Abstract
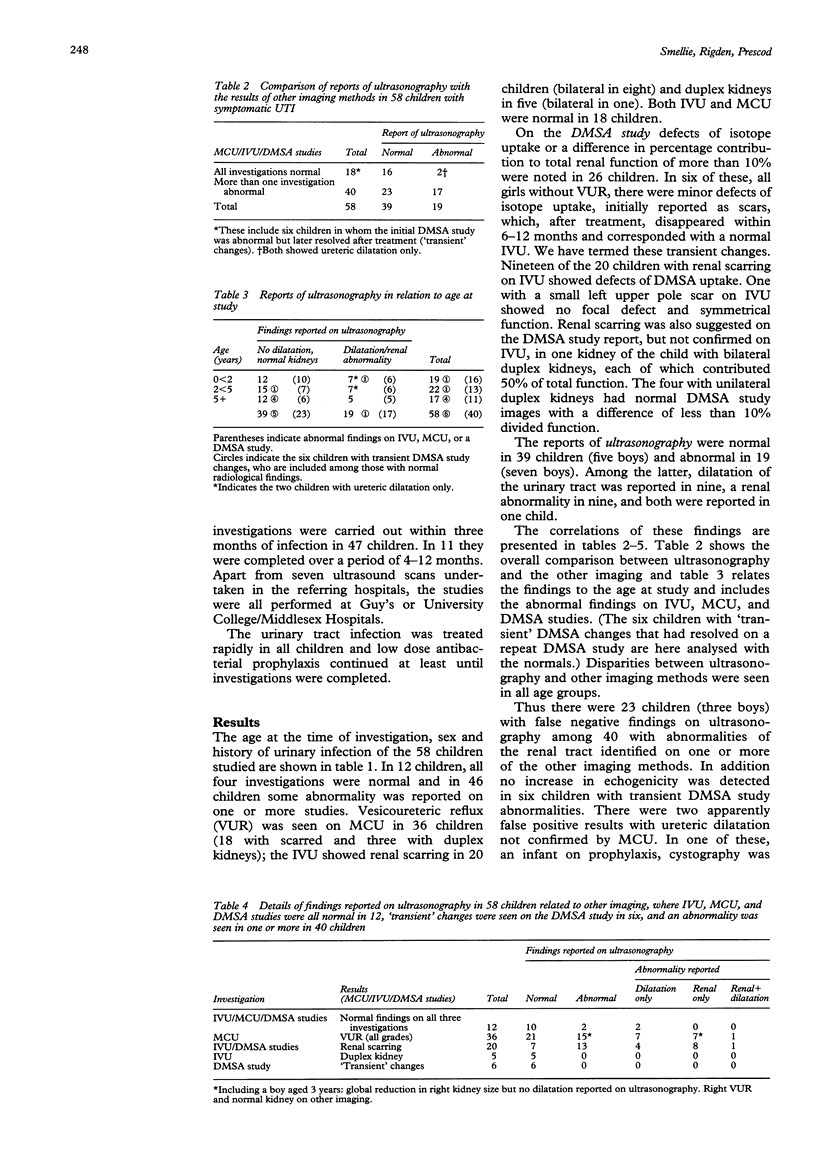
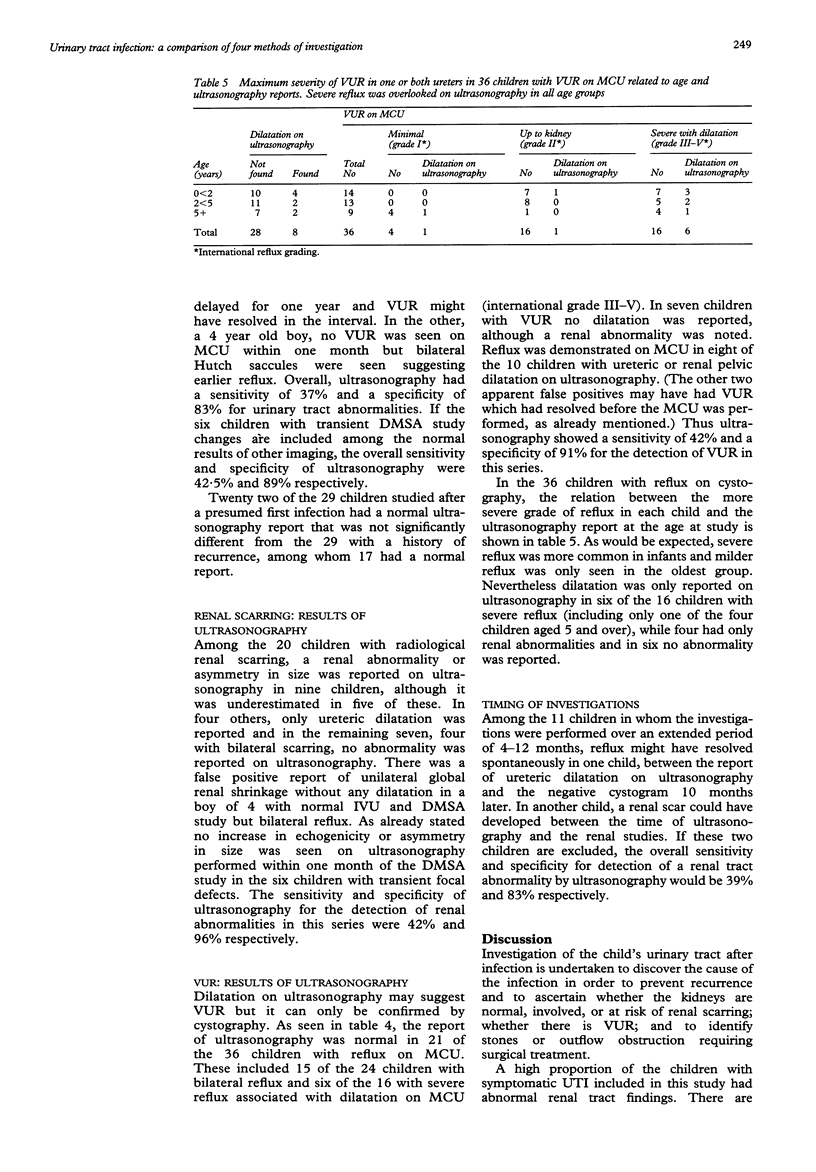
The optimal regimen for investigating children with urinary tract infection (UTI) remains uncertain. Ultrasonography, contrast micturating cystourethrography (MCU), intravenous urography (IVU), and technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) studies were performed in 58 children with UTI under 14 years of age attending two teaching hospitals and the results compared. All four investigations were normal in 12 children. In 36 with vesicoureteric reflux (VUR) on MCU, dilatation was reported on ultrasonography in eight children. Radiological renal scarring was seen in 20 children; it was suspected on ultrasonography in nine, with dilatation alone in four, and a normal report in seven. Duplex kidneys identified on IVU were unrecognised on ultrasonography or DMSA studies; ultrasonography showed no change corresponding to presumed acute defects on DMSA studies that later resolved. Disparities were observed at all ages. This study suggests that ultrasonography is unreliable in detecting VUR, renal scarring, or inflammatory change and, alone, is inadequate for investigating UTI in children.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrich M. P., Majd M. Diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of the first urinary tract infection in infants and young children. Pediatrics. 1992 Sep;90(3):436–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwell J. D., Cook P. L., Strong L., Hyde I. The interrelationship between vesico-ureteric reflux, trigonal abnormalities and a bifid pelvicalyceal collecting system: a family study. Br J Urol. 1977 Apr;49(2):97–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1977.tb04079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. C., Thomas D. F., Arthur R. J., Irving H. C., Smith S. E. Prenatally diagnosed reflux: a follow-up study. Br J Urol. 1990 Apr;65(4):407–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1990.tb14766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon I. Urinary tract infection in paediatrics: the role of diagnostic imaging. Br J Radiol. 1990 Jul;63(751):507–511. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-63-751-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock G. B. A practical approach to evaluating urinary tract infection in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 1991 Jul;5(4):401–403. doi: 10.1007/BF01453665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson B., Nolstedt L., Svensson L., Söderlundh S., Berg U. 99mTechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan in the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children: relation to clinical and radiological findings. Pediatr Nephrol. 1992 Jul;6(4):328–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00869725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff S. A. A practical approach to evaluating urinary tract infection in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 1991 Jul;5(4):398–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01453663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najmaldin A., Burge D. M., Atwell J. D. Fetal vesicoureteric reflux. Br J Urol. 1990 Apr;65(4):403–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1990.tb14765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickwood A. M., Carty H. M., McKendrick T., Williams M. P., Jackson M., Pilling D. W., Sprigg A. Current imaging of childhood urinary infections: prospective survey. BMJ. 1992 Mar 14;304(6828):663–665. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6828.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smellie J. M., Poulton A., Prescod N. P. Retrospective study of children with renal scarring associated with reflux and urinary infection. BMJ. 1994 May 7;308(6938):1193–1196. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6938.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smellie J. M., Rigden S. P. Pitfalls in the investigation of children with urinary tract infection. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Mar;72(3):251–258. doi: 10.1136/adc.72.3.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte K. M., Abbott G. D., Kennedy J. C., Maling T. M. A protocol for the investigation of infants and children with urinary tract infection. Clin Radiol. 1988 May;39(3):278–280. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(88)80532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


