Abstract
An animal model for acute multiple sclerosis (ms) is experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (eae). eae is produced by intradermal injection of a protein component of central nervous system (cns) myelin. Ultrastructural studies of eae and of a peripheral nerve analog, experimental allergic neuritis (ean), have revealed an orderly sequence of cellular events leading to the destruction and removal of myelin with sparing of axons (primary demyelination). Acute ms has not been studied electron microscopically, but the ultrastructural similarities between ean and a case of acute Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome, a primary demyelinating disease of the peripheral nervous system, suggest that a similar sequence of events might be found in acute ms. While the pathological findings support a cellmediated or delayed hypersensitivity response, there is also evidence for the pathogenetic role of circulating antibodies. Among such evidence is included the finding that sera from animals with eae and humans with acute ms rapidly produce a reversible block of complex (polysynaptic) electrical activity when applied to cns tissue cultures, which suggests a possible mechanism for transient symptoms in ms. Epidemiological and other studies link ms with a viral cause, although no direct evidence that ms is caused by a virus exists. Viral and immunological mechanisms are not mutually exclusive in considering pathogenetic possibilities for ms, for it can be postulated that a viral infection of the central nervous system acts as a triggering agent for a series of immune responses, including production of a bioelectric blocking antibody and demyelination mediated by sensitized cells, the combination of which ultimately produces the total clinical picture of ms.
Full text
PDF


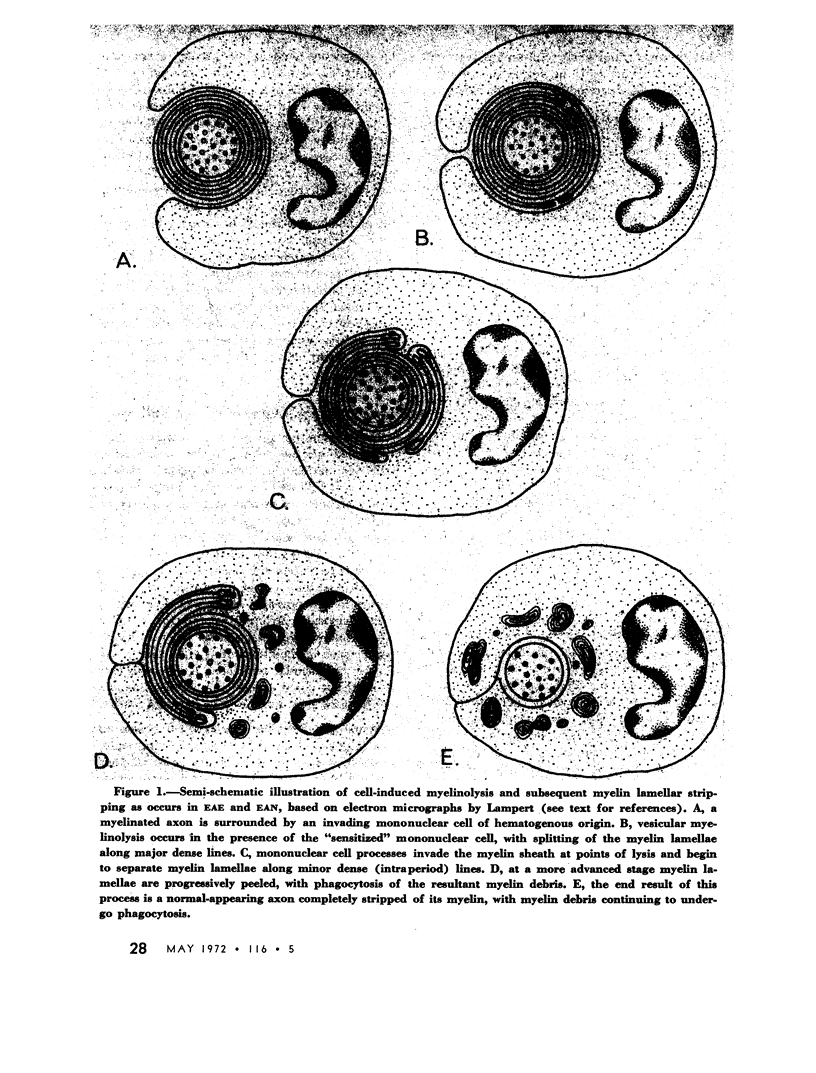





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALTER M., HALPERN L., KURLAND L. T., BORNSTEIN B., LEIBOWITZ U., SILBERSTEIN J. Multiple sclerosis in Israel. Prevalence among immigrants and native inhabitants. Arch Neurol. 1962 Oct;7:253–263. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210040005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALVORD E. C., Jr, KIES M. W. Clinico-pathologic correlations in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. II. Development of an index for quantitative assay of encephalitogenic activity of antigens. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1959 Jul;18(3):447–457. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195907000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALVORD E. C., Jr, MAGEE K. R., KIES M. W., GOLDSTEIN N. P. Clinico-pathologic correlations in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. I. Observations on the early lesion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1959 Jul;18(3):442–446. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195907000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- APPEL S. H., BORNSTEIN M. B. THE APPLICATION OF TISSUE CULTURE TO THE STUDY OF EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. II. SERUM FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR DEMYELINATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 1;119:303–312. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G., Adams R. D. The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):173–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G. Experimental allergic neuritis: a radioautographic study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Oct;27(4):581–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aström K. E., Webster H. D., Arnason B. G. The initial lesion in experimental allergic neuritis. A phase and electron microscopic study. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):469–495. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORNSTEIN M. B. A tissue-culture approach to demyelinative disorders. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1963 Mar;11:197–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORNSTEIN M. B., APPEL S. H. TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES OF DEMYELINATION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:280–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORNSTEIN M. B., CRAIN S. M. FUNCTIONAL STUDIES OF CULTURED BRAIN TISSUES AS RELATED TO "DEMYELINATIVE DISORDERS". Science. 1965 May 28;148(3674):1242–1244. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3674.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfeld H., Atoynatan T. In vitro delayed (cellular) hypersensitivity in multiple sclerosis to central nervous system antigens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(4):361–367. doi: 10.1159/000230364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein M. B., Crain S. M. Lack of correlation between changes in bioelectric functions and myelin in cultured CNS tissues chronically exposed to sera from animals with EAE. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jan;30(1):129–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein M. B., Raine C. S. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Antiserum inhibition of myelination in vitro. Lab Invest. 1970 Nov;23(5):536–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody J. A., Sever J. L., Henson T. E. Virus antibody titers in multiple sclerosis patients, siblings, and controls. JAMA. 1971 May 31;216(9):1441–1446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf J. A., Carels G. Multiple sclerosis: serum factor producing reversible alterations in bioelectric responses. Science. 1966 May 20;152(3725):1066–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3725.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R., Paterson P. Y. In vitro demonstration of cellular sensitivity in allergic encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1161–1171. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean G. The multiple sclerosis problem. Sci Am. 1970 Jul;223(1):40–46. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0770-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Caccam J., Jackson J. J., Westall F. C., Robinson A. B. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: synthesis of disease-inducing site of the basic protein. Science. 1970 Jun 5;168(3936):1220–1223. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3936.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Alpers M. Transmission and passage of experimenal "kuru" to chimpanzees. Science. 1967 Jan 13;155(3759):212–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection as the etiology of spongiform encephalopathy (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease). Science. 1969 Sep 5;165(3897):1023–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3897.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson T. E., Brody J. A., Sever J. L., Dyken M. L., Cannon J. Measles antibody titers in multiple sclerosis patients, siblings, and controls. JAMA. 1970 Mar 23;211(12):1985–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D., Field E. J. Myelotoxicity of serum and spinal fluid in multiple sclerosis: a critical assessment. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 May;2(3):295–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D., Newman S. E. Lymphocyte sensitivity to encephalitogenic factor in guinea pigs with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis as shown by in vitro inhibition of macrophage migration. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(3):237–256. doi: 10.1159/000230116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIES M. W., THOMPSON E. B., ALVORD E. C., Jr THE RELATIONSHIP OF MYELIN PROTEINS TO EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:148–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPERT P., CARPENTER S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON THE VASCULAR PERMEABILITY AND THE MECHANISM OF DEMYELINATION IN EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1965 Jan;24:11–24. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196501000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., WENK E. J. A HYPERACUTE FORM OF ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Jul;47:61–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Experimental spongiform encephalopathy (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease) in chimpanzees. Electron microscopic studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jan;30(1):20–32. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197101000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Kies M. W. Mechanism of demyelination in allergic encephalomyelitis of guinea pigs. An electron microscopic study. Exp Neurol. 1967 Jun;18(2):210–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(67)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W. Mechanism of demyelination in experimental allergic neuritis. Electron microscopic studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Feb;20(2):127–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. Electron microscopic studies on ordinary and hyperacute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1967 Oct 20;9(2):99–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00691436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. Passive transfer of allergic adrenalitis and encephalomyelitis with whole blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):221–222. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Heinze R. G., Kies M. W., Alvord E. C., Jr Antibodies to encephalitogenic basic protein in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Mar;130(3):814–818. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Immunohistochemical study of allergic encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):251–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATERSON P. Y. Transfer of allergic encephalomyelitis in rats by means of lymph node cells. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:119–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y. Immune processes and infectious factors in central nervous system disease. Annu Rev Med. 1969;20:75–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.20.020169.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J., Raine C. S., Wísniewski H. An ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination and remyelination. 3. Chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the central nervous system. Lab Invest. 1969 Dec;21(6):472–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périer O., Grégoire A. Electron microscopic features of multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain. 1965 Dec;88(5):937–952. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.5.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Bornstein M. B. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: a light and electron microscope study of remyelination and "sclerosis" in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Oct;29(4):552–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Bornstein M. B. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: an ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Apr;29(2):177–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. P., Paterson P. Y. Temporal dissociation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis transfer activity and gamma globulin staining of lymphoid cells from sensitized Lewis rats. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1563–1564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Sheremata W. A., Feldman R. G., Kies M. W., David J. R. The Guillain-Barré syndrome and multiple sclerosis. In vitro cellular responses to nervous-tissue antigens. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 15;284(15):803–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104152841501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross L. L., Bornstein M. B. An electron microscopic study of synaptic alterations in cultured mammalian central nervous tissues exposed to serum from animals with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):26–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW C. M., ALVORD E. C., Jr, KAKU J., KIES M. W. CORRELATION OF EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS WITH DELAYED-TYPE SKIN SENSITIVITY TO SPECIFIC HOMOLOGOUS ENCEPHALITOGEN. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:318–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seil F. J., Falk G. A., Kies M. W., Alvord E. C., Jr The in vitro demyelinating activity of sera from guinea pigs sensitized with whole CNS and with purified encephalitogen. Exp Neurol. 1968 Dec;22(4):545–555. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. H. Transfedotr of Allergic Encephalomyelitis by Lymph Node Cells in Inbred Guinea Pigs. Science. 1961 Sep 1;134(3479):619–620. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3479.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Andrews J. M., Waltz J. M., Terry R. D. Ultrastructural studies of multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest. 1969 May;20(5):444–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., ADAMS R. D. Allergic neuritis: an experimental disease of rabbits induced by the injection of peripheral nervous tissue and adjuvants. J Exp Med. 1955 Aug 1;102(2):213–236. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Prineas J., Raine C. S. An ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination and remyelination. I. Acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the peripheral nervous system. Lab Invest. 1969 Aug;21(2):105–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Terry R. D., Whitaker J. N., Cook S. D., Dowling P. C. Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome. A primary demyelinating disease. Arch Neurol. 1969 Sep;21(3):269–276. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480150059008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


