Abstract
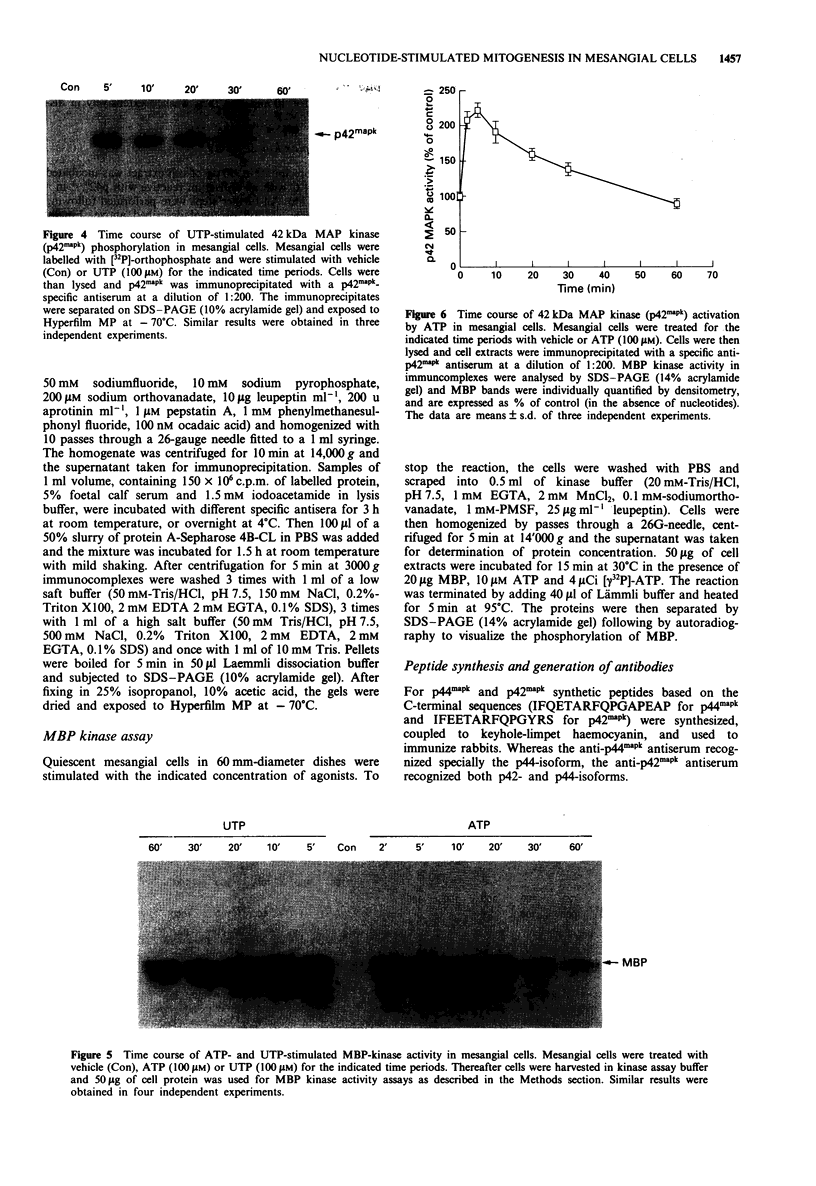
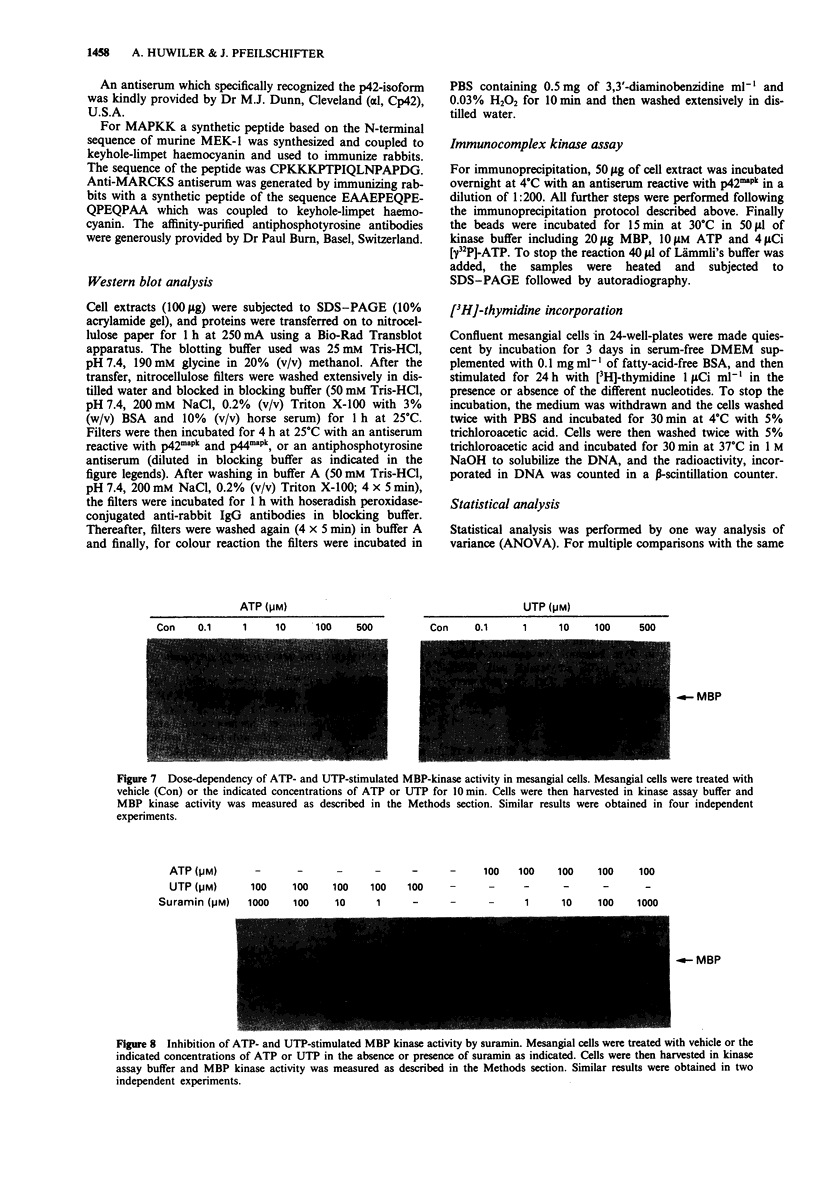
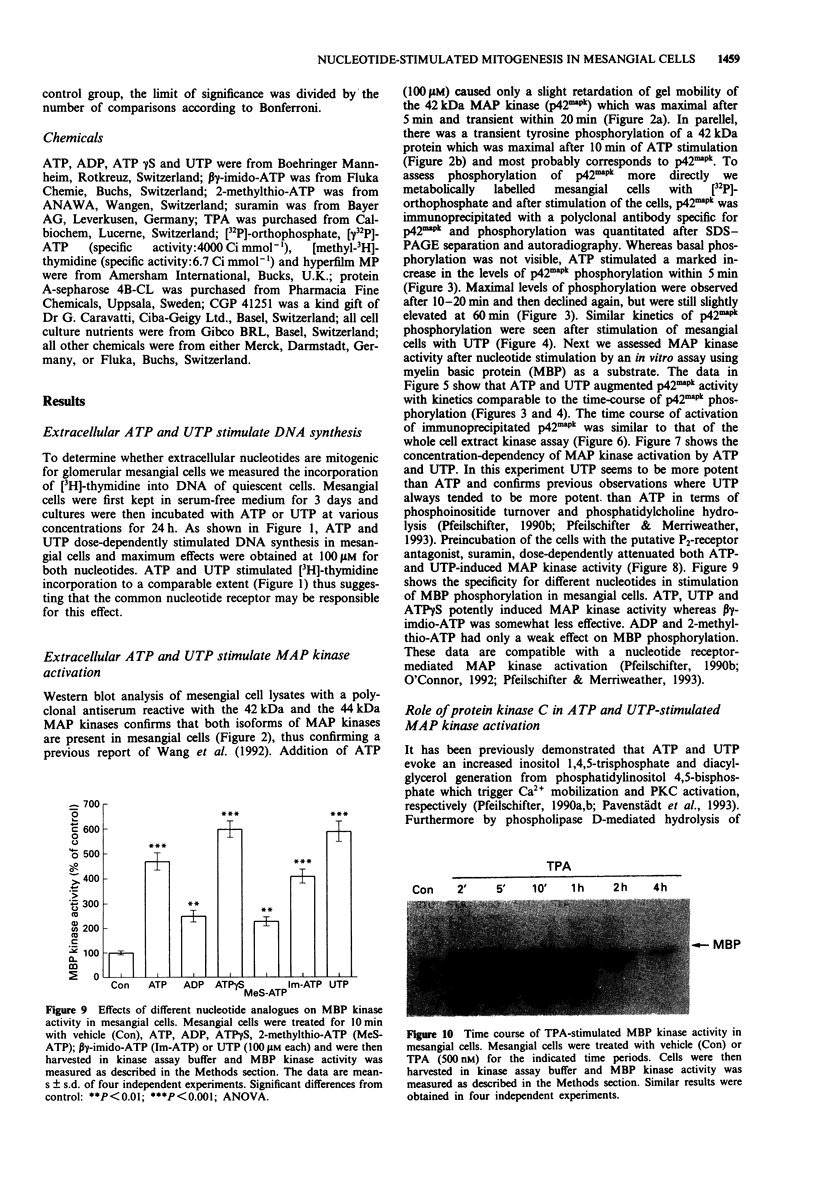
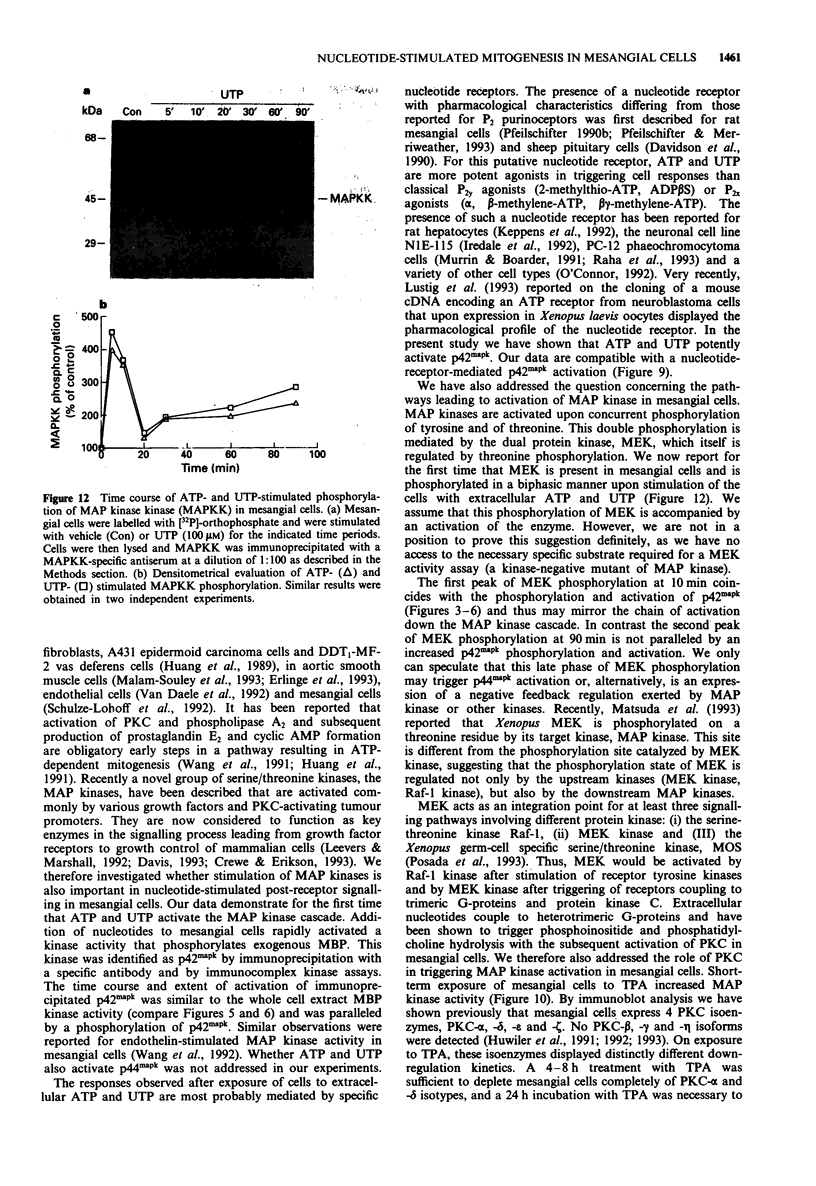
1. Extracellular ATP and UTP have been reported to activate a nucleotide receptor that mediates phosphoinositide and phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by phospholipases C and D, respectively. Here we report that ATP and UTP potently stimulate mesangial cell proliferation. 2. Both nucleotides stimulate phosphorylation and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and a biphasic phosphorylation of the up-stream mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. 3. When added at 100 microM, ATP gamma S, UTP and ATP were the most potent activators of mitogen-activated protein kinase. beta gamma-imido-ATP was somewhat less active and ADP and 2-methylthio-ATP caused a weak induction of enzyme activity. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by both ATP and UTP is dose-dependently attenuated by the P2-receptor antagonist, suramin. 4. The protein kinase C activator 12-0-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate, but not the biologically inactive 4 alpha-phorbol 12,13-didecanoate, increased mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in mesangial cells, suggesting that protein kinase C may mediate nucleotide-induced stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. 5. Down-regulation of protein kinase C -alpha and -delta isoenzymes by 4 h or 8 h treatment with phorbol ester partially inhibited ATP- and UTP-triggered mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Moreover, a 24 h treatment of mesangial cells with phorbol ester, a regimen that also causes depletion of protein kinase C-epsilon did not further reduce the level of mitogen-activated protein kinase stimulation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
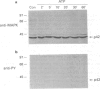
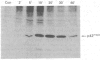
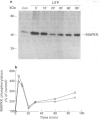
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. The role of myristoylated protein kinase C substrates in intracellular signaling pathways in macrophages. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181:189–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77377-8_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G. Pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int Suppl. 1993 Jul;42:S19–S26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. S., Wakefield I. K., Sohnius U., van der Merwe P. A., Millar R. P. A novel extracellular nucleotide receptor coupled to phosphoinositidase-C in pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Jan;126(1):80–87. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinge D., Yoo H., Edvinsson L., Reis D. J., Wahlestedt C. Mitogenic effects of ATP on vascular smooth muscle cells vs. other growth factors and sympathetic cotransmitters. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 2):H1089–H1097. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.4.H1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang N. N., Wang D. J., Gonzalez F., Heppel L. A. Multiple signal transduction pathways lead to extracellular ATP-stimulated mitogenesis in mammalian cells: II. A pathway involving arachidonic acid release, prostaglandin synthesis, and cyclic AMP accumulation. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Mar;146(3):483–494. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang N., Wang D. J., Heppel L. A. Extracellular ATP is a mitogen for 3T3, 3T6, and A431 cells and acts synergistically with other growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7904–7908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huwiler A., Fabbro D., Pfeilschifter J. Possible regulatory functions of protein kinase C-alpha and -epsilon isoenzymes in rat renal mesangial cells. Stimulation of prostaglandin synthesis and feedback inhibition of angiotensin II-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 15;279(Pt 2):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj2790441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huwiler A., Fabbro D., Stabel S., Pfeilschifter J. Immunocharacterization of delta- and zeta-isoenzymes of protein kinase C in rat renal mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 6;300(3):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80858-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huwiler A., Schulze-Lohoff E., Fabbro D., Pfeilschifter J. Immunocharacterization of protein kinase C isoenzymes in rat kidney glomeruli, and cultured glomerular epithelial and mesangial cells. Exp Nephrol. 1993 Jan-Feb;1(1):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iredale P. A., Martin K. F., Alexander S. P., Hill S. J., Kendall D. A. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate generation and calcium mobilisation via activation of an atypical P2 receptor in the neuronal cell line, N1E-115. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1083–1087. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., Vandekerckhove A., De Wulf H. Extracellular ATP and UTP exert similar effects on rat isolated hepatocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):475–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Nishida E., Gotoh Y. cDNA cloning of MAP kinase kinase reveals kinase cascade pathways in yeasts to vertebrates. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):787–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. MAP kinase regulation--the oncogene connection. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;2(10):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90105-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig K. D., Shiau A. K., Brake A. J., Julius D. Expression cloning of an ATP receptor from mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5113–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malam-Souley R., Campan M., Gadeau A. P., Desgranges C. Exogenous ATP induces a limited cell cycle progression of arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):C783–C788. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.4.C783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marte B. M., Meyer T., Stabel S., Standke G. J., Jaken S., Fabbro D., Hynes N. E. Protein kinase C and mammary cell differentiation: involvement of protein kinase C alpha in the induction of beta-casein expression. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Mar;5(3):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Phosphorylation of Xenopus mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase by MAP kinase kinase kinase and MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3277–3281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Regenass U., Fabbro D., Alteri E., Rösel J., Müller M., Caravatti G., Matter A. A derivative of staurosporine (CGP 41 251) shows selectivity for protein kinase C inhibition and in vitro anti-proliferative as well as in vivo anti-tumor activity. Int J Cancer. 1989 May 15;43(5):851–856. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrin R. J., Boarder M. R. Neuronal "nucleotide" receptor linked to phospholipase C and phospholipase D? Stimulation of PC12 cells by ATP analogues and UTP. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E. Recent developments in the classification and functional significance of receptors for ATP and UTP, evidence for nucleotide receptors. Life Sci. 1992;50(22):1657–1664. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90420-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner M., Huwiler A., Fleck T., Pfeilschifter J. Protein kinase C inhibitors potentiate angiotensin II-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in renal mesangial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 15;245(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavenstädt H., Gloy J., Leipziger J., Klär B., Pfeilschifter J., Schollmeyer P., Greger R. Effect of extracellular ATP on contraction, cytosolic calcium activity, membrane voltage and ion currents of rat mesangial cells in primary culture. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):953–959. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Angiotensin II B-type receptor mediates phosphoinositide hydrolysis in mesangial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 2;184(1):201–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90684-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Comparison of extracellular ATP and UTP signalling in rat renal mesangial cells. No indications for the involvement of separate purino- and pyrimidino-ceptors. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):469–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2720469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Extracellular ATP stimulates polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis and prostaglandin synthesis in rat renal mesangial cells. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding protein and feedback inhibition by protein kinase C. Cell Signal. 1990;2(2):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Huwiler A. A role for protein kinase C-epsilon in angiotensin II stimulation of phospholipase D in rat renal mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 4;331(3):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80350-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Merriweather C. Extracellular ATP and UTP activation of phospholipase D is mediated by protein kinase C-epsilon in rat renal mesangial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):847–853. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13890.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Yew N., Ahn N. G., Vande Woude G. F., Cooper J. A. Mos stimulates MAP kinase in Xenopus oocytes and activates a MAP kinase kinase in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raha S., de Souza L. R., Reed J. K. Intracellular signalling by nucleotide receptors in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Mar;154(3):623–630. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Lohoff E., Zanner S., Ogilvie A., Sterzel R. B. Extracellular ATP stimulates proliferation of cultured mesangial cells via P2-purinergic receptors. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 2):F374–F383. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.3.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Posada J., Munar E. S., Jensen A. M., Cooper J. A., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of mitogen-activated protein kinase activator(s) from epidermal growth factor-stimulated A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14373–14381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Seger D., Lozeman F. J., Ahn N. G., Graves L. M., Campbell J. S., Ericsson L., Harrylock M., Jensen A. M., Krebs E. G. Human T-cell mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases are related to yeast signal transduction kinases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25628–25631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Daele P., Van Coevorden A., Roger P. P., Boeynaems J. M. Effects of adenine nucleotides on the proliferation of aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1992 Jan;70(1):82–90. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. J., Huang N. N., Gonzalez F. A., Heppel L. A. Multiple signal transduction pathways lead to extracellular ATP-stimulated mitogenesis in mammalian cells: I. Involvement of protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Mar;146(3):473–482. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Simonson M. S., Pouysségur J., Dunn M. J. Endothelin rapidly stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in rat mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 15;287(Pt 2):589–594. doi: 10.1042/bj2870589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Harrison J. K., Vincent L. A., Haystead C., Haystead T. A., Michel H., Hunt D. F., Lynch K. R., Sturgill T. W. Molecular structure of a protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase activating p42 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase: MAP kinase kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):173–177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. F., Guan K. L. Cloning and characterization of two distinct human extracellular signal-regulated kinase activator kinases, MEK1 and MEK2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11435–11439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Moatassim C., Dornand J., Mani J. C. Extracellular ATP and cell signalling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 19;1134(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]