Abstract
1. Monoarthritis was induced in Lewis rats by interdermal injection in the left hind paw of a suspension of Mycobacterium tubercolusis in mineral oil (500 micrograms 100 microliters-1). Controls were injected with 100 microliters mineral oil. 2. Withdrawal latencies to thermal stimuli of the inflamed paw, the contralateral and both paws of control rats were measured at daily intervals after injection by the plantar test. 3. After detection of the pain threshold, rat spinal cords were removed and horizontal dorsal slices were mounted in a 3-compartment bath to measure electrically-evoked release of substance P-like immunoreactivity (SP-LI). 4. The inflamed paw of monoarthritic rats exhibited a lower pain threshold to thermal stimuli than the contralateral paw of the same animals and both paws of control rats. Inflamed paw hyperalgesia was maximal two days after injection, and declined gradually between 7 to 21 days with no evidence of excitability of withdrawal reflexes after 28 days. 5. During the 28 days study, monoarthritic rats gained less weight than control rats. 6. Electrical stimulation of the dorsal roots attached to rat isolated spinal cord slices induced a significant increase (174 +/- 18% of basal outflow which was 30.3 fmol 8 ml-1, n = 5) in SP-LI release. 7. One-week after induction of inflammation no differences in the amount of SP-LI released from the spinal cord of incomplete Freund's adjuvant-treated rats (IFA) and Freund's adjuvant-treated rats (CFA) were detected.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

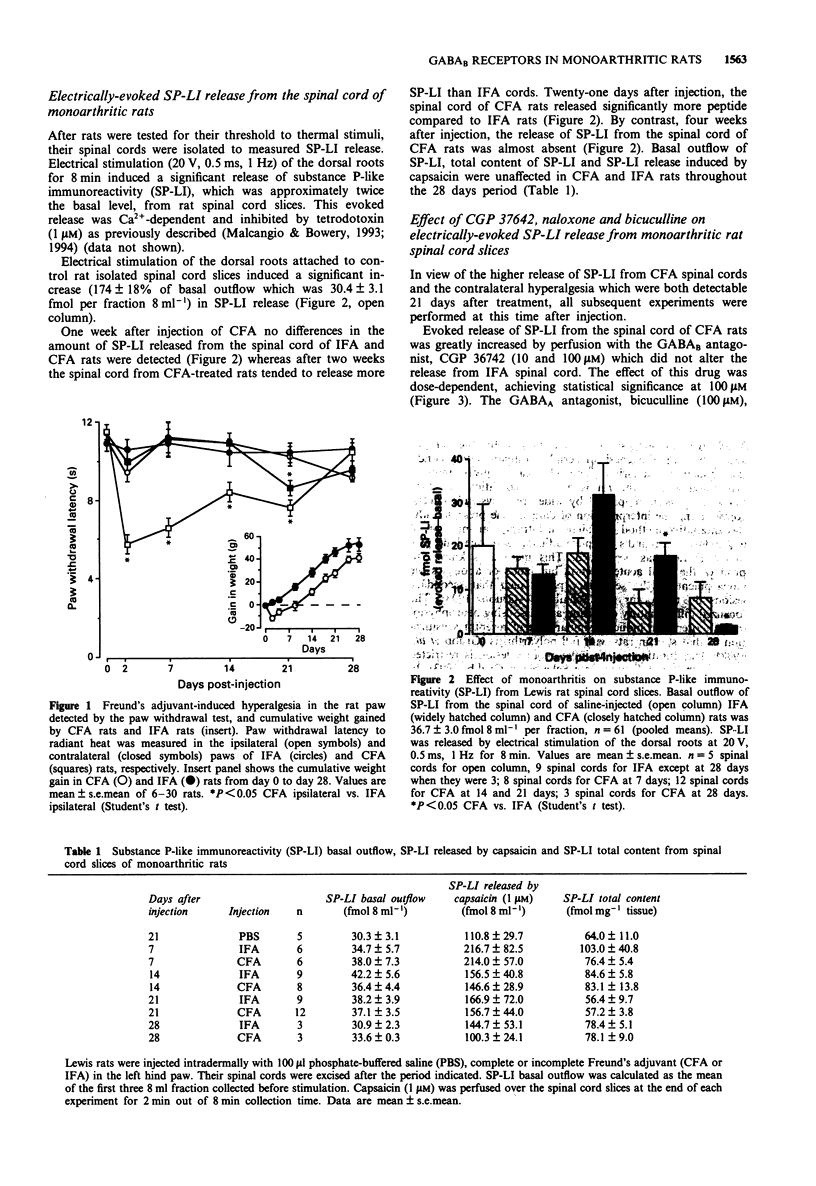
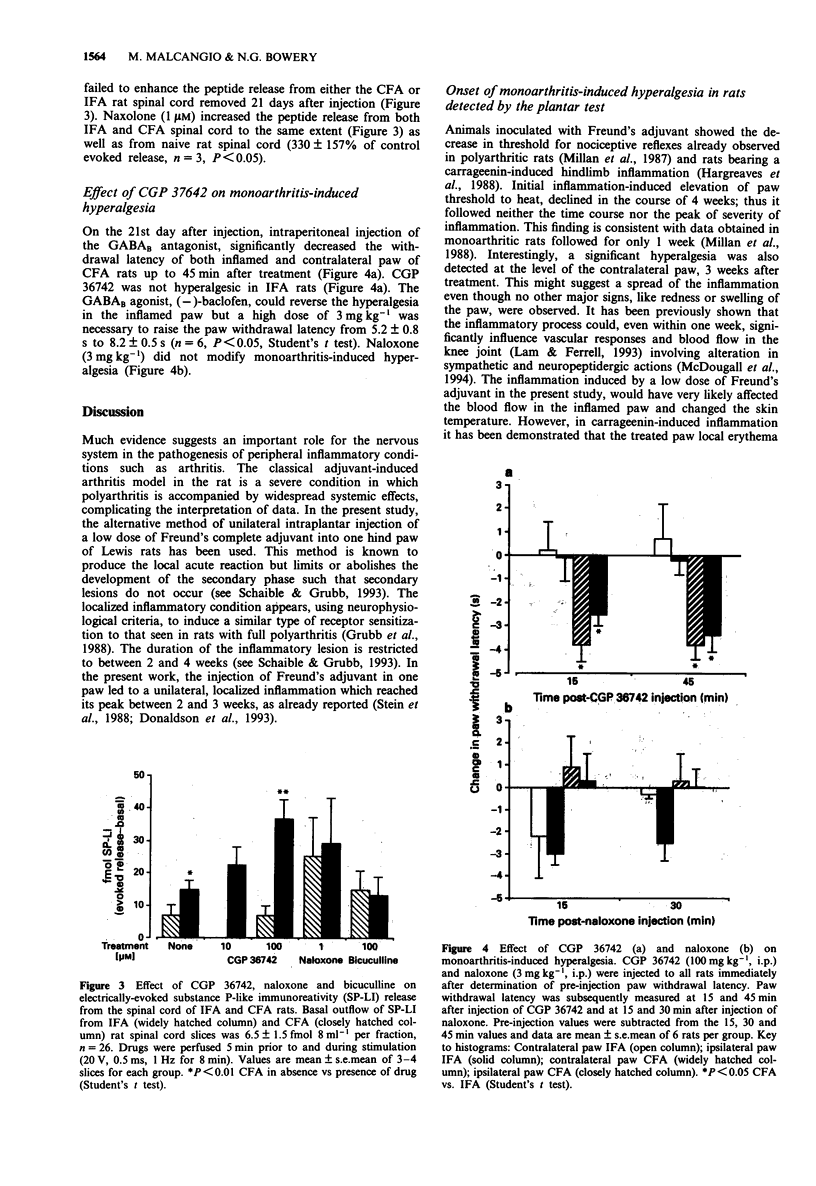


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowery N. G. GABAB receptor pharmacology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:109–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Lopes J. M., Tavares Isaura, Tölle T. R., Coito Ana, Coimbra A. Increase in GABAergic Cells and GABA Levels in the Spinal Cord in Unilateral Inflammation of the Hindlimb in the Rat. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4(4):296–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesselin F., Bourgoin S., Artaud F., Hamon M. Basic and regulatory mechanisms of in vitro release of Met-enkephalin from the dorsal zone of the rat spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1984 Sep;43(3):763–774. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colpaert F. C. Evidence that adjuvant arthritis in the rat is associated with chronic pain. Pain. 1987 Feb;28(2):201–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(87)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson L. F., Seckl J. R., McQueen D. S. A discrete adjuvant-induced monoarthritis in the rat: effects of adjuvant dose. J Neurosci Methods. 1993 Aug;49(1-2):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(93)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm G. H., Terrence C. F. Comparison of L-baclofen and racemic baclofen in trigeminal neuralgia. Neurology. 1987 Nov;37(11):1725–1728. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.11.1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go V. L., Yaksh T. L. Release of substance P from the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:141–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb B. D., McQueen D. S., Iggo A., Birrell G. J., Dutia M. B. A study of 5-HT-receptors associated with afferent nerves located in normal and inflamed rat ankle joints. Agents Actions. 1988 Dec;25(3-4):216–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01965015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves K., Dubner R., Brown F., Flores C., Joris J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 1988 Jan;32(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Kellerth J. O., Nilsson G., Pernow B. Substance p: localization in the central nervous system and in some primary sensory neurons. Science. 1975 Nov 28;190(4217):889–890. doi: 10.1126/science.242075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar S., Gibson S. J., Rees R. G., Jura W. G., Brewerton D. A., Polak J. M. Increased calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), substance P, and enkephalin immunoreactivities in dorsal spinal cord and loss of CGRP-immunoreactive motoneurons in arthritic rats depend on intact peripheral nerve supply. J Mol Neurosci. 1991;3(1):7–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02896844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser V., Guilbaud G. The analgesic effects of morphine, but not those of the enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan, are enhanced in arthritic rats. Brain Res. 1983 May 9;267(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam F. Y., Ferrell W. R. Acute inflammation in the rat knee joint attenuates sympathetic vasoconstriction but enhances neuropeptide-mediated vasodilatation assessed by laser Doppler perfusion imaging. Neuroscience. 1993 Jan;52(2):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90170-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Clark R., Devor M., Helms C., Moskowitz M. A., Basbaum A. I. Intraneuronal substance P contributes to the severity of experimental arthritis. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):547–549. doi: 10.1126/science.6208609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magoul R., Onteniente B., Geffard M., Calas A. Anatomical distribution and ultrastructural organization of the GABAergic system in the rat spinal cord. An immunocytochemical study using anti-GABA antibodies. Neuroscience. 1987 Mar;20(3):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcangio M., Bowery N. G. Effect of the tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonists, RP 67580 and SR 140333, on electrically-evoked substance P release from rat spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;113(2):635–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17037.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcangio M., Bowery N. G. Gamma-aminobutyric acidB, but not gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor activation, inhibits electrically evoked substance P-like immunoreactivity release from the rat spinal cord in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Sep;266(3):1490–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcangio M., Ghelardini C., Giotti A., Malmberg-Aiello P., Bartolini A. CGP 35348, a new GABAB antagonist, prevents antinociception and muscle-relaxant effect induced by baclofen. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1303–1308. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapp P. I., Terenghi G., Walsh D. A., Chen S. T., Cruwys S. C., Garrett N., Kidd B. L., Polak J. M., Blake D. R. Monoarthritis in the rat knee induces bilateral and time-dependent changes in substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the spinal cord. Neuroscience. 1993 Dec;57(4):1091–1096. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90051-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall J. J., Karimian S. M., Ferrell W. R. Alteration of substance P-mediated vasodilatation and sympathetic vasoconstriction in the rat knee joint by adjuvant-induced inflammation. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Jun 20;174(2):127–129. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J., Członkowski A., Morris B., Stein C., Arendt R., Huber A., Höllt V., Herz A. Inflammation of the hind limb as a model of unilateral, localized pain: influence on multiple opioid systems in the spinal cord of the rat. Pain. 1988 Dec;35(3):299–312. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J., Członkowski A., Pilcher C. W., Almeida O. F., Millan M. H., Colpaert F. C., Herz A. A model of chronic pain in the rat: functional correlates of alterations in the activity of opioid systems. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):77–87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami M., Kuraishi Y., Kawamura M., Yamaguchi T., Masu Y., Nakanishi S., Satoh M. Enhancement of preprotachykinin A gene expression by adjuvant-induced inflammation in the rat spinal cord: possible involvement of substance P-containing spinal neurons in nociception. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Mar 13;98(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley J. E., Bartness T. J., Gosnell B. A., Levine A. S. Peptidergic regulation of feeding. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1985;27:207–298. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudge A. W., Leeman S. E., Fischbach G. D. Enkephalin inhibits release of substance P from sensory neurons in culture and decreases action potential duration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):526–530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oku R., Satoh M., Takagi H. Release of substance P from the spinal dorsal horn is enhanced in polyarthritic rats. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Mar 9;74(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Steinmann M. W., Ferrat T., Pozza M. F., Greiner K., Brugger F., Froestl W., Mickel S. J., Bittiger H. The actions of orally active GABAB receptor antagonists on GABAergic transmission in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 23;233(2-3):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90048-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlík F., Zídek Z. Breeding experiments on the frequency of adjuvant arthritis in the rat. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jan;32(1):72–74. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przewłocka B., Lasoń W., Przewłocki R. Time-dependent changes in the activity of opioid systems in the spinal cord of monoarthritic rats--a release and in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience. 1992;46(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J. GABAergic mechanisms of analgesia: an update. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1987 Feb;26(2):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(87)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Grubb B. D. Afferent and spinal mechanisms of joint pain. Pain. 1993 Oct;55(1):5–54. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(93)90183-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Jarrott B., Hope P. J., Duggan A. W. Release of immunoreactive substance P in the spinal cord during development of acute arthritis in the knee joint of the cat: a study with antibody microprobes. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 8;529(1-2):214–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Time course of mechanosensitivity changes in articular afferents during a developing experimental arthritis. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Dec;60(6):2180–2195. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.6.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluka K. A., Dougherty P. M., Sorkin L. S., Willis W. D., Westlund K. N. Neural changes in acute arthritis in monkeys. III. Changes in substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and glutamate in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1992 Jan-Apr;17(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(92)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Harmar A. J., McQueen D. S., Seckl J. R. Increase in substance P and CGRP, but not somatostatin content of innervating dorsal root ganglia in adjuvant monoarthritis in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Mar 30;137(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90417-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Millan M. J., Herz A. Unilateral inflammation of the hindpaw in rats as a model of prolonged noxious stimulation: alterations in behavior and nociceptive thresholds. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988 Oct;31(2):445–451. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(88)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd A. J., McKenzie J. GABA-immunoreactive neurons in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience. 1989;31(3):799–806. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90442-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. R., Yaksh T. L. Baclofen is antinociceptive in the spinal intrathecal space of animals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct 15;51(4):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


