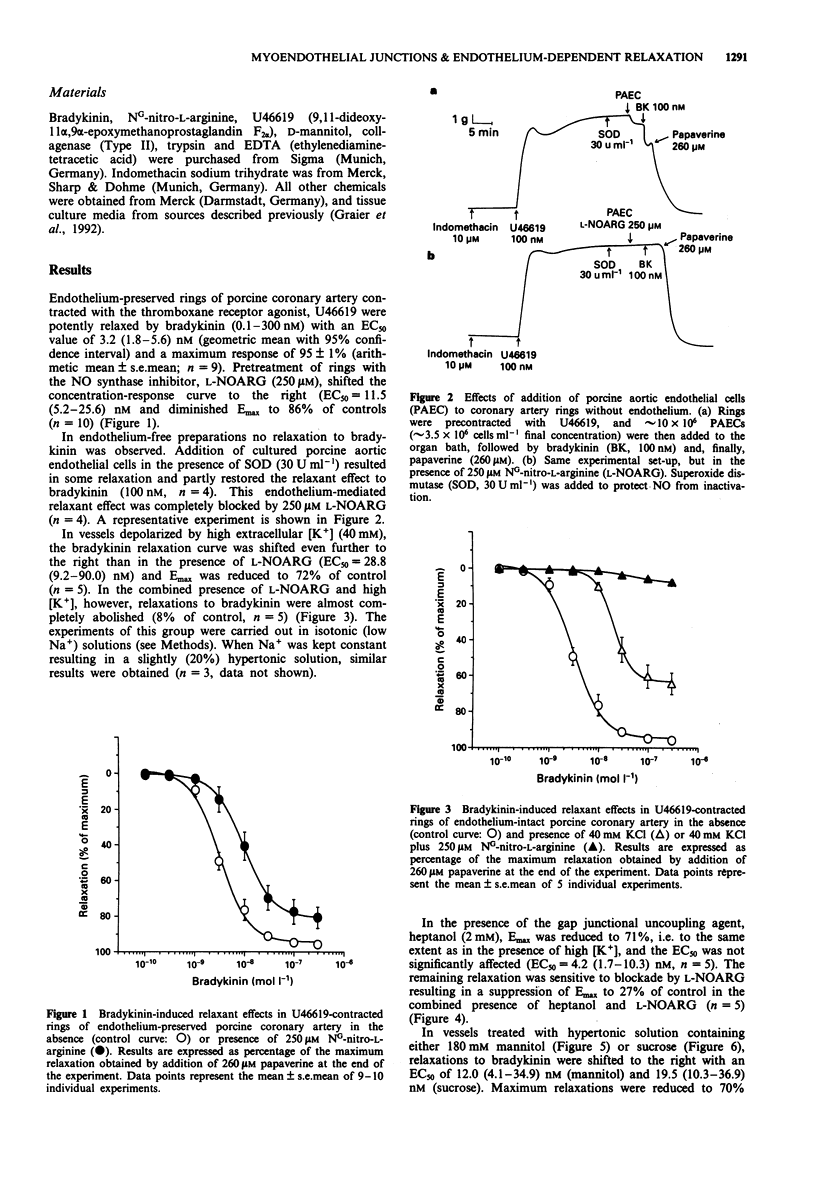
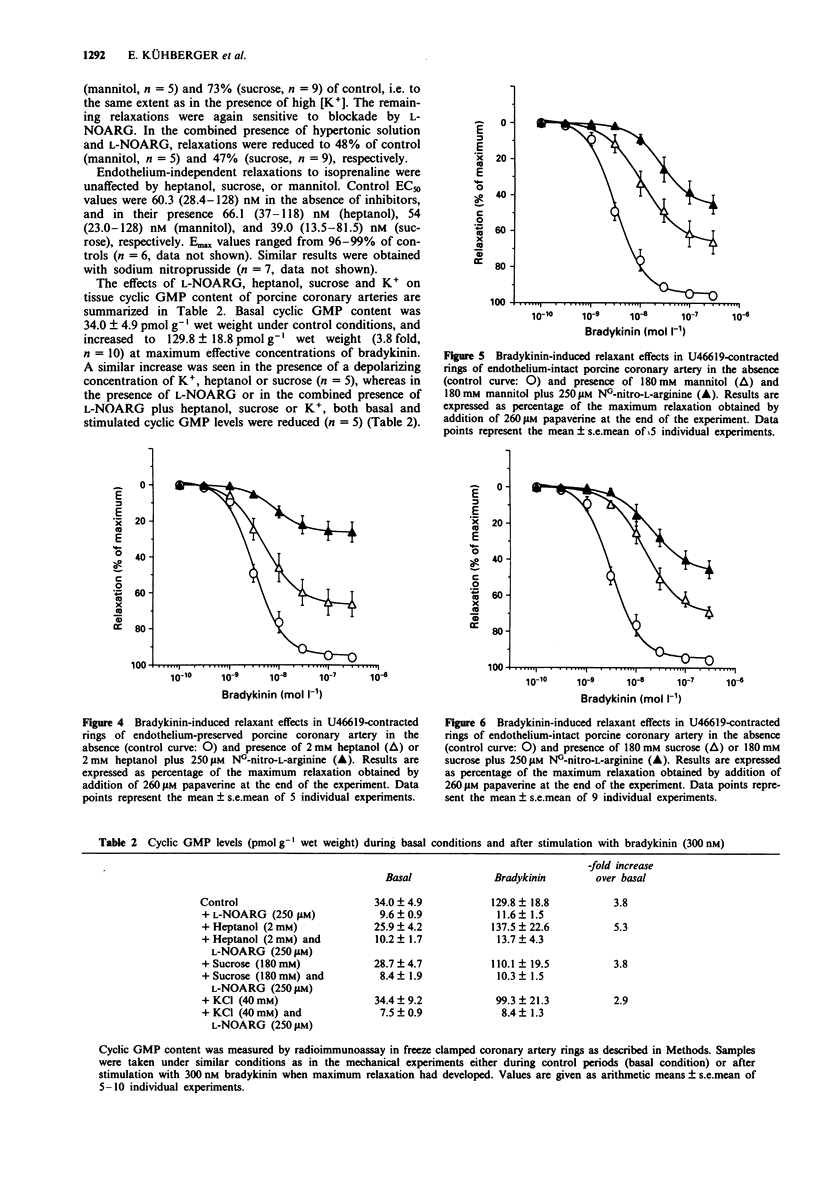


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adeagbo A. S., Triggle C. R. Varying extracellular [K+]: a functional approach to separating EDHF- and EDNO-related mechanisms in perfused rat mesenteric arterial bed. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;21(3):423–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Barrio L. C., Bargiello T. A., Spray D. C., Hertzberg E., Sáez J. C. Gap junctions: new tools, new answers, new questions. Neuron. 1991 Mar;6(3):305–320. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90241-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., Takewaki T. Mechanisms of action of noradrenaline and carbachol on smooth muscle of guinea-pig anterior mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:549–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayden J. E. Membrane hyperpolarization is a mechanism of endothelium-dependent cerebral vasodilation. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):H668–H673. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.3.H668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bény J. L., Brunet P. C. Neither nitric oxide nor nitroglycerin accounts for all the characteristics of endothelially mediated vasodilatation of pig coronary arteries. Blood Vessels. 1988;25(6):308–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bény J. L. Endothelial and smooth muscle cells hyperpolarized by bradykinin are not dye coupled. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):H836–H841. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.3.H836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Suzuki H., Weston A. H. Acetylcholine releases endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and EDRF from rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1165–1174. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Yamamoto Y., Miwa K., Suzuki H. Hyperpolarization of arterial smooth muscle induced by endothelial humoral substances. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):H1888–H1892. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.6.H1888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ G. J., Moreno A. P., Melman A., Spray D. C. Gap junction-mediated intercellular diffusion of Ca2+ in cultured human corporal smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):C373–C383. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan C. L., Cohen R. A. Two mechanisms mediate relaxation by bradykinin of pig coronary artery: NO-dependent and -independent responses. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):H830–H835. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.3.H830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Ganz P., Diehl P. S. Reversible microcarrier-mediated junctional communication between endothelial and smooth muscle cell monolayers: an in vitro model of vascular cell interactions. Lab Invest. 1985 Dec;53(6):710–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Olesen S. P., Clapham D. E., Morrel E. M., Schoen F. J. Endothelial communication. State of the art lecture. Hypertension. 1988 Jun;11(6 Pt 2):563–572. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.11.6.563.a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feletou M., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization of canine coronary smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):515–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graier W. F., Groschner K., Schmidt K., Kukovetz W. R. Increases in endothelial cyclic AMP levels amplify agonist-induced formation of endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF). Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):345–349. doi: 10.1042/bj2880345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groschner K., Graier W. F., Kukovetz W. R. Activation of a small-conductance Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channel contributes to bradykinin-induced stimulation of nitric oxide synthesis in pig aortic endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Oct 27;1137(2):162–170. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90198-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. H., Busse R., Bassenge E. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization of smooth muscle cells in rabbit femoral arteries is not mediated by EDRF (nitric oxide). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;338(4):438–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00172124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauser K., Rubanyi G. M. Bradykinin-induced, N omega-nitro-L-arginine-insensitive endothelium-dependent relaxation of porcine coronary arteries is not mediated by bioassayable relaxing substances. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992;20 (Suppl 12):S101–S104. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199204002-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauser K., Stekiel W. J., Rubanyi G., Harder D. R. Mechanism of action of EDRF on pressurized arteries: effect on K+ conductance. Circ Res. 1989 Jul;65(1):199–204. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori K., Lorenz R. R., Vanhoutte P. M. Nitric oxide, ACh, and electrical and mechanical properties of canine arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):H207–H212. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.1.H207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori K., Suzuki H. Electrical responses of smooth muscle cells during cholinergic vasodilation in the rabbit saphenous artery. Circ Res. 1987 Oct;61(4):586–593. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.4.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukovetz W. R., Holzmann S., Wurm A., Pöch G. Evidence for cyclic GMP-mediated relaxant effects of nitro-compounds in coronary smooth muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):129–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00500277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B., Brunner F., Schmidt K. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis by methylene blue. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 26;45(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao T., Vanhoutte P. M. Hyperpolarization as a mechanism for endothelium-dependent relaxations in the porcine coronary artery. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:355–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacicca C., von der Weid P. Y., Beny J. L. Effect of nitro-L-arginine on endothelium-dependent hyperpolarizations and relaxations of pig coronary arteries. J Physiol. 1992 Nov;457:247–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard V., Tanner F. C., Tschudi M., Lüscher T. F. Different activation of L-arginine pathway by bradykinin, serotonin, and clonidine in coronary arteries. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):H1433–H1439. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.5.H1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. G., Weston A. H. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor: a new endogenous inhibitor from the vascular endothelium. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):272–274. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


