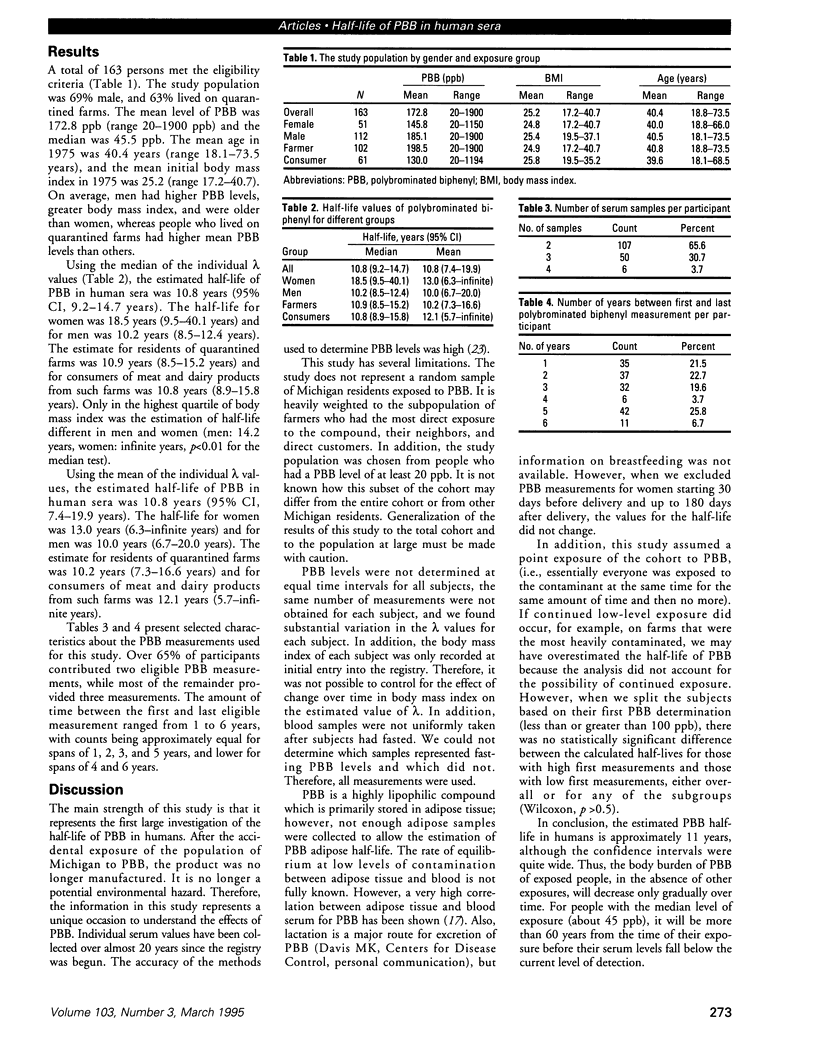
Abstract
Polybrominated biphenyl (PBB), a flame-retardant material, was introduced into the food chain in Michigan in 1973 due to a manufacturing and distribution mistake. Following public concern about the long-term health effects of PBB in humans, a cohort of PBB-exposed Michigan residents was assembled in 1975. We initiated this study to determine the half-life of PBB in human sera and to understand how continued body burden relates to the possible adverse health consequences of PBB exposure. To determine the half-life, eligible persons were selected from the cohort if they had at least two PBB measurements 1 year apart and had an initial level > or = 20 pbb. There were 163 persons who met the criteria with a median PBB level of 45.5 ppb. The estimated half-life is 10.8 years (95% CI, 9.2-14.7 years). The body burden of PBB in exposed persons will decrease only gradually over time. For persons with an initial level of 45.5 ppb of PBB, it will take more than 60 years for their PBB levels to fall below the current level of detection of 1 ppb.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aust S. D., Millis C. D., Holcomb L. Relationship of basic research in toxicology to environmental standard setting: the case of polybrominated biphenyls in Michigan. Arch Toxicol. 1987;60(1-3):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00296986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brilliant L. B., Wilcox K., Van Amburg G., Eyster J., Isbister J., Bloomer A. W., Humphrey H., Price H. Breast-milk monitoring to measure Michigan's contamination with polybrominated biphenyls. Lancet. 1978 Sep 23;2(8091):643–646. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burse V. W., Needham L. L., Liddle J. A., Bayse D. D., Price H. A. Interlaboratory comparison for results of analyses for polybrominated biphenyls in human serum. J Anal Toxicol. 1980 Jan-Feb;4(1):22–26. doi: 10.1093/jat/4.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudill S. P., Pirkle J. L., Michalek J. E. Effects of measurement error on estimating biological half-life. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 1992 Oct-Dec;2(4):463–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Carlo F. J., Seifter J., DeCarlo V. J. Assessment of the hazards of polybrominated biphenyls. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:351–365. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7823351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyster J. T., Humphrey H. E., Kimbrough R. D. Partitioning of polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) in serum, adipose tissue, breast milk, placenta, cord blood, biliary fluid, and feces. Arch Environ Health. 1983 Jan-Feb;38(1):47–53. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1983.10543978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss K., Roberts C., Humphrey H. E. Serial PBB levels, PCB levels, and clinical chemistries in Michigan's PBB cohort. Arch Environ Health. 1982 May-Jun;37(3):141–147. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1982.10667553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert G. H., Schoeller D. A., Humphrey H. E., Kotake A. N., Lietz H., Campbell M., Kalow W., Spielberg S. P., Budd M. The caffeine breath test and caffeine urinary metabolite ratios in the Michigan cohort exposed to polybrominated biphenyls: a preliminary study. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Nov;89:175–181. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9089175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landrigan P. J., Wilcox K. R., Jr, Silva J., Jr, Humphrey H. E., Kauffman C., Heath C. W., Jr Cohort study of Michigan residents exposed to polybrominated biphenyls: epidemiologic and immunologic findings. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:284–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meester W. D. The effect of polybrominated biphenyls on man: the Michigan PBB disaster. Vet Hum Toxicol. 1979;21 (Suppl):131–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miceli J. N., Marks B. H. Tissue distribution and elimination kinetics of polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) from rat tissue. Toxicol Lett. 1981 Dec;9(4):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(81)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek J. E., Tripathi R. C., Caudill S. P., Pirkle J. L. Investigation of TCDD half-life heterogeneity in veterans of Operation Ranch Hand. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1992 Jan;35(1):29–38. doi: 10.1080/15287399209531591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham L. L., Burse V. W., Price H. A. Temperature-programmed gas chromatographic determination of polychlorinated and polybrominated biphenyls in serum. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1981 Sep;64(5):1131–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle J. L., Wolfe W. H., Patterson D. G., Needham L. L., Michalek J. E., Miner J. C., Peterson M. R., Phillips D. L. Estimates of the half-life of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in Vietnam Veterans of Operation Ranch Hand. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1989;27(2):165–171. doi: 10.1080/15287398909531288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich M. R. Environmental politics and science: the case of PBB contamination in Michigan. Am J Public Health. 1983 Mar;73(3):302–313. doi: 10.2105/ajph.73.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J., Kauffman C. A., Simon D. G., Landrigan P. J., Humphrey H. E., Heath C. W., Jr, Wilcox K. R., Jr, VanAmburg G., Kaslow R. A., Ringel A. Lymphocyte function in humans exposed to polybrominated biphenyls. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Oct;26(4):341–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stross J. K., Smokler I. A., Isbister J., Wilcox K. R. The human health effects of exposure to polybrominated biphenyls. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 30;58(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuey D. B., Matthews H. B. Distribution and excretion of 2,2',4,4',5,5'-hexabromobiphenyl in rats and man: pharmacokinetic model predictions. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 May;53(3):420–431. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff M. S., Anderson H. A., Rosenman K. D., Selikoff I. J. Equilibrium of polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) residues in serum and fat of Michigan residents. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979 Apr;21(6):775–781. doi: 10.1007/BF01685504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


