Abstract
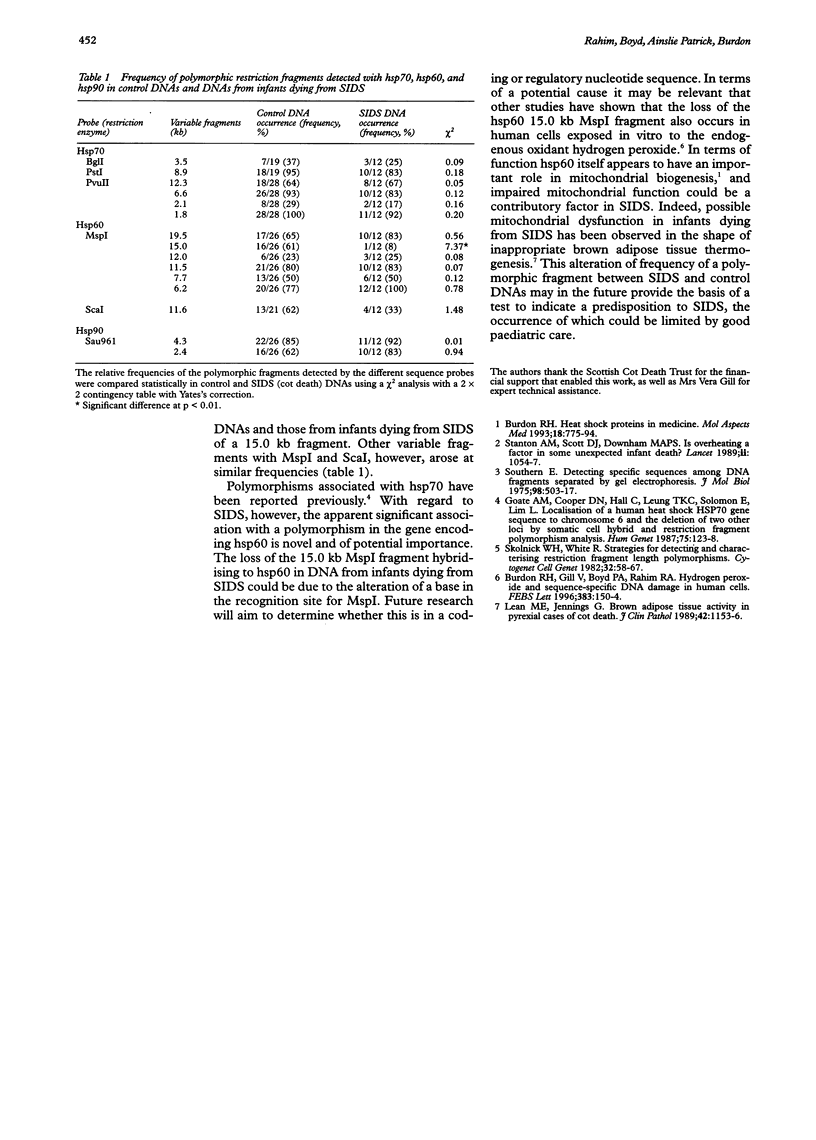
Comparison of the frequency of occurrence of restriction fragment length polymorphisms in control human DNAs and DNAs from infants dying from sudden infant death syndrome has indicated no significant difference in the case of restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with the heat shock protein genes hsp70 and hsp90. A highly significant difference was detected, however, in the case of the specific restriction fragment length polymorphisms detected by an hsp60 gene probe in MspI digests.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burdon R. H., Gill V., Boyd P. A., Rahim R. A. Hydrogen peroxide and sequence-specific DNA damage in human cells. FEBS Lett. 1996 Apr 1;383(3):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A. M., Cooper D. N., Hall C., Leung T. K., Solomon E., Lim L. Localization of a human heat-shock HSP 70 gene sequence to chromosome 6 and detection of two other loci by somatic-cell hybrid and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;75(2):123–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00591072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lean M. E., Jennings G. Brown adipose tissue activity in pyrexial cases of cot death. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Nov;42(11):1153–1156. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.11.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick M. H., White R. Strategies for detecting and characterizing restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP's). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;32(1-4):58–67. doi: 10.1159/000131687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


