Abstract
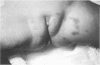
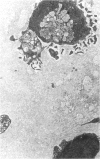
Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis is a rare disorder characterised by multiple subcutaneous tumours, gum hypertrophy, muscle weakness, and flexion contractures of the large joints. Histology shows an abundance of a homogenous, amorphous, acidophilic extracellular matrix in which spindle shaped cells are embedded forming minute streaks. It has been previously suggested that collagen abnormalities may be involved. A 14 month old girl with this syndrome is described in whom postmortem western blot studies were performed. These studies revealed an absent pro-alpha 2(I) chain and an absent collagen type III chain in skin but not in the other organs examined.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsh G. S., Byers P. H. Reduced secretion of structurally abnormal type I procollagen in a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., David K. E., Byers P. H. Type I osteogenesis imperfecta: a nonfunctional allele for pro alpha 1 (I) chains of type I procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3838–3842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Shapiro J. R., Rowe D. W., David K. E., Holbrook K. A. Abnormal alpha 2-chain in type I collagen from a patient with a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):689–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI110815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Siegel R. C., Peterson K. E., Rowe D. W., Holbrook K. A., Smith L. T., Chang Y. H., Fu J. C. Marfan syndrome: abnormal alpha 2 chain in type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7745–7749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay A. Y., Ferguson S. D., Holt P. J. Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1983 May;108(5):609–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb01065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano Y., Horiki M., Aoki T., Sagami S. Two cases of juvenile hyalin fibromatosis. Some histological, electron microscopic, and tissue culture observations. Arch Dermatol. 1972 Dec;106(6):877–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratochwil K., von der Mark K., Kollar E. J., Jaenisch R., Mooslehner K., Schwarz M., Haase K., Gmachl I., Harbers K. Retrovirus-induced insertional mutation in Mov13 mice affects collagen I expression in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90795-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihlajaniemi T., Dickson L. A., Pope F. M., Korhonen V. R., Nicholls A., Prockop D. J., Myers J. C. Osteogenesis imperfecta: cloning of a pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene with a frameshift mutation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):12941–12944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I. Heritable diseases of collagen. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):376–386. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Arai K., Ono M., Yamaguchi T., Furuta S., Nagai Y. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. A variant characterized by the deficiency of pro alpha 2 chain of type I procollagen. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Jan;123(1):76–79. doi: 10.1001/archderm.123.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B., Tuderman L., Peltonen L., Martin G. R., McKusick V. A., Prockop D. J. Evidence for a structural mutation of procollagen type I in a patient with the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8887–8893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESSNER J. F., Jr The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:440–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. J., Prockop D. J. Synthesis and processing of a type I procollagen containing shortened pro-alpha 1(I) chains by fibroblasts from a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woyke S., Domagala W., Olszewski W. Ultrastructure of a fibromatosis hyalinica multiplex juvenilis. Cancer. 1970 Nov;26(5):1157–1168. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197011)26:5<1157::aid-cncr2820260528>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W. J., Pihlajaniemi T., Myers J., Kelly T. E., Prockop D. J. Synthesis of a shortened pro-alpha 2(I) chain and decreased synthesis of pro-alpha 2(I) chains in a proband with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7721–7728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]