Abstract
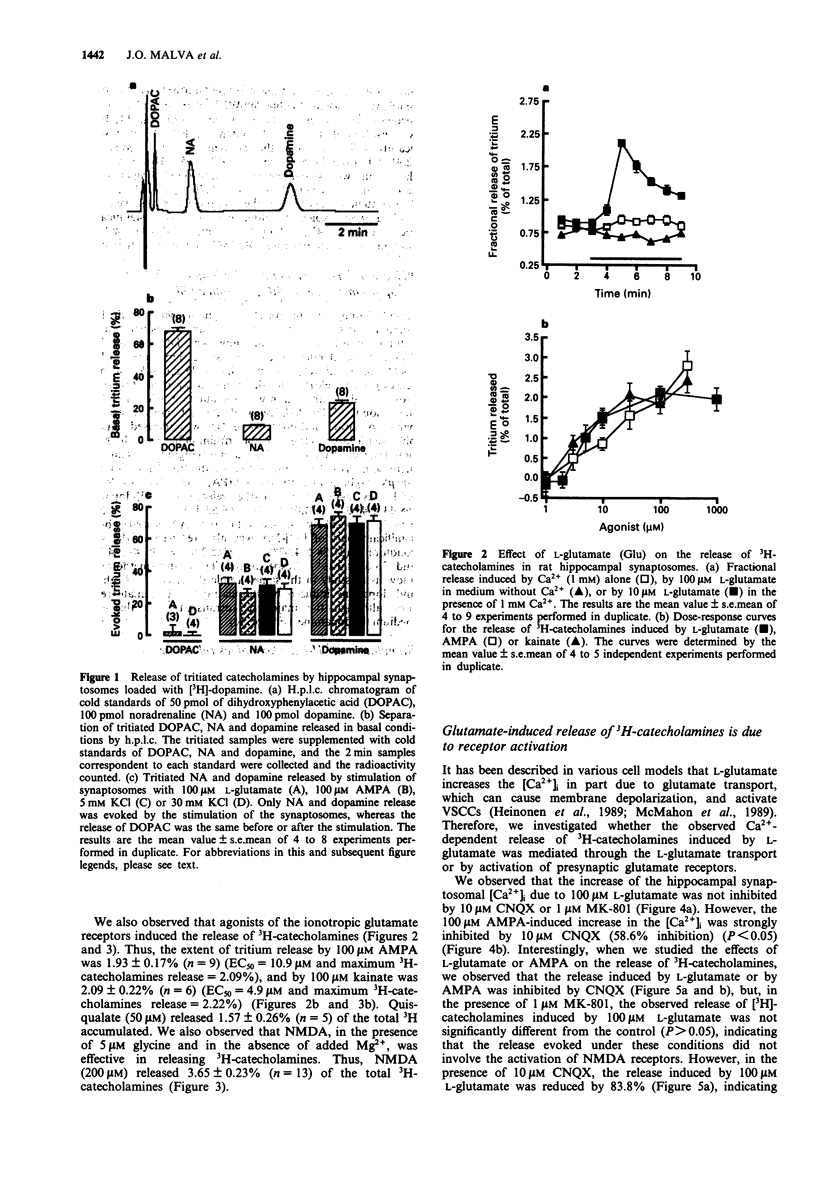
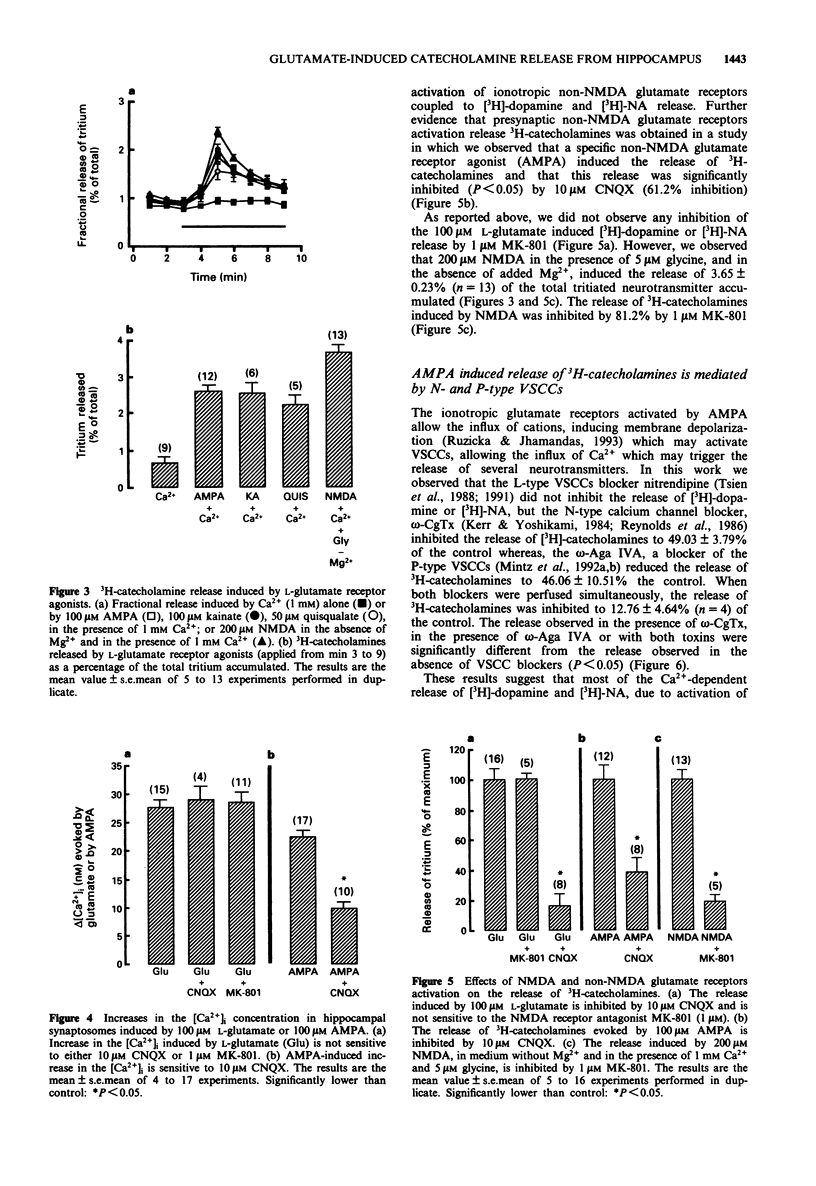
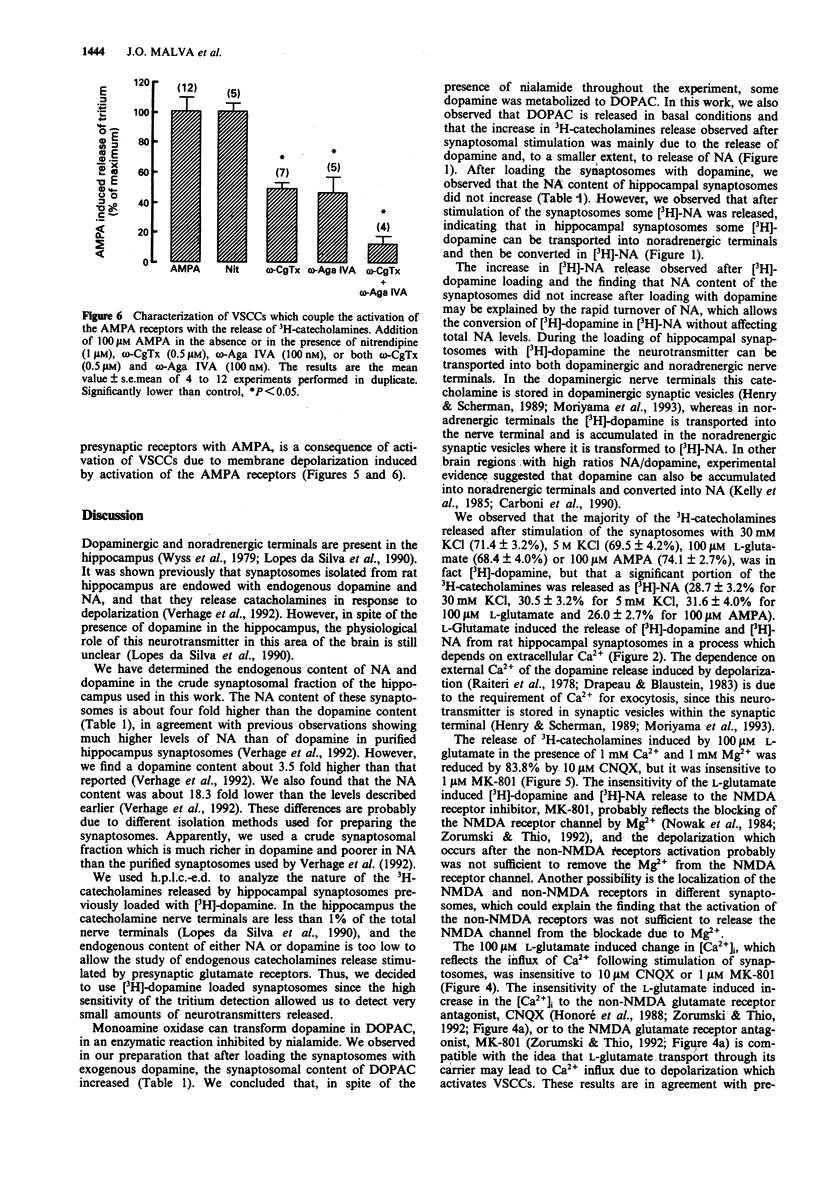
1. We studied the release of [3H]-dopamine and [3H]-noradrenaline (NA) from hippocampal synaptosomes induced by glutamate receptors and the associated Ca2+ influx through Ca2+ channels. The release of tritiated neurotransmitters was studied by use of superfusion system and the intracellular free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) was determined by a fluorimetric assay with Indo-1 as a probe for Ca2+. 2. Presynaptic glutamate receptor activation induced Ca(2+)-dependent release of [3H]-dopamine and [3H]-NA from rat hippocampal synaptosomes. Thus, L-glutamate induced the release of both neurotransmitters in a dose-dependent manner (EC50 = 5.62 microM), and the effect of 100 microM L-glutamate was inhibited by 83.8% in the presence of 10 microM 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dioxine (CNQX), but was not affected by 1 microM (+)-5-methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]-cyclohepten-5,10-imine (MK-801). 3. Other glutamate receptor agonists also stimulated the Ca(2+)-dependent release of [3H]-dopamine and [3H]-NA as follows: N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), at 200 microM, released 3.65 +/- 0.23% of the total 3H catecholamines, and this effect was inhibited by 81.2% in the presence of 1 microM MK-801; quisqualate (50 microM), S-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolopropionic acid (AMPA) (100 microM) or kainate (100 microM) released 1.57 +/- 0.26%, 1.93 +/- 0.17% and 2.09 +/- 0.22%, of the total 3H catecholamines, respectively. 4. The ionotropic glutamate receptor agonist, AMPA, induced an increase in the [Ca2+]i which was inhibited by 58.6% in the presence of 10 microM CNQX.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P., Smith S. J. Calcium action in synaptic transmitter release. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:633–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.003221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandina P., Johnson D., Walcott J., Goldfarb J. Release of endogenous norepinephrine from rat hypothalamus by stimulation of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carboni E., Tanda G. L., Frau R., Di Chiara G. Blockade of the noradrenaline carrier increases extracellular dopamine concentrations in the prefrontal cortex: evidence that dopamine is taken up in vivo by noradrenergic terminals. J Neurochem. 1990 Sep;55(3):1067–1070. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudieu I., Alonso R., Mount H., Quirion R., Boksa P. Effects of L- and N-type Ca2+ channel antagonists on excitatory amino acid-evoked dopamine release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 22;220(2-3):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90749-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desce J. M., Godeheu G., Galli T., Artaud F., Chéramy A., Glowinski J. L-glutamate-evoked release of dopamine from synaptosomes of the rat striatum: involvement of AMPA and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Neuroscience. 1992;47(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90249-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desce J. M., Godeheu G., Galli T., Artaud F., Chéramy A., Glowinski J. Presynaptic facilitation of dopamine release through D,L-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate receptors on synaptosomes from the rat striatum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Nov;259(2):692–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau P., Blaustein M. P. Initial release of [3H]dopamine from rat striatal synaptosomes: correlation with calcium entry. J Neurosci. 1983 Apr;3(4):703–713. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-04-00703.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte C. B., Carvalho C. A., Ferreira I. L., Carvalho A. P. Synaptosomal [Ca2+]i as influenced by Na+/Ca2+ exchange and K+ depolarization. Cell Calcium. 1991 Oct;12(9):623–633. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90059-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte C. B., Rosario L. M., Sena C. M., Carvalho A. P. A toxin fraction (FTX) from the funnel-web spider poison inhibits dihydropyridine-insensitive Ca2+ channels coupled to catecholamine release in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):908–913. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Bönisch H., Göthert M. Presynaptic NMDA receptors stimulate noradrenaline release in the cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 21;185(1):115–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90219-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinonen E., Akerman K. E., Panula P. Changes of the membrane potential in striatal synaptoneurosome, synaptosome and membrane sac preparations induced by glutamate, kainate and aspartate as measured with a cyanine dye DiS-C2-(5). Brain Res. 1989 Sep 4;496(1-2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. P., Scherman D. Radioligands of the vesicular monoamine transporter and their use as markers of monoamine storage vesicles. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 1;38(15):2395–2404. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Davies S. N., Drejer J., Fletcher E. J., Jacobsen P., Lodge D., Nielsen F. E. Quinoxalinediones: potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):701–703. doi: 10.1126/science.2899909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Ozawa S., Tsuzuki K. Permeation of calcium through excitatory amino acid receptor channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:151–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith R. A., Horn M. B., Piser T. M., Mangano T. J. Effects of stimulus intensity on the inhibition by omega-conotoxin GVIA and neomycin of K(+_-evoked [3H]norepinephrine release from hippocampal brain slices and synaptosomal calcium influx. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 7;45(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90389-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly E., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Evidence that [3H]dopamine is taken up and released from nondopaminergic nerve terminals in the rat substantia nigra in vitro. J Neurochem. 1985 Jul;45(1):137–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. A., Leeson P. D. The glycine site of the NMDA receptor--five years on. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jan;14(1):20–25. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90108-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. M., Yoshikami D. A venom peptide with a novel presynaptic blocking action. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):282–284. doi: 10.1038/308282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., von Grafenstein H., Athayde C. M. Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent exocytosis. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs M. O., Desce J. M., Kemel M. L., Gauchy C., Godeheu G., Cheramy A., Glowinski J. Glutamatergic control of dopamine release in the rat striatum: evidence for presynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. J Neurochem. 1991 Jan;56(1):81–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. Ascorbic acid specifically enhances dopamine beta-monooxygenase activity in resting and stimulated chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7347–7356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Lin J. W., Cherksey B. Blocking and isolation of a calcium channel from neurons in mammals and cephalopods utilizing a toxin fraction (FTX) from funnel-web spider poison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1689–1693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes da Silva F. H., Witter M. P., Boeijinga P. H., Lohman A. H. Anatomic organization and physiology of the limbic cortex. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):453–511. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. NMDA-receptor activation increases cytoplasmic calcium concentration in cultured spinal cord neurones. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):519–522. doi: 10.1038/321519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Barrie A. P., Lowe M., Nicholls D. G. Glutamate release from guinea-pig synaptosomes: stimulation by reuptake-induced depolarization. J Neurochem. 1989 Jul;53(1):71–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Foran P., Dolly J. O., Verhage M., Wiegant V. M., Nicholls D. G. Tetanus toxin and botulinum toxins type A and B inhibit glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, aspartate, and met-enkephalin release from synaptosomes. Clues to the locus of action. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21338–21343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Adams M. E., Bean B. P. P-type calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90223-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Bean B. P., Adams M. E. P-type calcium channels blocked by the spider toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):827–829. doi: 10.1038/355827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Tsai H. L., Futai M. Energy-dependent accumulation of neuron blockers causes selective inhibition of neurotransmitter uptake by brain synaptic vesicles. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Sep;305(2):278–281. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount H., Quirion R., Chaudieu I., Boksa P. Stimulation of dopamine release from cultured rat mesencephalic cells by naturally occurring excitatory amino acids: involvement of both N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and non-NMDA receptor subtypes. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):268–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Meek J. L., Iadarola M. J., Chuang D. M., Roth B. L., Costa E. Coupling of inositol phospholipid metabolism with excitatory amino acid recognition sites in rat hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):40–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittaluga A., Raiteri M. N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) and non-NMDA receptors regulating hippocampal norepinephrine release. I. Location on axon terminals and pharmacological characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):232–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittaluga A., Raiteri M. Release-enhancing glycine-dependent presynaptic NMDA receptors exist on noradrenergic terminals of hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 27;191(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94153-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Angelini F., Levi G. A simple apparatus for studying the release of neurotransmitters from synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;25(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Wagner J. A., Snyder S. H., Thayer S. A., Olivera B. M., Miller R. J. Brain voltage-sensitive calcium channel subtypes differentiated by omega-conotoxin fraction GVIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8804–8807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka B. B., Jhamandas K. H. Excitatory amino acid action on the release of brain neurotransmitters and neuromodulators: biochemical studies. Prog Neurobiol. 1993 Feb;40(2):223–247. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(93)90023-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D., Conn P. J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in brain function and pathology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jan;14(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90107-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Augustine G. J. Calcium ions, active zones and synaptic transmitter release. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Ito I., Hirono C. A new type of glutamate receptor linked to inositol phospholipid metabolism. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):531–533. doi: 10.1038/325531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tareilus E., Schoch J., Adams M., Breer H. Analysis of rapid calcium signals in synaptosomes. Neurochem Int. 1993 Oct;23(4):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(93)90077-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A. Molecular diversity of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90595-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Adams M. E., Dunlap K. Calcium channels coupled to glutamate release identified by omega-Aga-IVA. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):310–313. doi: 10.1126/science.1357749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Adams M. E., Dunlap K. Multiple Ca2+ channel types coexist to regulate synaptosomal neurotransmitter release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9518–9522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhage M., Ghijsen W. E., Boomsma F., Lopes da Silva F. H. Endogenous noradrenaline and dopamine in nerve terminals of the hippocampus: differences in levels and release kinetics. J Neurochem. 1992 Sep;59(3):881–887. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Andrews H., Thukral V. Presynaptic glutamate receptors regulate noradrenaline release from isolated nerve terminals. J Neurochem. 1992 Jan;58(1):204–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K. Presynaptic glutamate receptors modulate dopamine release from striatal synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):819–822. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyss J. M., Swanson L. W., Cowan W. M. A study of subcortical afferents to the hippocampal formation in the rat. Neuroscience. 1979;4(4):463–476. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorumski C. F., Thio L. L. Properties of vertebrate glutamate receptors: calcium mobilization and desensitization. Prog Neurobiol. 1992 Sep;39(3):295–336. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(92)90020-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


