Abstract
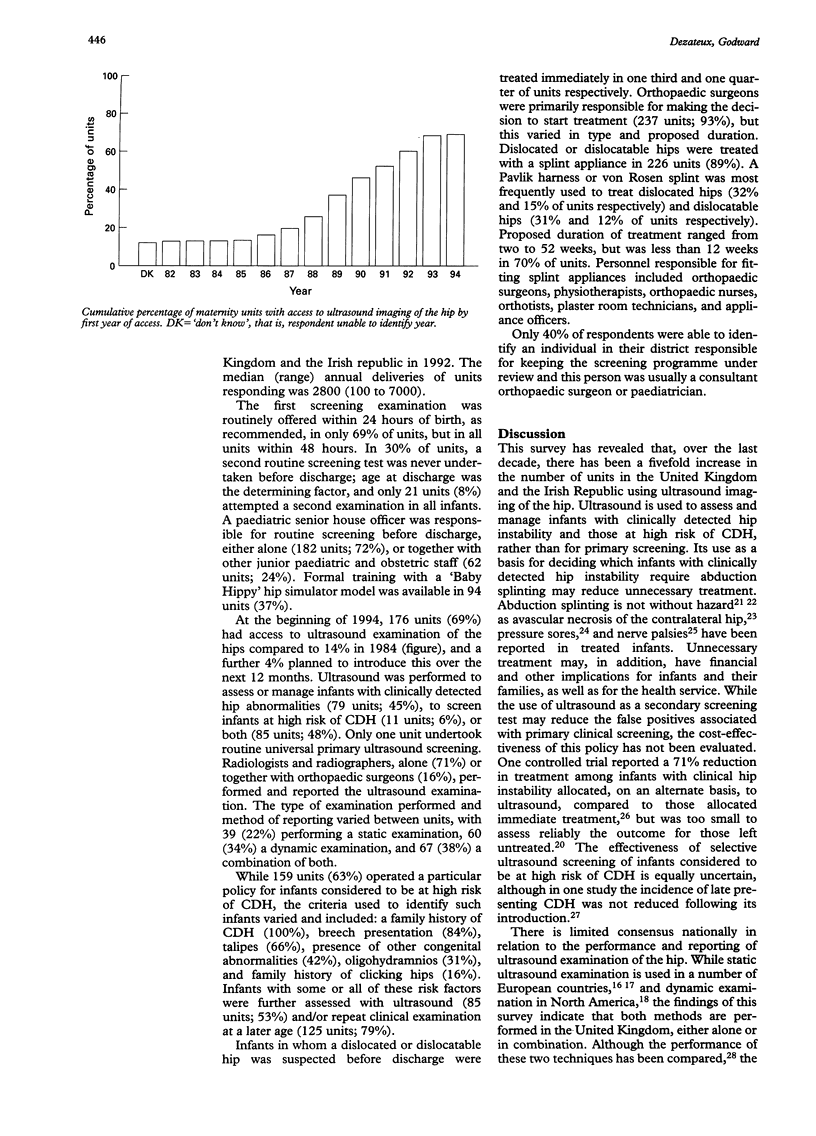
OBJECTIVE: To identify current screening and management practices for congenital dislocation of the hip (CDH), and determine the extent to which ultrasound imaging of the hips is practised throughout the United Kingdom and the Irish Republic. METHODS: Postal questionnaire to paediatricians responsible for the routine neonatal care of infants in all maternity units in the UK and the Irish Republic. RESULTS: Questionnaires were returned for 254 maternity units (92% response rate). By 1994, 69% of maternity units had access to ultrasound imaging of the hips, compared to 14% in 1984. Ultrasound imaging of the hip was not used for universal primary screening, but in 93% of units was undertaken for further assessment of infants with clinically detected hip instability or those identified as being at high risk of CDH, or both. Clinical screening of newborn infants was performed by junior paediatricians, but training with a 'Baby Hippy' hip simulator model was provided in only 37% of units. Treatment of clinically detected hip instability, initiated by an orthopaedic surgeon in 93% of units, varied widely in type and duration. CONCLUSIONS: Ultrasound imaging of the hip is increasingly used in the UK for secondary, rather than primary, screening. Current recommendations are implemented to a variable extent nationally, and the existing wide variation in screening and management for CDH reflects a lack of research evidence to support current screening practices. The effectiveness of screening for CDH needs to be established.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennet G. C. Screening for congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992 Sep;74(5):643–644. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.74B5.1527106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard A. A., O'Hara J. N., Bazin S., Humby B., Jarrett R., Dwyer N. S. An improved screening system for the early detection of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1987 May-Jun;7(3):277–282. doi: 10.1097/01241398-198705000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialik V., Fishman J., Katzir J., Zeltzer M. Clinical assessment of hip instability in the newborn by an orthopedic surgeon and a pediatrician. J Pediatr Orthop. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):703–705. doi: 10.1097/01241398-198611000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeree N. R., Clarke N. M. Ultrasound imaging and secondary screening for congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994 Jul;76(4):525–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J., Wetherill M., Benson M. K. Splintage for congenital dislocation of the hip. Is it safe and reliable? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987 Mar;69(2):257–263. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.69B2.3818757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartlidge P. H. Routine discharge examination of babies: is it necessary? Arch Dis Child. 1992 Dec;67(12):1421–1422. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.12.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. M., Clegg J., Al-Chalabi A. N. Ultrasound screening of hips at risk for CDH. Failure to reduce the incidence of late cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989 Jan;71(1):9–12. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.71B1.2644290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezateux C., Godward S. Evaluating the national screening programme for congenital dislocation of the hip. J Med Screen. 1995;2(4):200–206. doi: 10.1177/096914139500200406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias J. J., Thomas I. H., Lamont A. C., Mody B. S., Thompson J. R. The reliability of ultrasonographic assessment of neonatal hips. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993 May;75(3):479–482. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.75B3.8496227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Evans R. E., Thearle M. J., Griffiths H. E., Witherow P. J. Congenital dislocation of the hip: early and late diagnosis and management compared. Arch Dis Child. 1985 May;60(5):407–414. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.5.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engesaeter L. B., Wilson D. J., Nag D., Benson M. K. Ultrasound and congenital dislocation of the hip. The importance of dynamic assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990 Mar;72(2):197–201. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.72B2.2179221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddian N. J., Gardiner J. C. Screening for congenital dislocation of the hip by physiotherapists. Results of a ten-year study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994 May;76(3):458–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner H. M., Dunn P. M. Controlled trial of immediate splinting versus ultrasonographic surveillance in congenitally dislocatable hips. Lancet. 1990 Dec 22;336(8730):1553–1556. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93318-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gore D. R. Iatrogenic avascular necrosis of the hip in young children. A review of six cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974 Apr;56(3):493–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harcke H. T. The role of ultrasound in diagnosis and management of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatr Radiol. 1995;25(3):225–227. doi: 10.1007/BF02021542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B., Madan B. R., Parratt J. R. Polymyxin B sulphate protects cats against the haemodynamic and metabolic effects of E. coli endotoxin. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):701–707. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki K. Treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip by the Pavlik harness. Mechanism of reduction and usage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983 Jul;65(6):760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. A., Beynon D., Littlepage B. N. Audit of an official recommendation on screening for congenital dislocation of the hip. BMJ. 1991 Jun 15;302(6790):1435–1436. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6790.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox E. G., Armstrong E. H., Lancashire R. J. Effectiveness of screening for congenital dislocation of the hip. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1987 Dec;41(4):283–289. doi: 10.1136/jech.41.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikler S. J., Dwyer N. S. Comparison of results of two approaches to hip screening in infants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992 Sep;74(5):701–703. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.74B5.1527116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langkamer V. G., Clarke N. M., Witherow P. Complications of splintage in congenital dislocation of the hip. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Nov;66(11):1322–1325. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.11.1322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leck I. An epidemiological assessment of neonatal screening for dislocation of the hip. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1986 Jan;20(1):56–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennox I. A., McLauchlan J., Murali R. Failures of screening and management of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993 Jan;75(1):72–75. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.75B1.8421040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane A. Screening for congenital dislocation of the hip. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Apr 25;294(6579):1047–1047. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6579.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mubarak S., Garfin S., Vance R., McKinnon B., Sutherland D. Pitfalls in the use of the Pavlik harness for treatment of congenital dysplasia, subluxation, and dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981 Oct;63(8):1239–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmén K. Prevention of congenital dislocation of the hip. The Swedish experience of neonatal treatment of hip joint instability. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1984;208:1–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin D. M. How successful is screening for congenital disease of the hip? Am J Public Health. 1981 Dec;71(12):1378–1383. doi: 10.2105/ajph.71.12.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson C. C., Kernohan W. G., Mollan R. A., Haugh P. E., Trainor B. P. High incidence of congenital dislocation of the hip in Northern Ireland. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 1995 Jan;9(1):90–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3016.1995.tb00121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberton N. R. Screening for congenital hip dislocation. Lancet. 1984 Apr 21;1(8382):909–910. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91370-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendahl K., Aslaksen A., Lie R. T., Markestad T. Reliability of ultrasound in the early diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatr Radiol. 1995;25(3):219–224. doi: 10.1007/BF02021541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendahl K., Markestad T., Lie R. T. Ultrasound screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip in the neonate: the effect on treatment rate and prevalence of late cases. Pediatrics. 1994 Jul;94(1):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfridson J., Redlund-Johnell I., Udén A. Why is congenital dislocation of the hip still missed? Analysis of 96,891 infants screened in Malmö 1956-1987. Acta Orthop Scand. 1991 Apr;62(2):87–91. doi: 10.3109/17453679108999228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tönnis D., Storch K., Ulbrich H. Results of newborn screening for CDH with and without sonography and correlation of risk factors. J Pediatr Orthop. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2):145–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Shazly M., Trainor B., Kernohan W. G., Turner I., Haugh P. E., Johnston A. F., Mollan R. A. Reliability of the Barlow and Ortolani tests for neonatal hip instability. J Med Screen. 1994 Jul;1(3):165–168. doi: 10.1177/096914139400100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


