Abstract
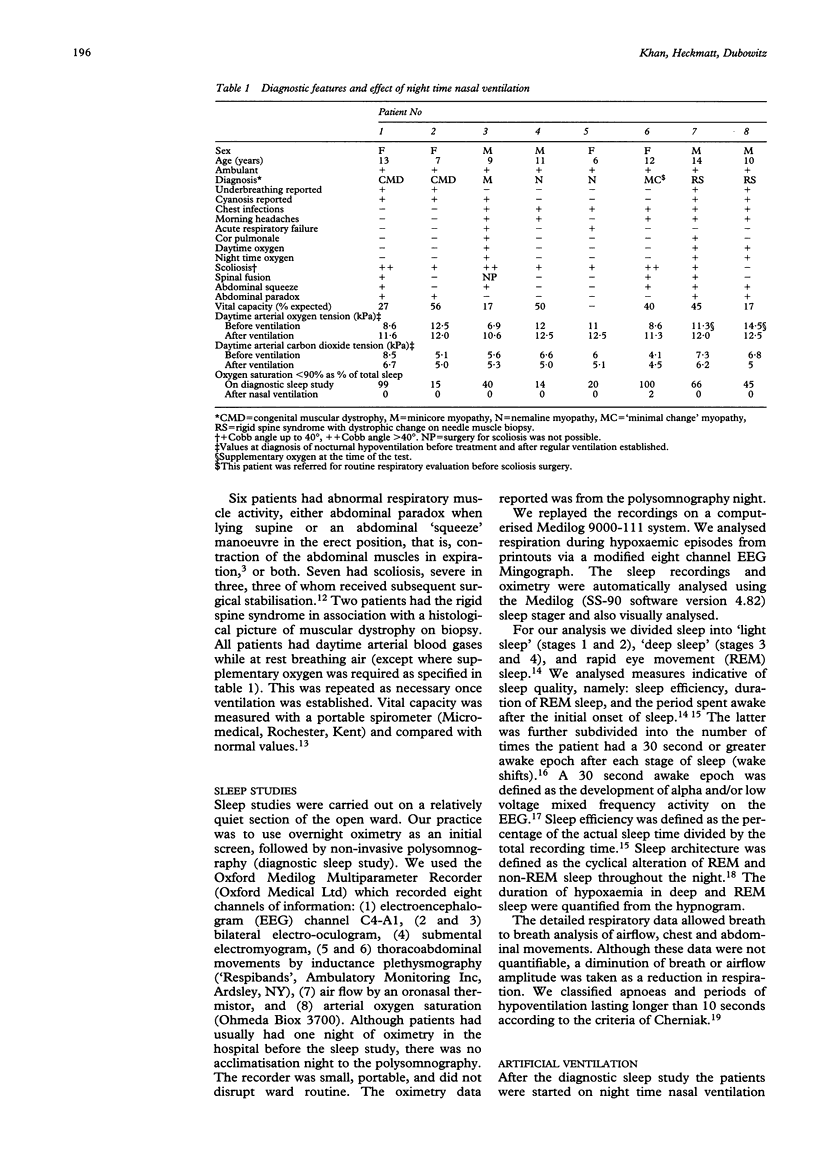
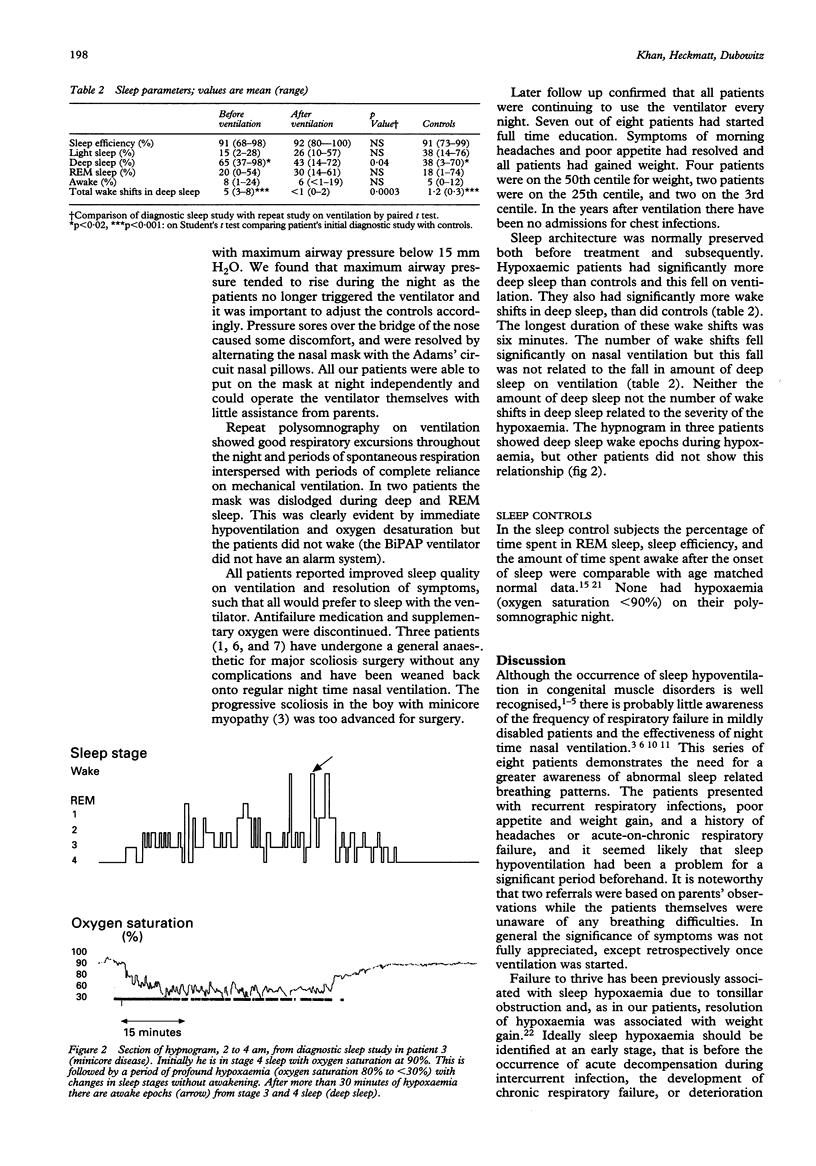
Eight ambulant children aged 6-13 years, four with congenital myopathy, two with congenital muscular dystrophy and two with the rigid spine syndrome, presented with recurrent chest infections, morning headaches, shallow breathing at night, or respiratory failure. Polysomnography confirmed the presence of nocturnal hypoxaemia with oxygen saturation on average less than 90% for 49% of sleep and less than 80% for 19% of sleep accompanied with severe hypoventilation. Additionally there was sleep disturbance characterised by an increased number of wake epochs from deep sleep (in comparison to 10 non-hypoxaemic subjects). The severity of sleep hypoxaemia did not correlate with symptoms. Treatment with night time nasal ventilation was started and repeat polysomnography showed normal overnight oxygen saturation and a reduced number of wake epochs during deep sleep. It is important to be vigilant for sleep hypoventilation in these patients and sleep studies should be part of the routine respiratory evaluation. Treatment with nasal ventilation is effective in reversing the nocturnal respiratory failure without significant disturbance to life style.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avital A., Steljes D. G., Pasterkamp H., Kryger M., Sanchez I., Chernick V. Sleep quality in children with asthma treated with theophylline or cromolyn sodium. J Pediatr. 1991 Dec;119(6):979–984. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. R., Alba A. S. Management of chronic alveolar hypoventilation by nasal ventilation. Chest. 1990 Jan;97(1):52–57. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. R., Alba A., Mosher R., Delaubier A. Intermittent positive pressure ventilation via nasal access in the management of respiratory insufficiency. Chest. 1987 Jul;92(1):168–170. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.1.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. L. Sleep apnea disorders. Introduction to sleep and sleep disorders. Med Clin North Am. 1985 Nov;69(6):1123–1152. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30979-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bye P. T., Ellis E. R., Issa F. G., Donnelly P. M., Sullivan C. E. Respiratory failure and sleep in neuromuscular disease. Thorax. 1990 Apr;45(4):241–247. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.4.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll N., Branthwaite M. A. Control of nocturnal hypoventilation by nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation. Thorax. 1988 May;43(5):349–353. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.5.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carskadon M. A., Brown E. D., Dement W. C. Sleep fragmentation in the elderly: relationship to daytime sleep tendency. Neurobiol Aging. 1982 Winter;3(4):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(82)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherniack N. S. Respiratory dysrhythmias during sleep. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 6;305(6):325–330. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108063050606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coble P. A., Kupfer D. J., Taska L. S., Kane J. EEG sleep of normal healthy children. Part I: Findings using standard measurement methods. Sleep. 1984;7(4):289–303. doi: 10.1093/sleep/7.4.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coccagna G., Mantovani M., Parchi C., Mironi F., Lugaresi E. Alveolar hypoventilation and hyperosmnia in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Oct;38(10):977–984. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.10.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagan Y., Lavie P., Bleich A. Elevated awakening thresholds in sleep stage 3-4 in war-related post-traumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 1991 Sep 15;30(6):618–622. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(91)90031-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J., Goldman M., Loh L., Casson M. Diaphragm function and alveolar hypoventilation. Q J Med. 1976 Jan;45(177):87–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis E. R., Bye P. T., Bruderer J. W., Sullivan C. E. Treatment of respiratory failure during sleep in patients with neuromuscular disease. Positive-pressure ventilation through a nose mask. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):148–152. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis E. R., McCauley V. B., Mellis C., Sullivan C. E. Treatment of alveolar hypoventilation in a six-year-old girl with intermittent positive pressure ventilation through a nose mask. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jul;136(1):188–191. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.1.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleetham J., West P., Mezon B., Conway W., Roth T., Kryger M. Sleep, arousals, and oxygen desaturation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The effect of oxygen therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Sep;126(3):429–433. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.3.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin J. J., Cooper B. G., Griffiths C. J., Walls T. J., Veale D., Stone T. N., Osselton J. W., Hudgson P., Gibson G. J. Breathing during sleep in patients with myotonic dystrophy and non-myotonic respiratory muscle weakness. Q J Med. 1991 Jan;78(285):21–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey S., Kamburoff P. L., Nairn J. R. Spirometry, lung volumes and airway resistance in normal children aged 5 to 18 years. Br J Dis Chest. 1970 Jan;64(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(70)80045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmatt J. Z., Loh L., Dubowitz V. Nocturnal hypoventilation in children with nonprogressive neuromuscular disease. Pediatrics. 1989 Feb;83(2):250–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata A., Suga M., Miyamoto K., Hirose K., Tanabe H. Rigid spine syndrome and nocturnal alveolar hypoventilation. Intern Med. 1993 Aug;32(8):638–640. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.32.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerby G. R., Mayer L. S., Pingleton S. K. Nocturnal positive pressure ventilation via nasal mask. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Mar;135(3):738–740. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.3.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan Y., Heckmatt J. Z. Obstructive apnoeas in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Thorax. 1994 Feb;49(2):157–161. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryger M. H., Steljes D. G., Yee W. C., Mate E., Smith S. A., Mahowald M. Central sleep apnoea in congenital muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Aug;54(8):710–712. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.8.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B., Roehrs T., Stepanski E., Zorick F., Roth T. Fragmenting sleep diminishes its recuperative value. Sleep. 1987 Dec;10(6):590–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luque E. R. Segmental spinal instrumentation for correction of scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 Mar;(163):192–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maayan C., Springer C., Armon Y., Bar-Yishay E., Shapira Y., Godfrey S. Nemaline myopathy as a cause of sleep hypoventilation. Pediatrics. 1986 Mar;77(3):390–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary J., King R., Leblanc M., Moss R., Liebhaber M., Lewiston N. Cuirass ventilation in childhood neuromuscular disease. J Pediatr. 1979 Mar;94(3):419–421. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80588-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palm L., Persson E., Elmqvist D., Blennow G. Sleep and wakefulness in normal preadolescent children. Sleep. 1989 Aug;12(4):299–308. doi: 10.1093/sleep/12.4.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D. J., Santiago T. V., Daniele R. P., Schall B., Edelman N. H. Blunted respiratory drive in congenital myopathy. Am J Med. 1977 Sep;63(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. E., Calverley P. M., Edwards R. H. Hypoxemia during sleep in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):884–888. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Thomas G., Warley A. R., Williams P., Freeland A. Effect of adenotonsillectomy on nocturnal hypoxaemia, sleep disturbance, and symptoms in snoring children. Lancet. 1990 Feb 3;335(8684):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90068-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan C. E., Issa F. G., Berthon-Jones M., Eves L. Reversal of obstructive sleep apnoea by continuous positive airway pressure applied through the nares. Lancet. 1981 Apr 18;1(8225):862–865. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


