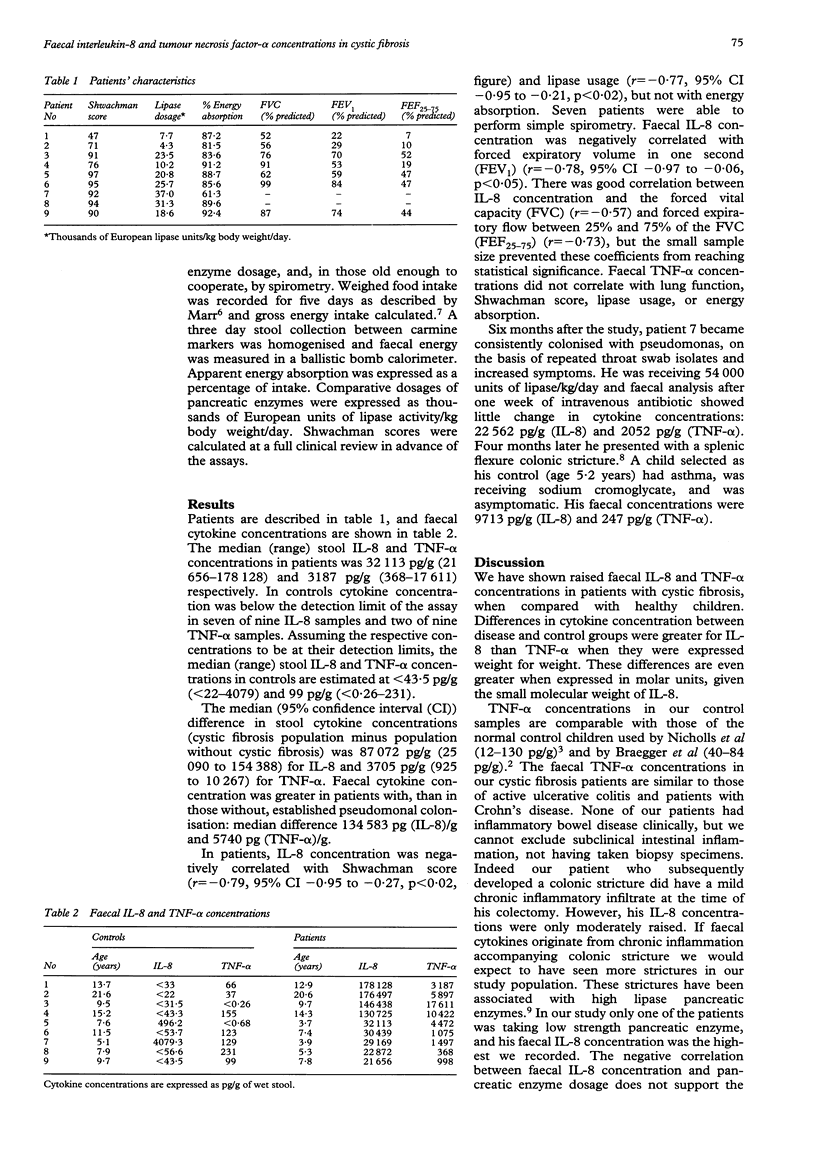
Abstract
Interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) concentrations were measured in faecal samples from nine patients with cystic fibrosis and nine healthy age matched controls. The patients were assessed with Shwachman score, apparent energy absorption, pancreatic enzyme dosage, simple spirometry, and presence of pseudomonal colonisation. Median (range) wet stool IL-8 and TNF-alpha concentrations in patients were 32,113 pg/g (21,656-178,128) and 3187 pg/g (368-17,611) respectively, compared with < 43.5 pg (IL-8)/g (< 22-4079) and 99 pg (TNF-alpha)/g (< 0.26-231) in controls. IL-8 concentration was negatively correlated with Shwachman score (r = -0.79) and pancreatic enzyme dosage (r = -0.77), but not with energy absorption. Seven patients were mature enough to cooperate with spirometry. Their IL-8 concentrations correlated with percentage predicted forced expiratory volume in one second (r = -0.78). IL-8 concentration was greater in four patients with, than five without, established pseudomonal colonisation: median difference 134,583 pg/g. TNF-alpha concentration was not correlated with measures of disease severity. Faecal IL-8 concentration might reflect the severity of pulmonary inflammation in cystic fibrosis and could provide an easily obtainable marker of disease activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braegger C. P., Nicholls S., Murch S. H., Stephens S., MacDonald T. T. Tumour necrosis factor alpha in stool as a marker of intestinal inflammation. Lancet. 1992 Jan 11;339(8785):89–91. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90999-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briars G. L., Griffiths D. M., Moore I. E., Williams P. H., Johnson K., Rolles C. J. High-strength pancreatic enzymes. Lancet. 1994 Mar 5;343(8897):600–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean T. P., Dai Y., Shute J. K., Church M. K., Warner J. O. Interleukin-8 concentrations are elevated in bronchoalveolar lavage, sputum, and sera of children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res. 1993 Aug;34(2):159–161. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199308000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greally P., Hussein M. J., Cook A. J., Sampson A. P., Piper P. J., Price J. F. Sputum tumour necrosis factor-alpha and leukotriene concentrations in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Mar;68(3):389–392. doi: 10.1136/adc.68.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Standiford T., Kasahara K., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 (IL-8): the major neutrophil chemotactic factor in the lung. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;17(1):17–23. doi: 10.3109/01902149109063278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. L., Wootton S. A., Bond S. A., Jackson A. A. Energy content of stools in normal healthy controls and patients with cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Apr;66(4):495–500. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls S., Stephens S., Braegger C. P., Walker-Smith J. A., MacDonald T. T. Cytokines in stools of children with inflammatory bowel disease or infective diarrhoea. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Aug;46(8):757–760. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.8.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Bird G., Koskinas J., Portmann B., Ceska M., Lindley I., Williams R. Circulating and tissue levels of the neutrophil chemotaxin interleukin-8 are elevated in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis, and tissue levels correlate with neutrophil infiltration. Hepatology. 1993 Jul;18(1):41–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth R. L., van Velzen D., Smyth A. R., Lloyd D. A., Heaf D. P. Strictures of ascending colon in cystic fibrosis and high-strength pancreatic enzymes. Lancet. 1994 Jan 8;343(8889):85–86. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90817-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva D. G., Mendis L. N., Sheron N., Alexander G. J., Candy D. C., Chart H., Rowe B. Concentrations of interleukin 6 and tumour necrosis factor in serum and stools of children with Shigella dysenteriae 1 infection. Gut. 1993 Feb;34(2):194–198. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



