Abstract
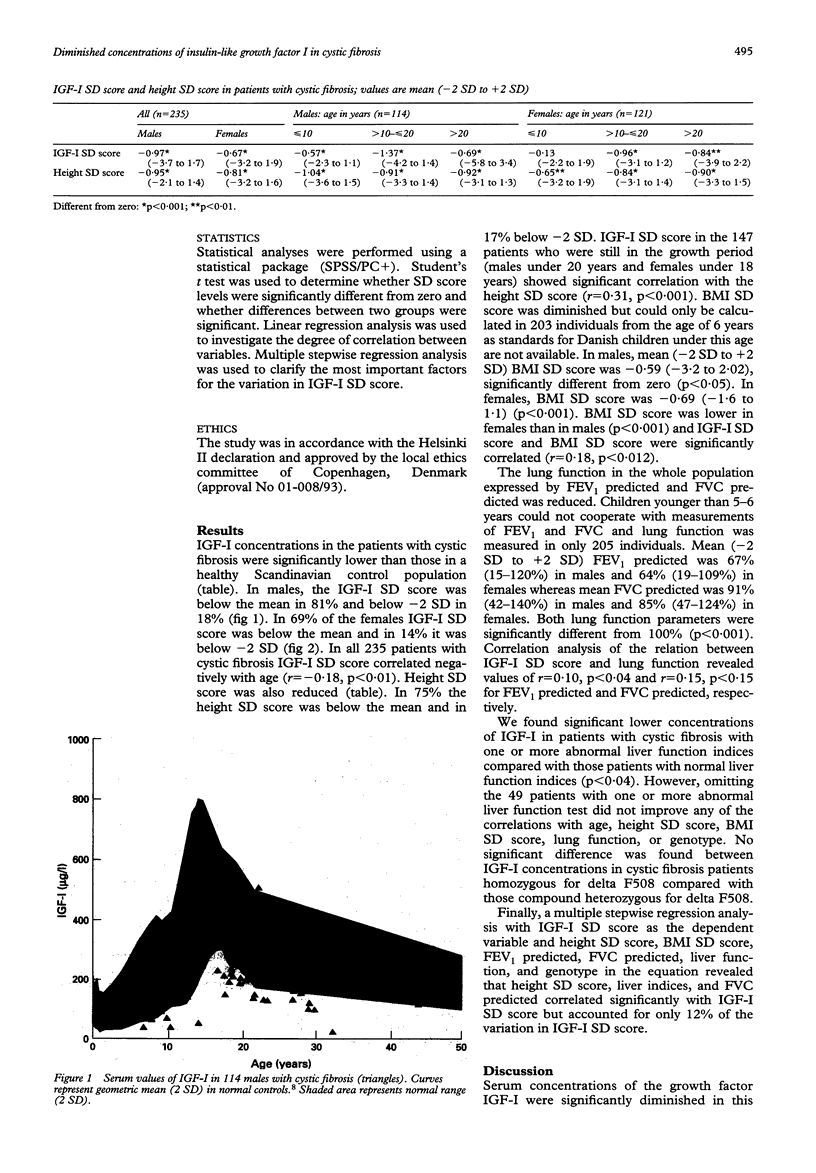
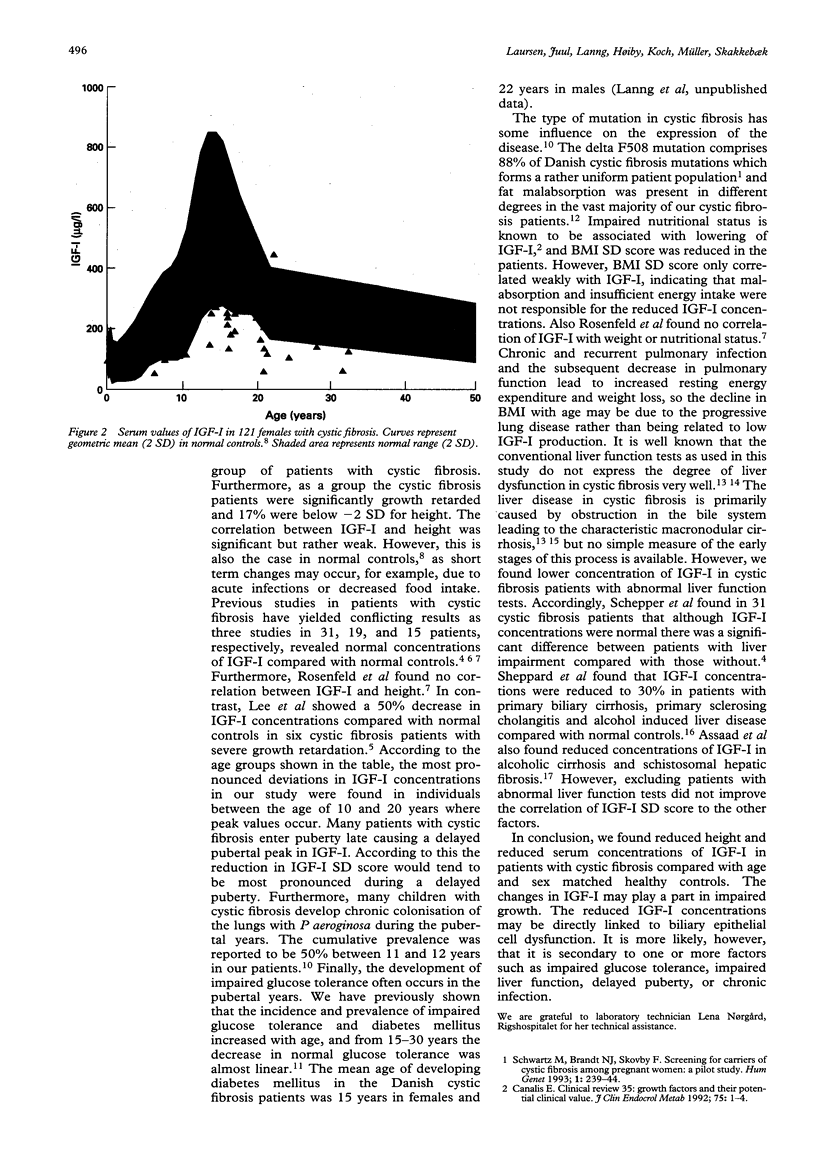
Cystic fibrosis is frequently accompanied by a catabolic condition with low body mass index caused by a number of disease complications. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) is an anabolic hormone and an important marker of nutritional status, liver function, and linear growth. Available data on IGF-I in cystic fibrosis are sparse and conflicting. From 1990-3, 235 of our 240 patients (114 males, 121 females, median age 16.2 years, ranged 0.1-44.0 years) had IGF-I measured once by radioimmunoassay. IGF-I was significantly reduced compared with a healthy Scandinavian control population: mean (-2 SD to +2 SD) IGF-I SD score was -0.97 (-3.7 to 1.7) in males and -0.67 (-3.2 to 1.9) in females. Height SD score was -0.95 (-3.3 to 1.4) in males and -0.81 (-3.2 to 1.6) in females. In patients who were still in the growth period a significant correlation of IGF-I SD score to height SD score (r = 0.28, p < 0.001) was found. The low IGF-I concentrations may reflect the catabolic state of many patients with cystic fibrosis and play a part in their abnormal growth pattern.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assaad S. N., Cunningham G. R., Samaan N. A. Abnormal growth hormone dynamics in chronic liver disease do not depend on severe parenchymal disease. Metabolism. 1990 Apr;39(4):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90248-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canalis E. Clinical review 35: Growth factors and their potential clinical value. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jul;75(1):1–4. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1618994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo C., Apostolo M. G., Assaisso M., Roman B., Bottani P. Liver disease in cystic fibrosis. Neth J Med. 1992 Oct;41(3-4):119–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Schepper J., Van Blerk M., Hachimi-Idrissi S., Dab I., Smitz J. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I determinations in patients with cystic fibrosis: Influence of the nutritional and liver status. Clin Nutr. 1992 Oct;11(5):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0261-5614(92)90007-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):137–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen H. K., Nir M., Høiby N., Koch C., Schwartz M. Severity of cystic fibrosis in patients homozygous and heterozygous for delta F508 mutation. Lancet. 1991 Mar 16;337(8742):631–634. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92449-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juul A., Bang P., Hertel N. T., Main K., Dalgaard P., Jørgensen K., Müller J., Hall K., Skakkebaek N. E. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I in 1030 healthy children, adolescents, and adults: relation to age, sex, stage of puberty, testicular size, and body mass index. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Mar;78(3):744–752. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.3.8126152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanng S., Schwartz M., Thorsteinsson B., Koch C. Endocrine and exocrine pancreatic function and the delta F508 mutation in cystic fibrosis. Clin Genet. 1991 Nov;40(5):345–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanng S., Thorsteinsson B., Erichsen G., Nerup J., Koch C. Glucose tolerance in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1991 May;66(5):612–616. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.5.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. A., Dickinson L. S., Kilgore B. S., Warren R. H., Elders M. J. Somatomedin activity in cystic fibrosis and reserpinized rats: possible explanation for growth retardation. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1980 May-Jun;10(3):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel R. A., Westaby D., Javaid A., Kavani J., Meire H. B., Lombard M. G., Wise A., Williams R., Hodson M. E. Liver disease and bile duct abnormalities in adults with cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1989 Dec 16;2(8677):1422–1425. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen P. S., Kastrup K. W. Somatomedin in cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Sep;72(5):757–758. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Landon C., Lewiston N., Nagashima R., Hintz R. L. Demonstration of normal plasma somatomedin concentrations in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1981 Aug;99(2):252–254. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80467-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Brandt N. J., Skovby F. Screening for carriers of cystic fibrosis among pregnant women: a pilot study. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(3):239–244. doi: 10.1159/000472417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard M. S., Minuk G. Y., Bhaumick B., Bala R. M. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in liver disease: differential changes of IGF-I and IGF-II. Clin Invest Med. 1987 Mar;10(2):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. G., Westaby D., Tanner M. S., Mowat A. P. Liver and biliary problems in cystic fibrosis. Br Med Bull. 1992 Oct;48(4):877–892. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


