Abstract
1. Human epicardial coronary artery rings, freshly obtained from cardiac transplant patients, were examined for their responses to endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF)-releasing agents. 2. Functional antagonism profoundly influenced relaxation responses in this tissue. Increasing force with concentrations of U46619 above 3 nM (40% of maximum contraction response) resulted in a reduction of the maximum response to four vasorelaxants which relax vascular smooth muscle via different mechanisms: the EDRF-releasing agents, substance P and bradykinin; the endothelium-independent nitro-vasodilator, sodium nitroprusside (SNP); and the beta-adrenoceptor agonist, isoprenaline. 3. Substance P, histamine, bradykinin and the Ca2+ ionophores ionomycin and A23187 all caused concentration- and endothelium-dependent relaxation in vessels pre-contracted with the thromboxane A2-mimetic, U46619 (3 nM) to an active force optimal for relaxation responses. Nifedipine (0.1 microM), added to prevent spontaneous contractions, had no effect or relaxation responses to substance P, bradykinin and histamine. 4. Substance P was the most potent of the EDRF-releasing agents examined and all agents except for bradykinin caused near-maximal relaxation. Bradykinin caused only 46.2% +/- 7.3% relaxation. Responses were abolished when the endothelium was removed and, except for histamine, were not significantly affected by indomethacin (3-10 microM, P > 0.05). Histamine (0.1-10 microM) caused a concentration-dependent contraction of arterial rings without endothelium. 5. The L-arginine analogues NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG, 0.1 mM) and NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA, 0.1 mM) both caused no further contraction in arteries precontracted with U46619 (3 nM) and were in general, poor inhibitors of responses to EDRF agonists.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

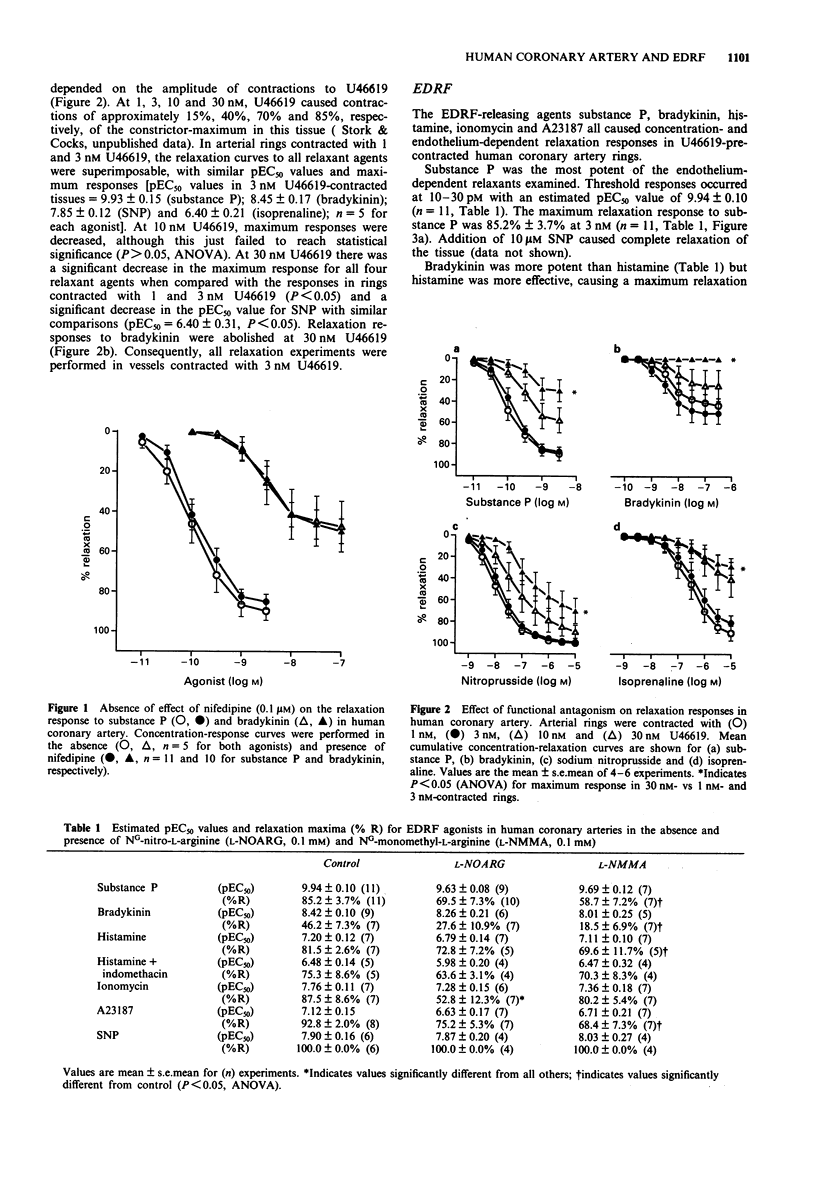
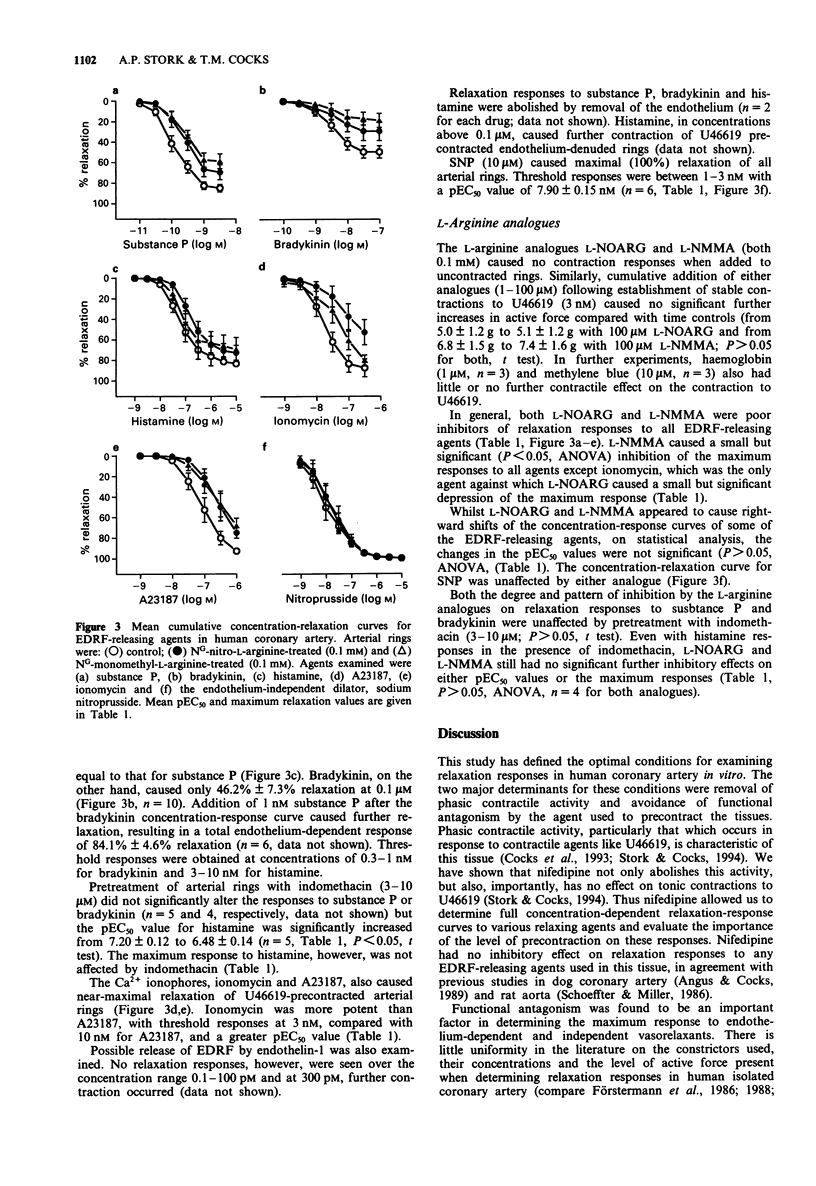


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus J. A., Cocks T. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41(1-2):303–352. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester A. H., O'Neil G. S., Moncada S., Tadjkarimi S., Yacoub M. H. Low basal and stimulated release of nitric oxide in atherosclerotic epicardial coronary arteries. Lancet. 1990 Oct 13;336(8720):897–900. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92269-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester A. H., O'Neil G. S., Tadjkarimi S., Palmer R. M., Moncada S., Yacoub M. H. The role of nitric oxide in mediating endothelium dependent relaxations in the human epicardial coronary artery. Int J Cardiol. 1990 Dec;29(3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(90)90118-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks T. M., Kemp B. K., Pruneau D., Angus J. A. Comparison of contractile responses to 5-hydroxytryptamine and sumatriptan in human isolated coronary artery: synergy with the thromboxane A2-receptor agonist, U46619. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):360–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13818.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossman D. C., Larkin S. W., Fuller R. W., Davies G. J., Maseri A. Substance P dilates epicardial coronary arteries and increases coronary blood flow in humans. Circulation. 1989 Sep;80(3):475–484. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elghozi J. L., Head G. A. Spinal noradrenergic pathways and pressor responses to central angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):H240–H246. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.1.H240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco-Cereceda A., Lundberg J. M. Potent effects of neuropeptide Y and calcitonin gene-related peptide on human coronary vascular tone in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Sep;131(1):159–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Mügge A., Alheid U., Haverich A., Frölich J. C. Selective attenuation of endothelium-mediated vasodilation in atherosclerotic human coronary arteries. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):185–190. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Mügge A., Frölich J. C. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of human epicardial coronary arteries: frequent lack of effect of acetylcholine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 9;128(3):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90778-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha S. S., Crossman D. C., Bustami M., Davies G. J., Mitchell A. G., Maseri A., Yacoub M. H. Substance P for evaluation of coronary endothelial function after cardiac transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991 Jun;17(7):1537–1544. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(91)90644-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludmer P. L., Selwyn A. P., Shook T. L., Wayne R. R., Mudge G. H., Alexander R. W., Ganz P. Paradoxical vasoconstriction induced by acetylcholine in atherosclerotic coronary arteries. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 23;315(17):1046–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610233151702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay D. An analysis of functional antagonism and synergism. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 May;73(1):127–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Bolofo M. L., Giles H. Inhibition of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation by arginine analogues: a pharmacological analysis of agonist and tissue dependence. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):643–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09033.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwan J., Larkin S., Davies G., Chierchia S., Brown M., Stevenson J., MacIntyre I., Maseri A. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: a potent dilator of human epicardial coronary arteries. Circulation. 1986 Dec;74(6):1243–1247. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.6.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Busse R. NG-nitro-L-arginine (N5-[imino(nitroamino)methyl]-L-ornithine) impairs endothelium-dependent dilations by inhibiting cytosolic nitric oxide synthesis from L-arginine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jan-Feb;341(1-2):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00195071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll G., Bühler F. R., Yang Z., Lüscher T. F. Different potency of endothelium-derived relaxing factors against thromboxane, endothelin, and potassium chloride in intramyocardial porcine coronary arteries. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;18(1):120–126. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199107000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil G. S., Chester A. H., Kushwaha S., Rose M., Tadjkarimi S., Yacoub M. H. Cyclosporin treatment does not impair the release of nitric oxide in human coronary arteries. Br Heart J. 1991 Sep;66(3):212–216. doi: 10.1136/hrt.66.3.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffter P., Miller R. C. Role of sodium-calcium exchange and effects of calcium entry blockers on endothelial-mediated responses in rat isolated aorta. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;30(1):53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stork A. P., Cocks T. M. Pharmacological reactivity of human epicardial coronary arteries: phasic and tonic responses to vasoconstrictor agents differentiated by nifedipine. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1093–1098. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. G., Weston A. H. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor: a new endogenous inhibitor from the vascular endothelium. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):272–274. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N. Mechanism of histamine actions in human coronary arteries. Circ Res. 1987 Aug;61(2):280–286. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Okamura T. Endothelium-dependent and -independent responses to vasoactive substances of isolated human coronary arteries. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):H988–H995. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.3.H988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita J. A., Treasure C. B., Nabel E. G., McLenachan J. M., Fish R. D., Yeung A. C., Vekshtein V. I., Selwyn A. P., Ganz P. Coronary vasomotor response to acetylcholine relates to risk factors for coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1990 Feb;81(2):491–497. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.2.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Yoshimura H., Noma M., Kai H., Suzuki S., Tajimi T., Sugihara M., Kikuchi Y. Preservation of endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the spastic segment of the human epicardial coronary artery by substance P. Am Heart J. 1992 Feb;123(2):298–303. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(92)90638-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasue H., Matsuyama K., Matsuyama K., Okumura K., Morikami Y., Ogawa H. Responses of angiographically normal human coronary arteries to intracoronary injection of acetylcholine by age and segment. Possible role of early coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1990 Feb;81(2):482–490. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.2.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiher A. M., Drexler H., Wollschläger H., Just H. Modulation of coronary vasomotor tone in humans. Progressive endothelial dysfunction with different early stages of coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1991 Feb;83(2):391–401. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


