Abstract
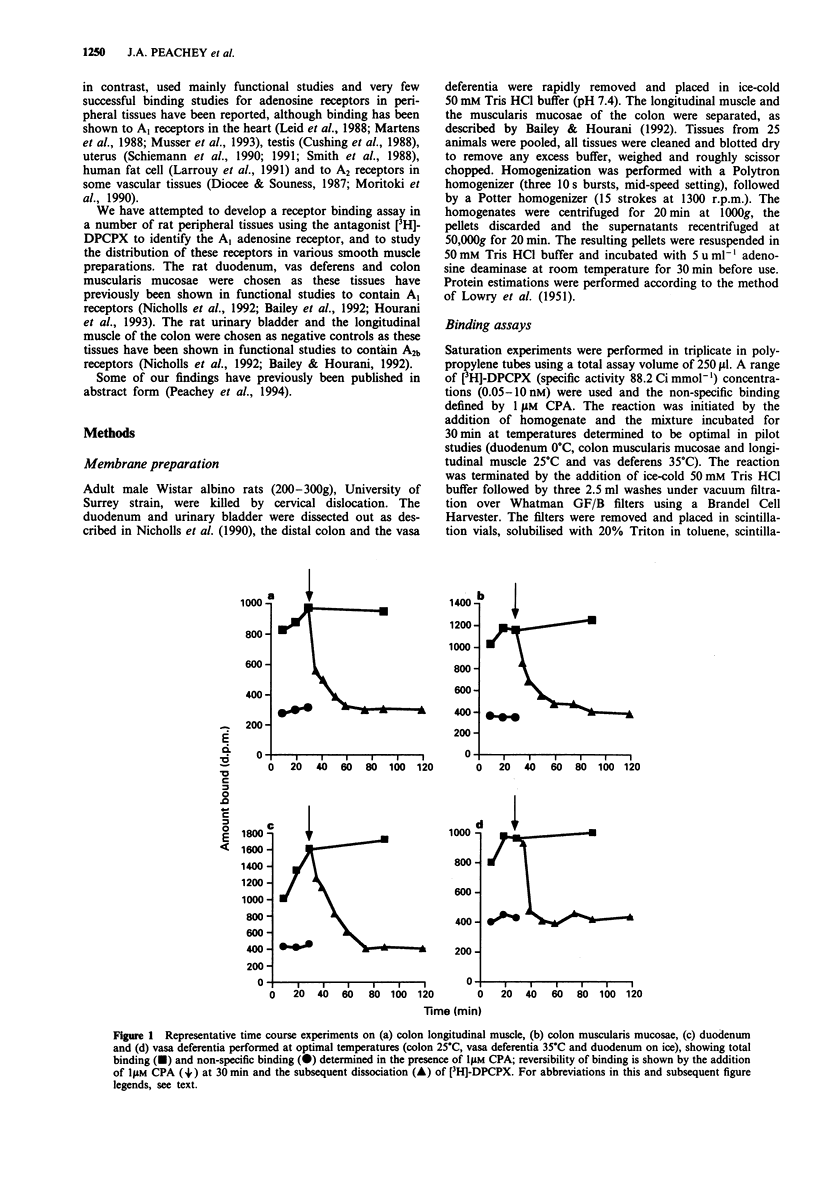
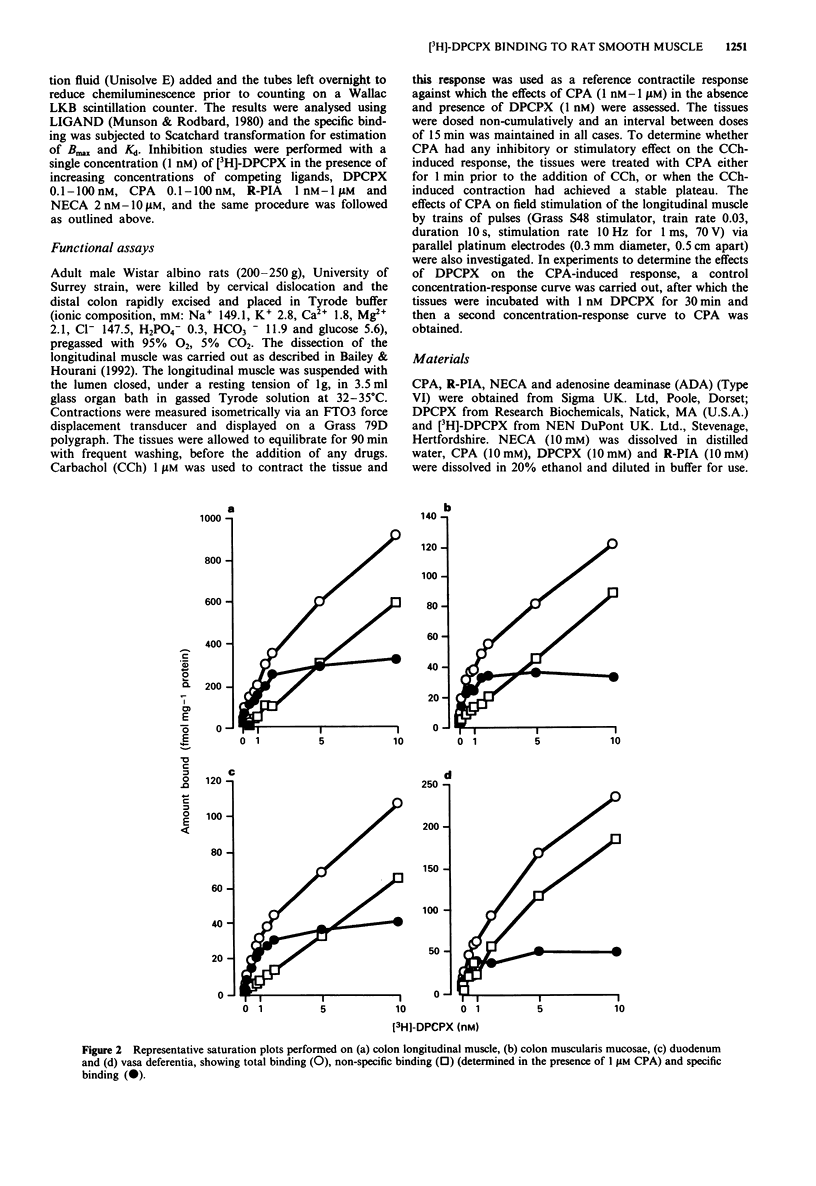
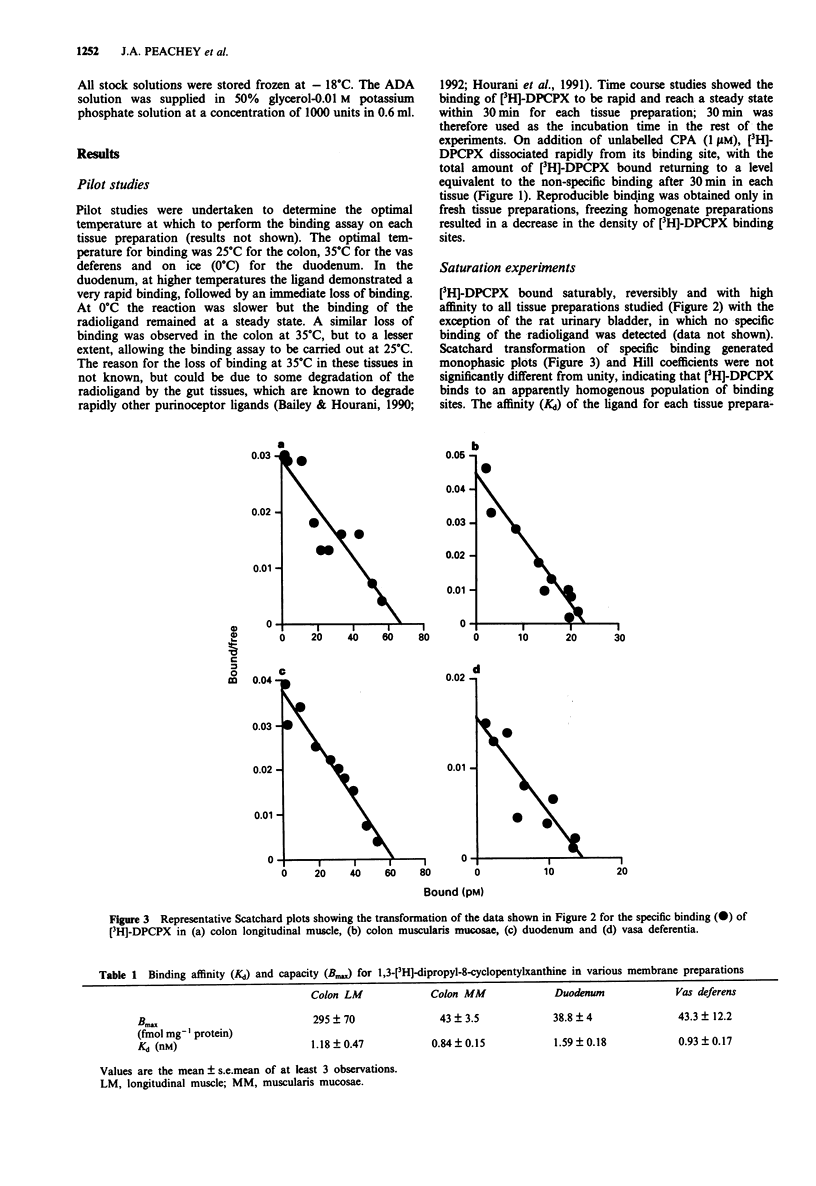
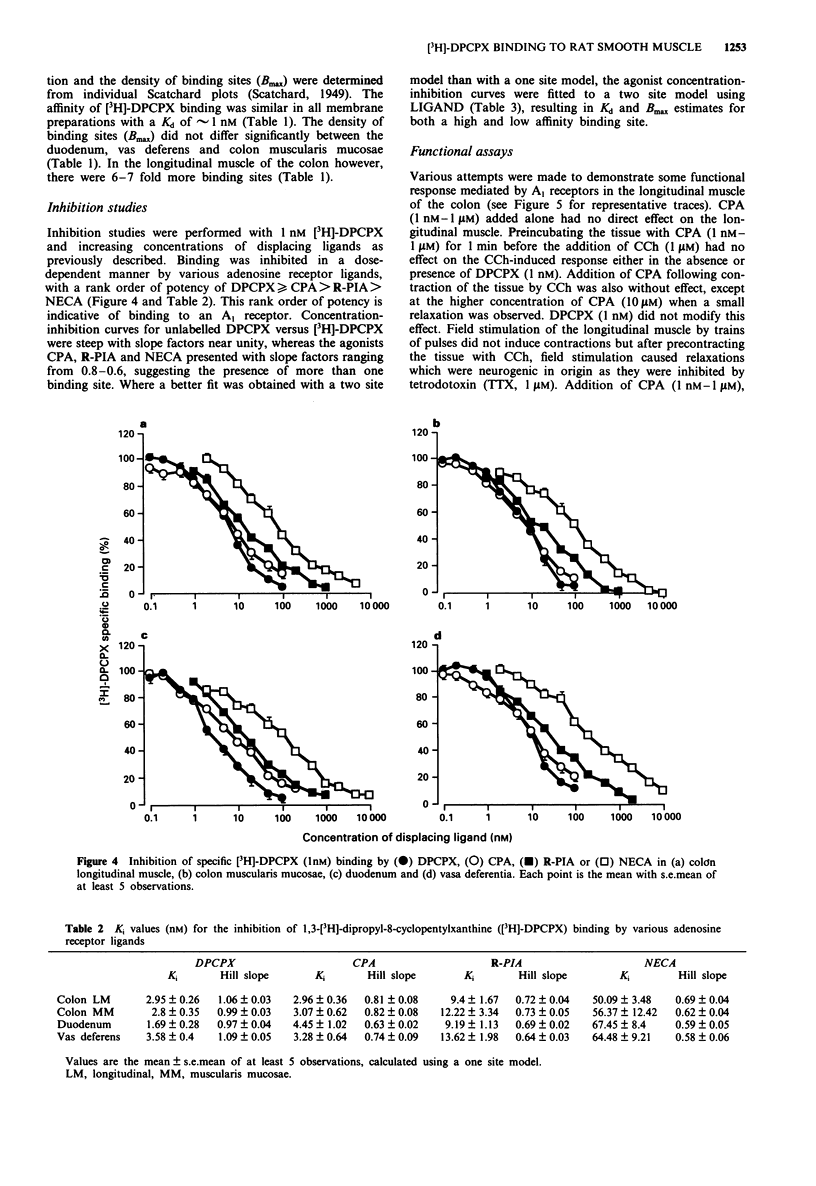
1. The binding of 1,3-[3H]-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine ([3H]-DPCPX), an antagonist radioligand selective for adenosine A1 receptors, was studied in rat duodenum, colon muscularis mucosae and longitudinal muscle, urinary bladder and vasa deferentia. 2. [3H]-DPCPX bound with high affinity to a single site in all membrane preparations studied with the exception of the rat urinary bladder in which no specific binding was detected. The affinity (Kd) of the binding site for [3H]-DPCPX was similar in all membrane preparations, the colon longitudinal muscle (1.18 +/- 0.47 nM), colon muscularis mucosae (0.84 +/- 0.15 nM), duodenum (1.59 +/- 0.18 nM) and vasa deferentia (0.93 +/- 0.17 nM). The density of [3H]-DPCPX binding sites was similar in the duodenum (38.8 +/- 4 fmol mg-1 protein), muscularis mucosae (43 +/- 3.5 fmol mg-1 protein) and vasa deferentia (43.3 +/- 12.2 fmol mg-1 protein), but in the longitudinal muscle 6-7 fold more binding sites (295 +/- 70 fmol mg-1 protein) were identified. 3. Inhibition studies using DPCPX (0.1-100 nM), N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) (0.1-100 nM), 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA) (2 nM-10 microM) and (R)-N6-phenylisopropyladenosine (R-PIA) (1 nM-1 microM) to displace the binding of [3H]-DPCPX at a concentration around the Kd value (1 nM), demonstrated an order of potency of displacement in all tissues of DPCPX > or = CPA > R-PIA > NECA. This potency order is characteristic of an A1 receptor, indicating that [3H]-DPCPX binds to adenosine A1 receptors in the rat duodenum, colon and vasa deferentia.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey S. J., Hickman D., Hourani S. M. Characterization of the P1-purinoceptors mediating contraction of the rat colon muscularis mucosae. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):400–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. A study of the purinoceptors mediating contraction in the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):753–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. Effects of purines on the longitudinal muscle of the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):885–892. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Daly J. W., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptors in brain membranes: binding of N6-cyclohexyl[3H]adenosine and 1,3-diethyl-8-[3H]phenylxanthine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Fergus J. H., Badger E. W., Bristol J. A., Santay L. A., Hartman J. D., Hays S. J., Huang C. C. Binding of the A1-selective adenosine antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine to rat brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;335(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00165037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lu G. H., Pugsley T. A. Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Hourani S. M. Adenosine receptor subtypes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Oct;14(10):360–366. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90094-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing D. J., McConnaughey M. M., Mustafa S. J. Characterization of adenosine binding sites in bovine testicular tissue using 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-[3H]dipropylxanthine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 2;152(3):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90731-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diocee B. K., Souness J. E. Characterization of 5'-N-ethylcarboxamido[3H]adenosine binding to pig aorta smooth muscle membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 1;36(21):3621–3627. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani S. M., Bailey S. J., Nicholls J., Kitchen I. Direct effects of adenylyl 5'-(beta,gamma-methylene)diphosphonate, a stable ATP analogue, on relaxant P1-purinoceptors in smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):685–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani S. M., Jones D. A. Post-junctional excitatory adenosine A1 receptors in the rat vas deferens. Gen Pharmacol. 1994 May;25(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(94)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani S. M., Nicholls J., Lee B. S., Halfhide E. J., Kitchen I. Characterization and ontogeny of P1-purinoceptors on rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):754–758. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12873.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz K. N., Keil R., Zimmer F. J., Schwabe U. Guanine nucleotide effects on 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-[3H]dipropylxanthine binding to membrane-bound and solubilized A1 adenosine receptors of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):1988–1994. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz K. N., Vogt H., Tawfik-Schlieper H. Comparison of A1 adenosine receptors in brain from different species by radioligand binding and photoaffinity labelling. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;343(2):196–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00168610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrouy D., Galitzky J., Lafontan M. A1 adenosine receptors in the human fat cell: tissue distribution and regulation of radioligand binding. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb 25;206(2):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90022-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Franklin P. H., Murray T. F. Labeling of A1 adenosine receptors in porcine atria with the antagonist radioligand 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-[3H]dipropylxanthine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 16;147(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90644-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung E., Jacobson K. A., Green R. D. Analysis of agonist-antagonist interactions at A1 adenosine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;38(1):72–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens D., Lohse M. J., Schwabe U. [3H]-8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine binding to A1 adenosine receptors of intact rat ventricular myocytes. Circ Res. 1988 Sep;63(3):613–620. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.3.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritoki H., Matsugi T., Takase H., Ueda H., Tanioka A. Evidence for the involvement of cyclic GMP in adenosine-induced, age-dependent vasodilatation. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):569–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser B., Morgan M. E., Leid M., Murray T. F., Linden J., Vestal R. E. Species comparison of adenosine and beta-adrenoceptors in mammalian atrial and ventricular myocardium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul 15;246(2):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90086-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J., Hourani S. M., Kitchen I. Characterization of P1-purinoceptors on rat duodenum and urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):639–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J., Hourani S. M., Kitchen I. The ontogeny of purinoceptors in rat urinary bladder and duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):874–878. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira J. C., Sebastião A. M., Ribeiro J. A. Solubilized rat brain adenosine receptors have two high-affinity binding sites for 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1165–1171. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann W. P., Doggwiler K. O., Buxton I. L. Action of adenosine in estrogen-primed nonpregnant guinea pig myometrium: characterization of the smooth muscle receptor and coupling to phosphoinositide metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Aug;258(2):429–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann W. P., Walther J. M., Buxton I. L. On the ability of endogenous adenosine to regulate purine nucleoside receptor binding of antagonists in smooth muscle membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):886–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Buxton I. L., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological classification of receptors for adenyl purines in guinea pig myometrium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1059–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan W., Sutherland G. R., Geiger J. D. Binding of the adenosine A2 receptor ligand [3H]CGS 21680 to human and rat brain: evidence for multiple affinity sites. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1763–1771. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Braunwalder A., Erickson T. J. Evaluation of the binding of the A-1 selective adenosine radioligand, cyclopentyladenosine (CPA), to rat brain tissue. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;332(2):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00511410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Valentine H. L. Binding of [3H]cyclohexyladenosine to adenosine recognition sites in guinea pig ileal membranes: comparison with binding in brain membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jun 4;57(1):79–83. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Li C., Olah M. E., Johnson R. A., Stiles G. L., Civelli O. Molecular cloning and characterization of an adenosine receptor: the A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7432–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


