Abstract
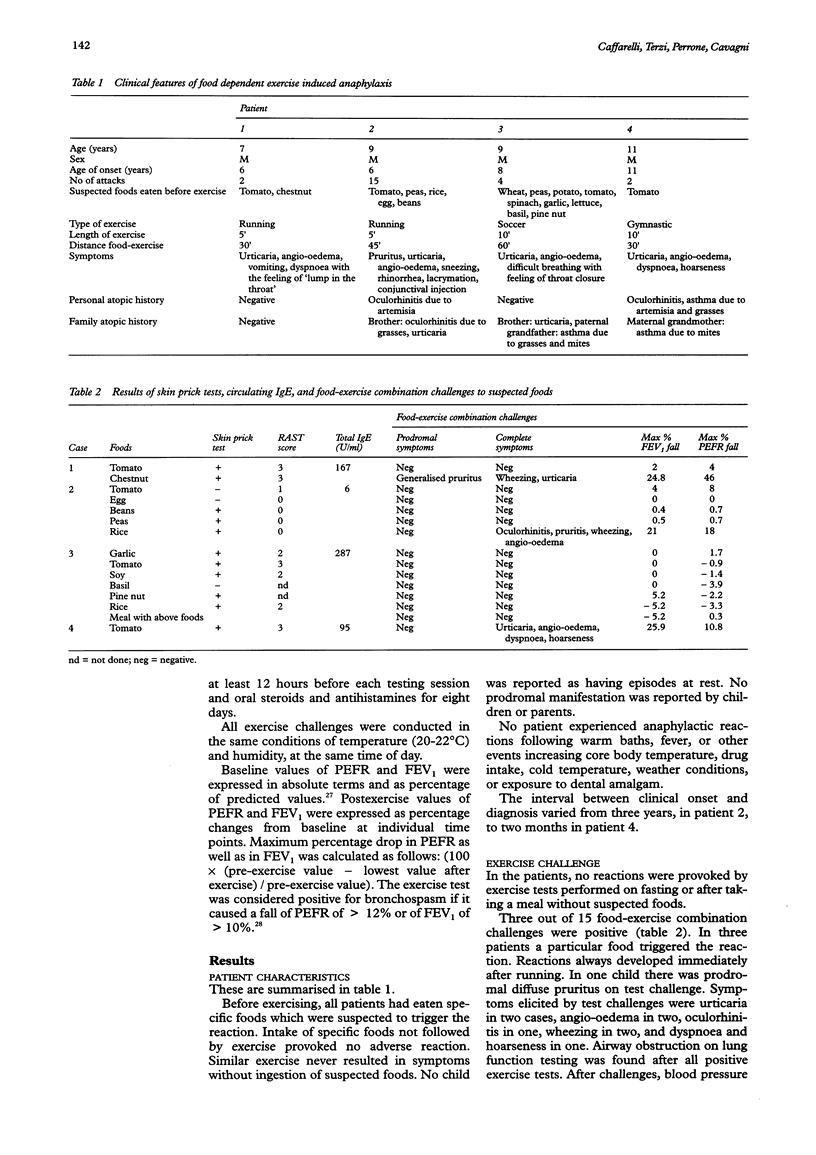
Four children under 12 years of age with food dependent, exercise induced anaphylaxis (EIAn) were investigated. These children and five controls performed exercise challenges when fasting and one hour after a meal without food suspected to predispose to the reaction. Patients then performed exercise tests after intake of each suspected food. Three out of 15 food-exercise combination challenges were positive, but no reactions were provoked after exercise without prior intake of suspected foods. Patients underwent skin prick tests to foods and serum total and specific IgE antibodies were measured. Skin prick test results were positive and RAST results were positive in two of three instances. In case 3, food-exercise combination challenges did not provoke any clinical reaction. The diagnosis of food dependent EIAn should be considered in young children with EIAn of unknown origin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aas K. Some variables in skin prick testing. Allergy. 1980 Apr;35(3):250–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1980.tb01763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akutsu I., Motojima S., Ikeda Y., Fukuda T., Ikemori R., Makino S. [Three cases of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis]. Arerugi. 1989 Mar;38(3):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armentia A., Martin-Santos J. M., Blanco M., Carretero L., Puyo M., Barber D. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to grain flours. Ann Allergy. 1990 Aug;65(2):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Añbarro B., Domínguez C., Díaz J. M., Martín M. F., García-Ara M. C., Boyano M. T., Ojeda J. A. Apple-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Allergy. 1994 Jul;49(6):481–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1994.tb00844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchbinder E. M., Bloch K. J., Moss J., Guiney T. E. Food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis. JAMA. 1983 Dec 2;250(21):2973–2974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casale T. B., Keahey T. M., Kaliner M. Exercise-induced anaphylactic syndromes. Insights into diagnostic and pathophysiologic features. JAMA. 1986 Apr 18;255(15):2049–2053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cropp G. J. The exercise bronchoprovocation test: standardization of procedures and evaluation of response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Dec;64(6 Pt 2):627–633. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debavelaere C., De Blic J., Bodemer C., Teillac D., Paupe J., Scheinmann P. Syndrome d'anaphylaxie induite par l'exercice. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1989 Apr;46(4):281–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreborg S., Foucard T. Allergy to apple, carrot and potato in children with birch pollen allergy. Allergy. 1983 Apr;38(3):167–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1983.tb01602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukutomi O., Kondo N., Agata H., Shinoda S., Shinbara M., Orii T. Abnormal responses of the autonomic nervous system in food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Ann Allergy. 1992 May;68(5):438–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juji F., Suko M. Effectiveness of disodium cromoglycate in food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a case report. Ann Allergy. 1994 May;72(5):452–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsunuma T., Iikura Y., Nagakura T., Saitoh H., Akimoto K., Akasawa A., Kindaichi S. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: improvement after removal of amalgam in dental caries. Ann Allergy. 1990 May;64(5):472–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattan M., Keens T. G., Mellis C. M., Levison H. The response to exercise in normal and asthmatic children. J Pediatr. 1978 May;92(5):718–721. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd J. M., 3rd, Cohen S. H., Sosman A. J., Fink J. N. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Apr;71(4):407–411. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson R. J., Slatin R. C., Lebowitz M. D., Burrows B. The maximal expiratory flow-volume curve. Normal standards, variability, and effects of age. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 May;113(5):587–600. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushimoto H., Aoki T. Masked type I wheat allergy. Relation to exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Arch Dermatol. 1985 Mar;121(3):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J., Lieberman P., Treadwell G., Erffmeyer J. Exercise-induced urticaria, angioedema, and anaphylactoid episodes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Dec;68(6):432–437. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley S., Panush R. S. Familial exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Ann Allergy. 1987 Apr;58(4):257–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín Muñoz F., López Cazaña J. M., Villas F., Contreras J. F., Díaz J. M., Ojeda J. A. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to hazelnut. Allergy. 1994 May;49(5):314–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1994.tb02274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maulitz R. M., Pratt D. S., Schocket A. L. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Jun;63(6):433–434. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil D., Strauss R. H. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis related to food intake. Ann Allergy. 1988 Dec;61(6):440–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novey H. S., Fairshter R. D., Salness K., Simon R. A., Curd J. G. Postprandial exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 May;71(5):498–504. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90468-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki M., Kitani H., Mifune T., Mitsunobu F., Saito S., Asaumi N., Tanizaki Y. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Intern Med. 1992 Aug;31(8):1052–1055. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.31.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., Albergo R. Comparison of results of skin tests, RAST, and double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenges in children with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Jul;74(1):26–33. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro G. G., Pierson W. E., Furukawa C. T., Bierman C. W. A comparison of the effectiveness of free-running and treadmill exercise for assessing exercise-induced bronchospasm in clinical practice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Dec;64(6 Pt 2):609–611. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffer A. L., Soter N. A., McFadden E. R., Jr, Austen K. F. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a distinct form of physical allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Mar;71(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilles S., Schocket A., Milgrom H. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis related to specific foods. J Pediatr. 1995 Oct;127(4):587–589. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(95)70118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



