Abstract
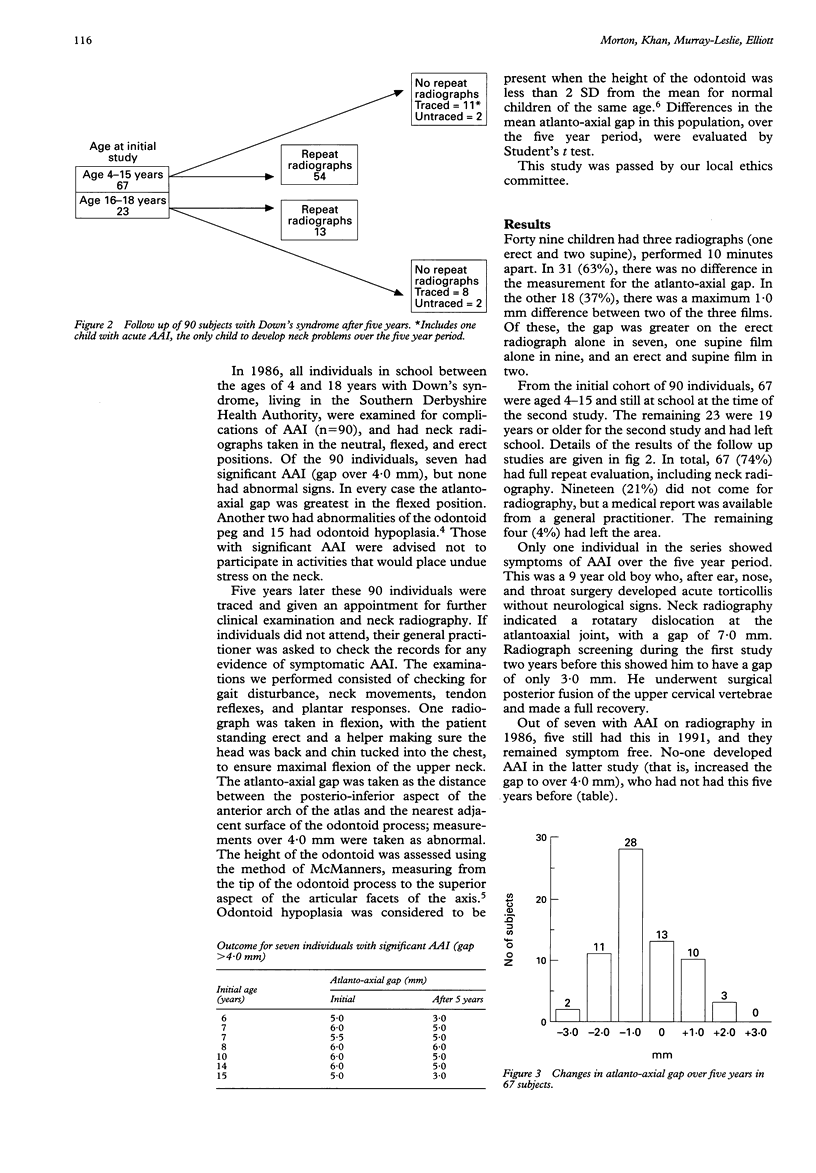
In 1986 all 90 children aged 4-19 years with Down's syndrome attending school in the area served by the Southern Derbyshire Health Authority underwent radiography to identify atlantoaxial instability (AAI). This study details repeat observations five years later. Full results were available on 67 (74%), information on health status was available on the remaining 19 (21%); four (4%) were untraced. There was an overall significant reduction in the atlanto-axial gap over five years. No one developed AAI on repeat testing who had not had it earlier. One child who had previously had normal neck radiography developed acute symptomatic AAI after ear, nose, and throat surgery. Radiographs were done on three occasions on the same day in 49 individuals, ensuring full flexion of the upper neck. There were no significant differences between the radiographs, even in five subjects with AAI. Management of AAI in Down's syndrome is discussed in the light of these findings. Radiography can reliably detect children with chronic AAI who may be at risk of gradually developing symptoms; this may justify a screening programme. This must be distinguished from those who develop symptoms after acute trauma or anaesthesia, for which specific precautions are needed, and previous screening radiographs are unhelpful.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke S. W., French H. G., Roberts J. M., Johnston C. E., 2nd, Whitecloud T. S., 3rd, Edmunds J. O., Jr Chronic atlanto-axial instability in Down syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985 Dec;67(9):1356–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers M. J., Bol E., de Roos F., van Gijn J. Risk of sports activities in children with Down's syndrome and atlantoaxial instability. Lancet. 1993 Aug 28;342(8870):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91644-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers M. J., Ramos L., Bol E., van Gijn J. Radiological assessment of the atlantoaxial distance in Down's syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Sep;69(3):347–350. doi: 10.1136/adc.69.3.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. G. Atlantoaxial instability in individuals with Down syndrome: a fresh look at the evidence. Pediatrics. 1988 Jun;81(6):857–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson E. G., Smith L. Atlanto-axial subluxation in children due to vertebral anomalies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979 Jun;61(4):582–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S., Morton R. E., Whitelaw R. A. Atlantoaxial instability and abnormalities of the odontoid in Down's syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Dec;63(12):1484–1489. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.12.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. The odontoid process in children--is it hypoplastic? Clin Radiol. 1988 Jul;39(4):391–393. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(88)80278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagjivan B., Spencer P. A., Hosking G. Radiological screening for atlanto-axial instability in Down's syndrome. Clin Radiol. 1988 Nov;39(6):661–663. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(88)80088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke G. R., Gardner J. I., Van Epps E. F. Atlas-dens interval (ADI) in children: a survey based on 200 normal cervical spines. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1966 May;97(1):135–140. doi: 10.2214/ajr.97.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel W., Uyham R., Stimson C. W. Subluxation of the atlas causing spinal cord compression in a case of Down's syndrome with a "manifestation of an occipital vertebra". Radiology. 1969 Oct;93(4):839–840. doi: 10.1148/93.4.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManners T. Odontoid hypoplasia. Br J Radiol. 1983 Dec;56(672):907–910. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-56-672-907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msall M. E., Reese M. E., DiGaudio K., Griswold K., Granger C. V., Cooke R. E. Symptomatic atlantoaxial instability associated with medical and rehabilitative procedures in children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics. 1990 Mar;85(3 Pt 2):447–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordt J. C., Stauffer E. S. Sequelae of atlantoaxial stabilization in two patients with Down's syndrome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1981 Sep-Oct;6(5):437–440. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198109000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa T., Izawa T., Kuroki Y., Ohnari K. Follow-up study of atlanto-axial instability in Down's syndrome without separate odontoid process. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1989 Nov;14(11):1149–1153. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198911000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S. Radiological reliability in atlantoaxial subluxation. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Feb;67(2):256–256. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueschel S. M., Herndon J. H., Gelch M. M., Senft K. E., Scola F. H., Goldberg M. J. Symptomatic atlantoaxial subluxation in persons with Down syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop. 1984 Nov;4(6):682–688. doi: 10.1097/01241398-198411000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueschel S. M., Scola F. H., Pezzullo J. C. A longitudinal study of atlanto-dens relationships in asymptomatic individuals with Down syndrome. Pediatrics. 1992 Jun;89(6 Pt 2):1194–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby K. A., Newton R. W., Gupta S., Hunt L. Clinical predictors and radiological reliability in atlantoaxial subluxation in Down's syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Jul;66(7):876–878. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.7.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. P., Somerville G. M., Miner M. E., Reilly D. Atlanto-axial subluxation and trisomy-21: another perioperative complication. Anesthesiology. 1987 Aug;67(2):253–254. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198708000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


