Abstract
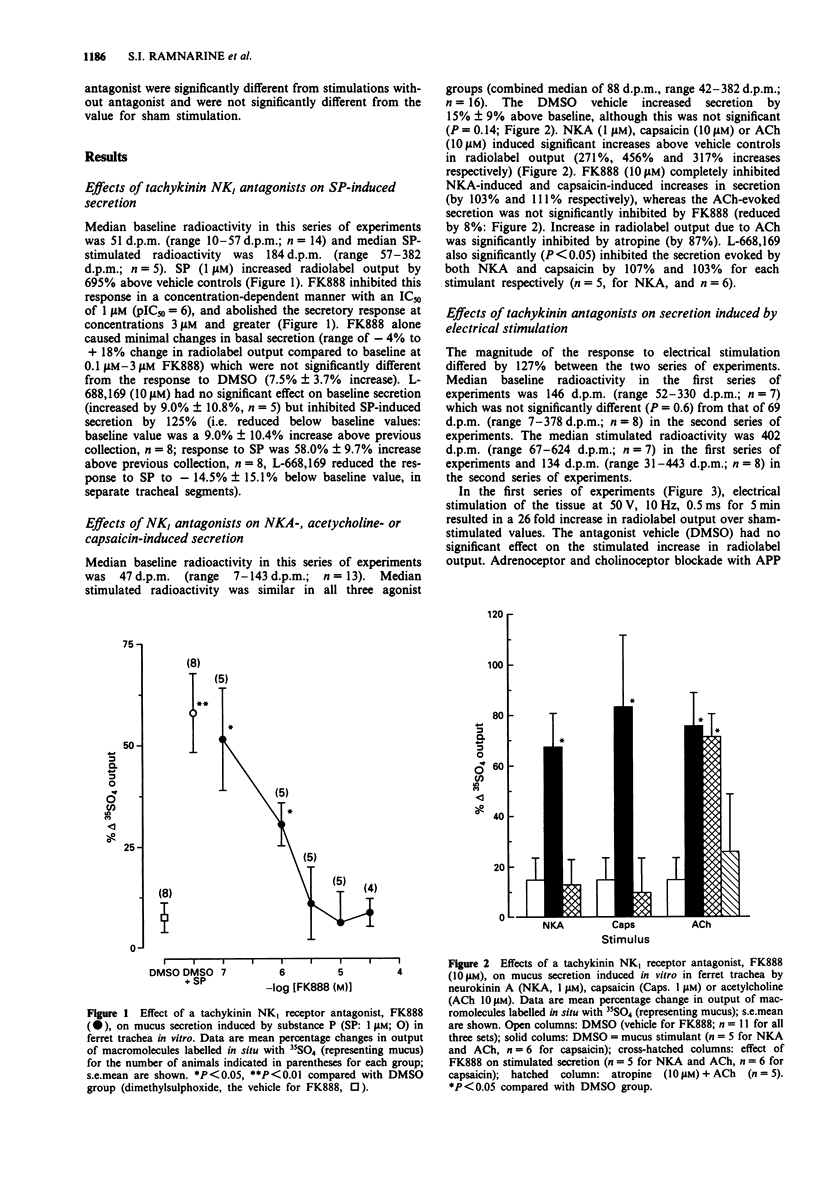
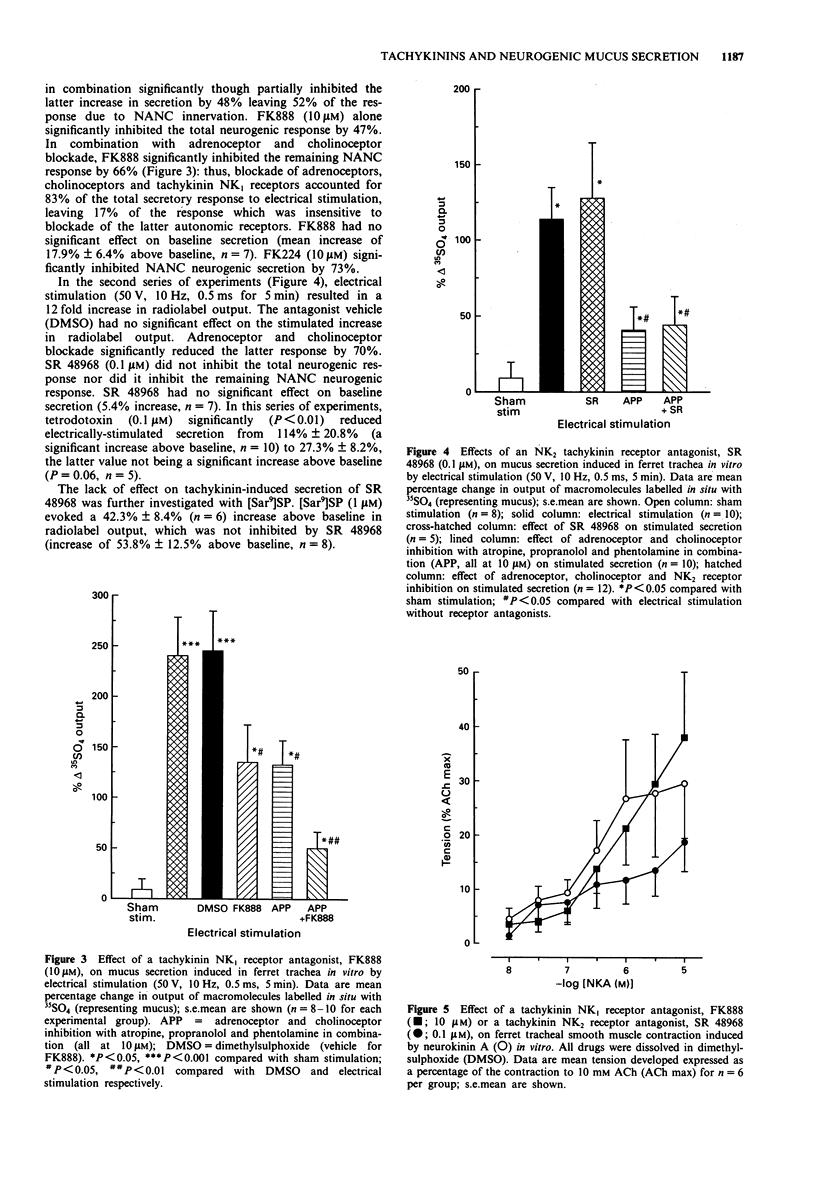
1. We characterized the tachykinin receptor(s) mediating 'sensory-efferent' neural control of release of 35SO4-labelled macromolecules (mucus) from ferret trachea in vitro in Ussing chambers using selective tachykinin antagonists. Secretion was induced by substance P (SP), neurokinin A (NKA), capsaicin, the NK1 tachykinin receptor agonist [Sar9, Met(O2)11]substance P ([Sar9]SP), or acetylcholine (ACh), or by electrical stimulation of nerves. Antagonists used were FK888 and L-668,169, selective for the NK1 receptor, SR 48968, selective for the NK2 receptor, and FK224, a dual antagonist at NK1 and NK2 receptors. The selectivity of FK888 and SR 48968 was examined on NKA-induced contraction of ferret tracheal smooth muscle in vitro. 2. SP (1 microM) increased mucus secretion by 695% above vehicle controls. FK888 (0.1 microM-30 microM) inhibited SP-induced secretion in a dose-dependent manner, with complete inhibition at 10 microM and an IC50 of 1 microM. L-668,169 (1 microM) also completely inhibited SP-induced secretion. 3. NKA (1 microM) significantly increased mucus secretion by 271% above baseline, a response which was completely inhibited by FK888 (10 microM) or L-668,169 (microM). Secretion induced by ACh (10 microM: 317% above baseline) was not inhibited by FK888 but was inhibited by atropine. Capsaicin (10 microM)-induced secretion (456% above vehicle controls) was significantly inhibited by FK888 and by L-668,169 (111% and 103% inhibition respectively). 4. Electrical stimulation (50 V, 10 Hz, 0.5 ms, 5 min) increased mucus output above baseline (increased by 12 to 26 fold), a response blocked by tetrodotoxin (0.1 microM). FK888 (10 microM) inhibited the increase in secretion due to electrical stimulation by 47%.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adcock I. M., Peters M., Gelder C., Shirasaki H., Brown C. R., Barnes P. J. Increased tachykinin receptor gene expression in asthmatic lung and its modulation by steroids. J Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Aug;11(1):1–7. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0110001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Advenier C., Naline E., Toty L., Bakdach H., Emonds-Alt X., Vilain P., Brelière J. C., Le Fur G. Effects on the isolated human bronchus of SR 48968, a potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist of the neurokinin A (NK2) receptors. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Nov;146(5 Pt 1):1177–1181. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.5_Pt_1.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Advenier C., Rouissi N., Nguyen Q. T., Emonds-Alt X., Breliere J. C., Neliat G., Naline E., Regoli D. Neurokinin A (NK2) receptor revisited with SR 48968, a potent non-peptide antagonist. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1418–1424. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B., Peatfield A. C., Richardson P. S. Nervous control of mucin secretion into human bronchi. J Physiol. 1985 Aug;365:297–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Stretton C. D., Barnes P. J. Modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways by opioids. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borson D. B., Charlin M., Gold B. D., Nadel J. A. Neural regulation of 35SO4-macromolecule secretion from tracheal glands of ferrets. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Aug;57(2):457–466. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.2.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles S. J., Neill K. H., Reid L. M. Potent stimulation of glycoprotein secretion in canine trachea by substance P. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Nov;57(5):1323–1327. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.5.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. R., Corbishley C. M., Richardson P. S. The uptake of radiolabelled precursors of mucus glycoconjugates by secretory tissues in the feline trachea. J Physiol. 1990 Jan;420:19–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Murai M., Morimoto H., Maeda Y., Yamaoka M., Hagiwara D., Miyake H., Ikari N., Matsuo M. Pharmacological profile of a high affinity dipeptide NK1 receptor antagonist, FK888. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):785–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung D. C., Allenby M. I., Richardson P. S. NANC nerve pathways controlling mucus glycoconjugate secretion into feline trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Aug;73(2):625–630. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.2.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung D. C., Beacock D. J., Richardson P. S. Vagal control of mucus glycoconjugate secretion into the feline trachea. J Physiol. 1992;453:435–447. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry S. E. Tachykinin receptors mediating airway macromolecular secretion. Life Sci. 1991;48(17):1609–1618. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90120-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppetti P., Bertrand C., Bacci E., Huber O., Nadel J. A. Characterization of tachykinin receptors in ferret trachea by peptide agonists and nonpeptide antagonists. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):L164–L169. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.265.2.L164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie R. G. Receptors in asthmatic airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3 Pt 2):S151–S156. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3_Pt_2.S151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Caulfield M. P., Watson S. P., Guard S. Receptor subtypes or species homologues: relevance to drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Oct;14(10):376–383. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama Y., Lei Y. H., Barnes P. J., Rogers D. F. Effects of two novel tachykinin antagonists, FK224 and FK888, on neurogenic airway plasma exudation, bronchoconstriction and systemic hypotension in guinea-pigs in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):844–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Capsaicin: cellular targets, mechanisms of action, and selectivity for thin sensory neurons. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):143–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren J. D., Wiedermann C. J., Logun C., Plutchok J., Kaliner M., Shelhamer J. H. Substance P receptor-mediated secretion of respiratory glycoconjugate from feline airways in vitro. Exp Lung Res. 1989;15(1):17–29. doi: 10.3109/01902148909069606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luts A., Sundler F. Peptide-containing nerve fibers in the respiratory tract of the ferret. Cell Tissue Res. 1989 Nov;258(2):259–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00239446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Meli A. The sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Gen Pharmacol. 1988;19(1):1–43. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(88)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Rovero P., Giachetti A. Tachykinin receptors and tachykinin receptor antagonists. J Auton Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;13(1):23–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1993.tb00396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. A., Naline E., Emonds-Alt X., Advenier C. Influence of (+/-)-CP-96,345 and SR 48968 on electrical field stimulation of the isolated guinea-pig main bronchus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 2;224(2-3):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meini S., Mak J. C., Rohde J. A., Rogers D. F. Tachykinin control of ferret airways: mucus secretion, bronchoconstriction and receptor mapping. Neuropeptides. 1993 Feb;24(2):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(93)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyayasu K., Mak J. C., Nishikawa M., Barnes P. J. Characterization of guinea pig pulmonary neurokinin type 1 receptors using a novel antagonist ligand, [3H]FK888. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;44(3):539–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi H., Hicks C. R. Effects of neurokinins on ion transport and sulfated macromolecule release in the isolated ferret trachea. Exp Lung Res. 1989 Dec;15(6):837–848. doi: 10.3109/01902148909069630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto H., Murai M., Maeda Y., Yamaoka M., Nishikawa M., Kiyotoh S., Fujii T. FK 224, a novel cyclopeptide substance P antagonist with NK1 and NK2 receptor selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):398–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai M., Morimoto H., Maeda Y., Kiyotoh S., Nishikawa M., Fujii T. Effects of FK224, a novel compound NK1 and NK2 receptor antagonist, on airway constriction and airway edema induced by neurokinins and sensory nerve stimulation in guinea pigs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollerenshaw S. L., Jarvis D., Sullivan C. E., Woolcock A. J. Substance P immunoreactive nerves in airways from asthmatics and nonasthmatics. Eur Respir J. 1991 Jun;4(6):673–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peatfield A. C., Richardson P. S. Evidence for non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic nervous control of mucus secretion into the cat trachea. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:335–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramnarine S. I., Rogers D. F. Non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neural control of mucus secretion in the airways. Pulm Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;7(1):19–33. doi: 10.1006/pulp.1994.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson N. P., Venning L., Kyle H., Widdicombe J. G. Quantitation of the secretory cells of the ferret tracheobronchial tree. J Anat. 1986 Apr;145:173–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. F., Aursudkij B., Barnes P. J. Effects of tachykinins on mucus secretion in human bronchi in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 19;174(2-3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. F., Barnes P. J. Opioid inhibition of neurally mediated mucus secretion in human bronchi. Lancet. 1989 Apr 29;1(8644):930–932. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92509-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura S., Sasaki T., Okayama H., Sasaki H., Takishima T. Effect of substance P on mucus secretion of isolated submucosal gland from feline trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):646–653. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Tung S. R., Strichartz G. R., Håkanson R. Investigation of the specificity of FK 888 as a tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber S. E., Lim J. C., Widdicombe J. G. The effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide on submucosal gland secretion and epithelial albumin transport in the ferret trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber S. E. Receptors mediating the effects of substance P and neurokinin A on mucus secretion and smooth muscle tone of the ferret trachea: potentiation by an enkephalinase inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1197–1206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



