Abstract
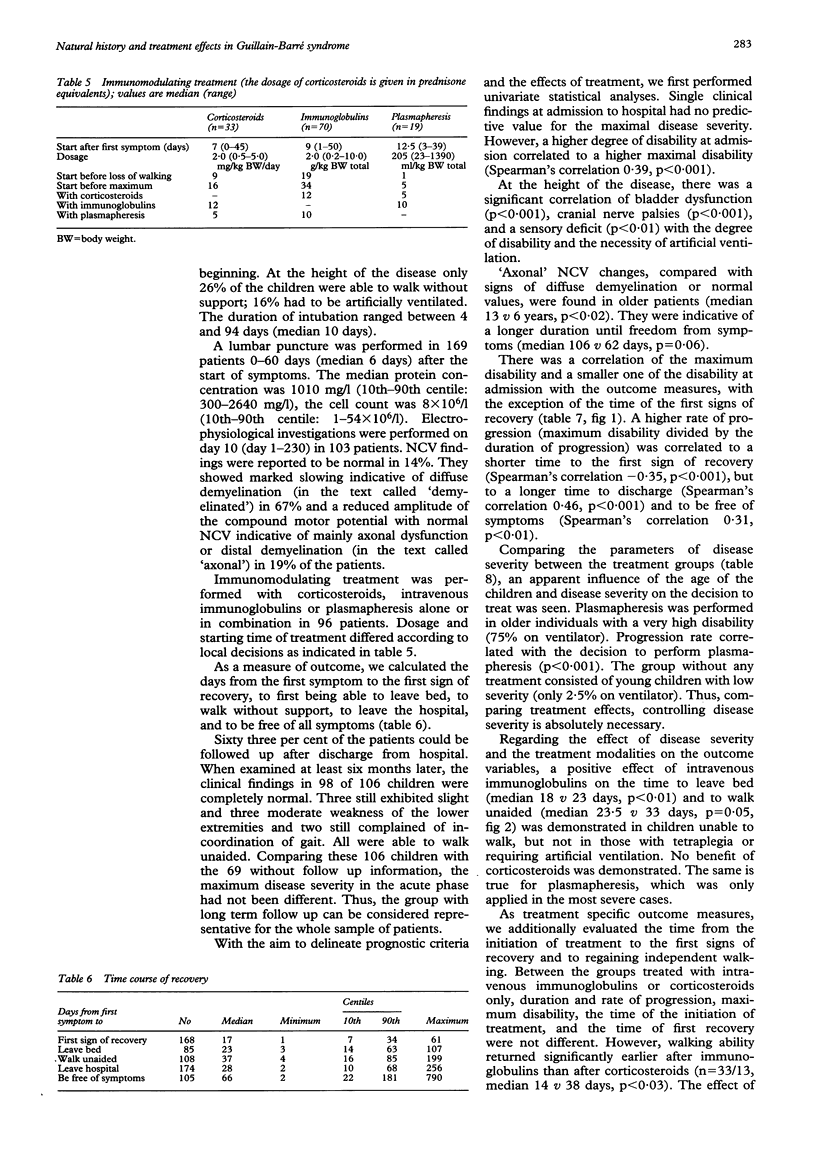
A retrospective multicentre study was performed to investigate the natural history and treatment effects in childhood Guillain-Barré syndrome in a large number of patients. Structured questionnaires were sent to 155 paediatric hospitals for details of patients who conformed to internationally accepted diagnostic criteria and who were treated from spring 1989 to summer 1994. Sixty nine hospitals reported data of 175 patients aged 11 months to 17.7 years. At the height of the disease 26% of the patients remained able to walk, but 16% had to be artificially ventilated. The median time from onset of symptoms to first recovery was 17 days, to walk unaided 37 days, and to be free of symptoms 66 days. There was a large group with a benign and a smaller one with a more protracted course. At long term follow up, 98/106 patients were free of symptoms and the remainder were able to walk unaided. Maximum disability grade was the most powerful prognostic factor. In children unable to walk but not yet tetraplegic, immunoglobulins were able to accelerate recovery. Corticosteroids were less potent. Plasmapheresis could not be evaluated because it was administered only in the most severe cases. The natural history of Guillain-Barré syndrome in children is extremely variable and more benign than in adults. Treatment with immunoglobulins should be considered in patients unable to walk. Corticosteroids are not as effective and should be withheld except when, in protracted courses, suspicion of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy arises.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa Y., Yoshimura M., Kobayashi S., Ichihashi K., Miyao M., Momoi M. Y., Yanagisawa M. The use of intravenous immunoglobulin in Miller Fisher syndrome. Brain Dev. 1993 May-Jun;15(3):231–233. doi: 10.1016/0387-7604(93)90071-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbury A. K., Cornblath D. R. Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1990;27 (Suppl):S21–S24. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos A. P., van der Meché F. G., Witsenburg M., van der Voort E. Experiences with Guillain-Barré syndrome in a pediatric intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 1987;13(5):328–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00255788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw D. Y., Jones H. R., Jr Guillain-Barré syndrome in children: clinical course, electrodiagnosis, and prognosis. Muscle Nerve. 1992 Apr;15(4):500–506. doi: 10.1002/mus.880150415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe D. M., McMenamin J. B., O'Donohoe N. V. Prognosis in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Jul;62(7):733–735. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.7.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro L. H., Ropper A. H. Human immune globulin infusion in Guillain-Barré syndrome: worsening during and after treatment. Neurology. 1993 May;43(5):1034–1036. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.5.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli M., Assanta N., Chiaravalloti G., Rocopou C., Caiulo V. A. L'impiego delle immunoglobuline per via endovenosa nella sindrome di Guillain-Barré. Minerva Pediatr. 1992 May;44(5):237–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comenzo R. L., Malachowski M. E., Meissner H. C., Fulton D. R., Berkman E. M. Immune hemolysis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and serum sickness after large doses of immune globulin given intravenously for Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 1992 Jun;120(6):926–928. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81964-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantopoulos A., Langona E. Intravenous immune globulin in children with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neuropediatrics. 1994 Jun;25(3):165–165. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1073017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornblath D. R., Hughes R. A. Guillain-Barré syndrome: the evolution of therapy. J Neurol. 1994 May;241(6):404–405. doi: 10.1007/BF02033360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakas M. C. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin and serum viscosity: risk of precipitating thromboembolic events. Neurology. 1994 Feb;44(2):223–226. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Sladky J. T. The role of plasmapheresis in childhood Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jul;28(1):65–69. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gürses N., Uysal S., Cetinkaya F., Işlek I., Kalayci A. G. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in children with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Scand J Infect Dis. 1995;27(3):241–243. doi: 10.3109/00365549509019016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammersjö J. A. Plasma exchange in childhood Guillain-Barré syndrome. Acta Paediatr. 1995 Mar;84(3):355–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1995.tb13646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. E., Rojas L. A., Rosário J. A., Recalde H., Román G. C. Childhood Guillain-Barré syndrome in Paraguay, 1990 to 1991. Ann Neurol. 1994 Dec;36(6):859–863. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Pollard J. D., Harvey G. K., Toyka K. V. Immunopathogenesis and treatment of the Guillain-Barré syndrome--Part II. Muscle Nerve. 1995 Feb;18(2):154–164. doi: 10.1002/mus.880180203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horneff G., Huppertz H. I., Müller K., Voit T., Karch H. Demonstration of Borrelia burgdorferi infection in a child with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Oct;152(10):810–812. doi: 10.1007/BF02073376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung K. L., Wang H. S., Liou W. Y., Mak S. C., Chi C. S., Shen E. Y., Lin M. I., Wang P. J., Shen Y. Z., Chang K. P. Guillain-Barré syndrome in children: a cooperative study in Taiwan. Brain Dev. 1994 May-Jun;16(3):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0387-7604(94)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani D. N., Cornblath D. R., Chaudhry V., Borel C., Hanley D. F. Relapse in Guillain-Barré syndrome after treatment with human immune globulin. Neurology. 1993 May;43(5):872–875. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.5.872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. C., Godwin-Austen R. B., Whiteley A. M. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome: a preliminary open study. J Neurol. 1993 Jan;240(1):51–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00838447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyweg R. P., van der Meché F. G., Loonen M. C., de Jonge J., Knip B. The natural history of the Guillain-Barré syndrome in 18 children and 50 adults. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Jul;52(7):853–856. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.7.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyweg R. P., van der Meché F. G., Meulstee J. Treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome with high-dose gammaglobulin. Neurology. 1988 Oct;38(10):1639–1641. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.10.1639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyweg R. P., van der Meché F. G. Treatment related fluctuations in Guillain-Barré syndrome after high-dose immunoglobulins or plasma-exchange. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Nov;54(11):957–960. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.11.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korinthenberg R., Sauer M. Das Guillain-Barré-Syndrom im Kindesalter. Verlaufscharakteristik und therapeutische Möglichkeiten. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1992 Nov;140(11):792–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee B., Jarjour I. T. Single-dose intravenous immune globulin for treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1994 Jan 1;51(1):97–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. K., Howard R. S., Hirsch N. P., Miller D. H. Intravenous immunoglobulin versus plasma exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology. 1993 Dec;43(12):2729–2731. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.12.2729-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notarangelo L. D., Duse M., Tiberti S., Guarneri B., Brunori A., Negrini A., Ugazio A. G. Intravenous immunoglobulin in two children with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Apr;152(4):372–374. doi: 10.1007/BF01956757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. J. Subacute demyelinating polyneuropathy responding to corticosteroid treatment. Arch Neurol. 1978 Aug;35(8):509–516. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500320029007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rantala H., Cherry J. D., Shields W. D., Uhari M. Epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome in children: relationship of oral polio vaccine administration to occurrence. J Pediatr. 1994 Feb;124(2):220–223. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(94)70307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rantala H., Uhari M., Niemelä M. Occurrence, clinical manifestations, and prognosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Jun;66(6):706–709. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.6.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raphael J. C., Chastang C., Chevret S., Gajdos P. Intravenous immune globulin versus plasma exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 10;327(11):816–817. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209103271117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropper A. H. The Guillain-Barré syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 23;326(17):1130–1136. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204233261706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakihara Y., Kamoshita S. Age-associated changes in the symptomatology of Guillain-Barré syndrome in children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1991 Jul;33(7):611–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1991.tb14931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchardt V., Hotz M., Hund E., Sun S., Heitmann R., Hacke W. Erfahrungen mit hochdosiertem Immunglobulin G bei neuromuskulären Erkrankungen. Nervenarzt. 1993 Feb;64(2):98–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahar E., Murphy E. G., Roifman C. M. Benefit of intravenously administered immune serum globulin in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Pediatr. 1990 Jan;116(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemes H., Emerich R., Merlin M., Reitter B. Die akute Polyradikuloneuritis (Guillain-Barré-Syndrom) im Kindesalter. Klin Padiatr. 1983 Jan-Feb;195(1):38–44. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1034038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E., Hajinazarian M., Bay W., Neff J., Mendell J. R. Acute renal failure resulting from intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Arch Neurol. 1993 Feb;50(2):137–139. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1993.00540020015010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vajsar J., Sloane A., Wood E., Murphy E. G. Plasmapheresis vs intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in childhood Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1994 Nov;148(11):1210–1212. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1994.02170110096019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallée L., Dulac O., Nuyts J. P., Leclerc F., Vamecq J. Intravenous immune globulin is also an efficient therapy of acute Guillain-Barré syndrome in affected children. Neuropediatrics. 1993 Aug;24(4):235–236. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. D., Gibson J., Joshua D. E., Kronenberg H. Aseptic meningitis associated with high dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Mar;54(3):275–276. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer J. B., Hughes R. A., Osmond C. A prospective study of acute idiopathic neuropathy. I. Clinical features and their prognostic value. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 May;51(5):605–612. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.5.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Qudah A. A. Immunoglobulins in the treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome in early childhood. J Child Neurol. 1994 Apr;9(2):178–180. doi: 10.1177/088307389400900215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meché F. G., Schmitz P. I. A randomized trial comparing intravenous immune globulin and plasma exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Dutch Guillain-Barré Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 23;326(17):1123–1129. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204233261705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meché F. G. The Guillain-Barré syndrome: plasma exchange or immunoglobulins intravenously. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Nov;57 (Suppl):33–34. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.suppl.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


