Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving K., Weitzberg E., Lundberg J. M. Increased amount of nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatics. Eur Respir J. 1993 Oct;6(9):1368–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård E. Nitric oxide: mediator, murderer, and medicine. Lancet. 1994 May 14;343(8907):1199–1206. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92405-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
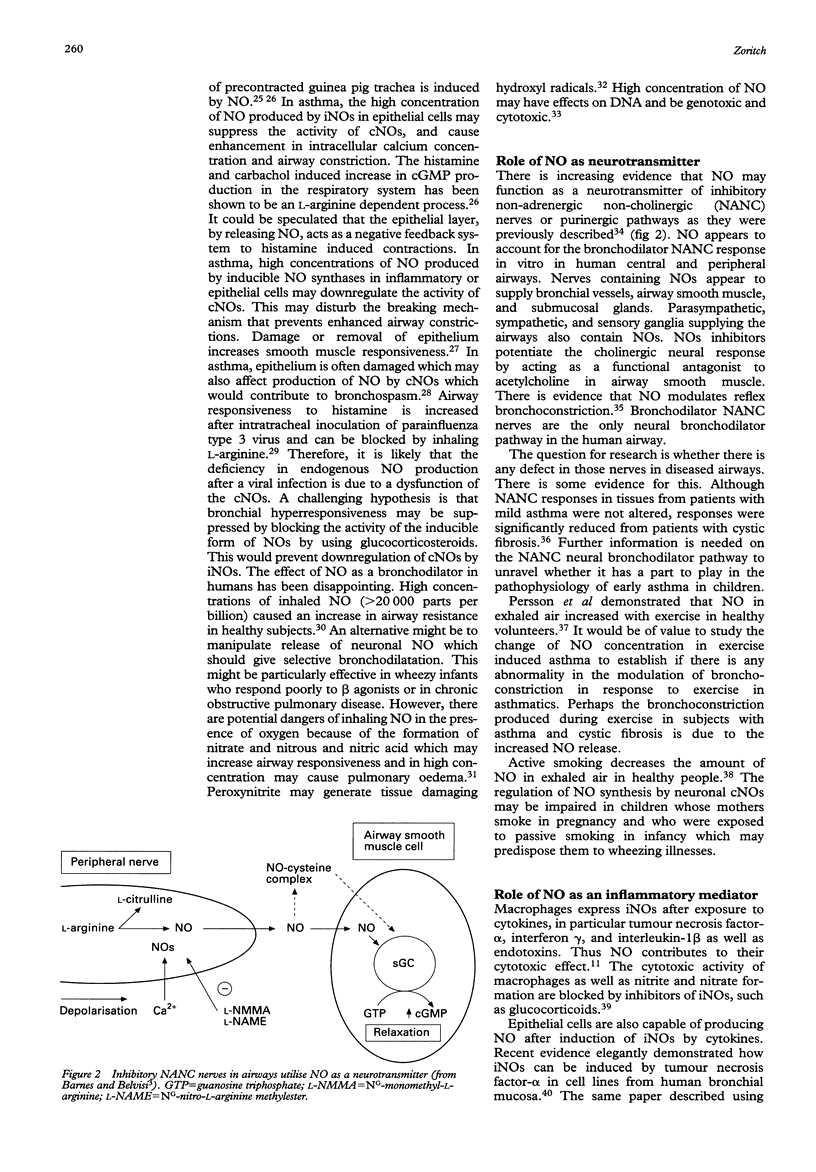
- Barnes P. J., Belvisi M. G. Nitric oxide and lung disease. Thorax. 1993 Oct;48(10):1034–1043. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.10.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Nitric oxide and airways. Eur Respir J. 1993 Feb;6(2):163–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman J. S., Beckman T. W., Chen J., Marshall P. A., Freeman B. A. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1620–1624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Stretton C. D., Yacoub M., Barnes P. J. Nitric oxide is the endogenous neurotransmitter of bronchodilator nerves in humans. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):221–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90676-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borland C., Cox Y., Higenbottam T. Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide in man. Thorax. 1993 Nov;48(11):1160–1162. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.11.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calver A., Collier J., Vallance P. Nitric oxide and cardiovascular control. Exp Physiol. 1993 May;78(3):303–326. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1993.sp003687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinh-Xuan A. T., Higenbottam T. W., Clelland C. A., Pepke-Zaba J., Cremona G., Butt A. Y., Large S. R., Wells F. C., Wallwork J. Impairment of endothelium-dependent pulmonary-artery relaxation in chronic obstructive lung disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 30;324(22):1539–1547. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105303242203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djukanović R., Roche W. R., Wilson J. W., Beasley C. R., Twentyman O. P., Howarth R. H., Holgate S. T. Mucosal inflammation in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Aug;142(2):434–457. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.2.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy P. M., Shore S. A., Drazen J. M., Frostell C., Hill W. A., Zapol W. M. Bronchodilator action of inhaled nitric oxide in guinea pigs. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):421–428. doi: 10.1172/JCI115877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filep J. G., Battistini B., Sirois P. Induction by endothelin-1 of epithelium-dependent relaxation of guinea-pig trachea in vitro: role for nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):637–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frostell C., Fratacci M. D., Wain J. C., Jones R., Zapol W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide. A selective pulmonary vasodilator reversing hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Circulation. 1991 Jun;83(6):2038–2047. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.6.2038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston B., Drazen J. M., Loscalzo J., Stamler J. S. The biology of nitrogen oxides in the airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Feb;149(2 Pt 1):538–551. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.2.7508323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamid Q., Springall D. R., Riveros-Moreno V., Chanez P., Howarth P., Redington A., Bousquet J., Godard P., Holgate S., Polak J. M. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in asthma. Lancet. 1993 Dec 18;342(8886-8887):1510–1513. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)80083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):473–476. doi: 10.1126/science.2432665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Vavrin Z., Taintor R. R. L-arginine is required for expression of the activated macrophage effector mechanism causing selective metabolic inhibition in target cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):550–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgate S. Mediator and cytokine mechanisms in asthma. Thorax. 1993 Feb;48(2):103–109. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharitonov S. A., Yates D., Robbins R. A., Logan-Sinclair R., Shinebourne E. A., Barnes P. J. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Lancet. 1994 Jan 15;343(8890):133–135. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90931-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. P., Neish S. R., Shaffer E., Abman S. H. Low-dose inhalation nitric oxide in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Lancet. 1992 Oct 3;340(8823):819–820. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92687-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 1;298(Pt 2):249–258. doi: 10.1042/bj2980249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leurs R., Brozius M. M., Jansen W., Bast A., Timmerman H. Histamine H1-receptor-mediated cyclic GMP production in guinea-pig lung tissue is an L-arginine-dependent process. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 5;42(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90713-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Li Y., Severn A., Millott S., Schmidt J., Salter M., Moncada S. A possible novel pathway of regulation by murine T helper type-2 (Th2) cells of a Th1 cell activity via the modulation of the induction of nitric oxide synthase on macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2489–2494. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. F., Crawley D. E., Rohde J. A., Evans T. W., Barnes P. J. Role of nitric oxide and guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate in mediating nonadrenergic, noncholinergic relaxation in guinea-pig pulmonary arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):861–866. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14538.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. O., Weitzberg E., Nordvall S. L., Kuylenstierna R., Lundberg J. M., Alving K. Primarily nasal origin of exhaled nitric oxide and absence in Kartagener's syndrome. Eur Respir J. 1994 Aug;7(8):1501–1504. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07081501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall T. B., Boughton-Smith N. K., Palmer R. M., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Synthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine by neutrophils. Release and interaction with superoxide anion. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):293–296. doi: 10.1042/bj2610293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs A. The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):2002–2012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munakata M., Masaki Y., Sakuma I., Ukita H., Otsuka Y., Homma Y., Kawakami Y. Pharmacological differentiation of epithelium-derived relaxing factor from nitric oxide. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Aug;69(2):665–670. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.69.2.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp F. P., van der Linde H. J., Folkerts G. Nitric oxide synthesis inhibitors induce airway hyperresponsiveness in the guinea pig in vivo and in vitro. Role of the epithelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Sep;148(3):727–734. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.3.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepke-Zaba J., Higenbottam T. W., Dinh-Xuan A. T., Stone D., Wallwork J. Inhaled nitric oxide as a cause of selective pulmonary vasodilatation in pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 1991 Nov 9;338(8776):1173–1174. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson M. G., Gustafsson L. E., Wiklund N. P., Moncada S., Hedqvist P. Endogenous nitric oxide as a probable modulator of pulmonary circulation and hypoxic pressor response in vivo. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 Dec;140(4):449–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb09021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson M. G., Zetterström O., Agrenius V., Ihre E., Gustafsson L. E. Single-breath nitric oxide measurements in asthmatic patients and smokers. Lancet. 1994 Jan 15;343(8890):146–147. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90935-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the expression of an inducible, but not the constitutive, nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10043–10047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen T. R., Kjaergaard S. K., Tarp U., Pedersen O. F. Delayed effects of NO2 exposure on alveolar permeability and glutathione peroxidase in healthy humans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Sep;146(3):654–659. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.3.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Polaner D. M., Lang P., Zapol W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Lancet. 1992 Oct 3;340(8823):818–819. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92686-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossaint R., Falke K. J., López F., Slama K., Pison U., Zapol W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide for the adult respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 11;328(6):399–405. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302113280605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Masini E., Anggard E., Mannaioni P. F., Vane J. Synthesis of a nitric oxide-like factor from L-arginine by rat serosal mast cells: stimulation of guanylate cyclase and inhibition of platelet aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):596–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90372-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling J., Holzer P., Guggenbach M., Gyurech D., Marathia K., Geroulanos S. Reduced endogenous nitric oxide in the exhaled air of smokers and hypertensives. Eur Respir J. 1994 Mar;7(3):467–471. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07030467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M. Epithelium-derived relaxing factor(s) and bronchial reactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 May;83(5):855–861. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Biochemical mechanisms underlying vascular smooth muscle relaxation: the guanylate cyclase-cyclic GMP system. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 (Suppl 5):S115–S118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


