Abstract
Several groups have reported the development of systems, based on the principle of X-ray fluorescence, for the in vivo measurement of bone lead concentrations. These systems have used the detection of either the characteristic L or K X-rays resulting from excitation by a suitable photon source. This paper examines design issues related to the development of these systems. These design issues are, in most instances, a result of consideration of the physical principles involved, and hence there are many features common to the systems developed by the individual groups. Design issues discussed in this paper include the selection of the site for measurement, source-sample-detector configuration, and collimation. Specific examples from published work are used to demonstrate the relevant features.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
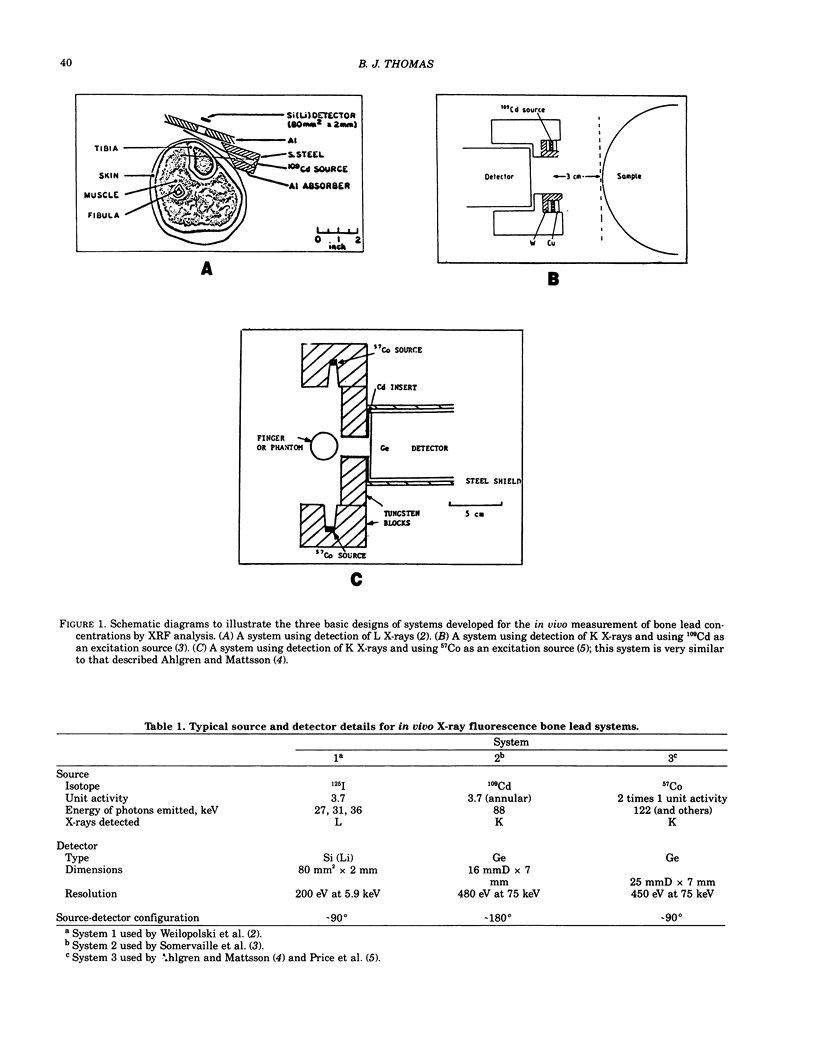
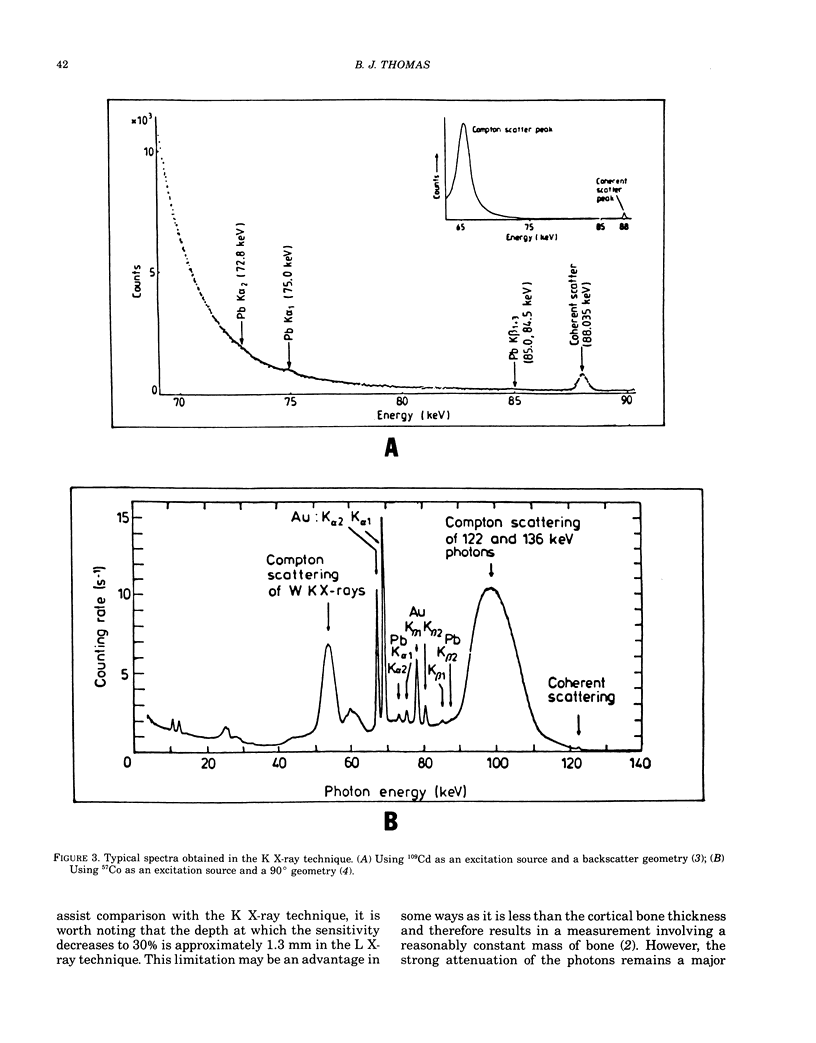
- Ahlgren L., Mattsson S. An X-ray fluorescence technique for in vivo determination of lead concentration in a bone matrix. Phys Med Biol. 1979 Jan;24(1):136–145. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/24/1/011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry P. S. A comparison of concentrations of lead in human tissues. Br J Ind Med. 1975 May;32(2):119–139. doi: 10.1136/oem.32.2.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Baddeley H., Kenardy J. A., Thomas B. J., Thomas B. W. In vivo X-ray fluorescence estimation of bone lead concentrations in Queensland adults. Br J Radiol. 1984 Jan;57(673):29–33. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-57-673-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
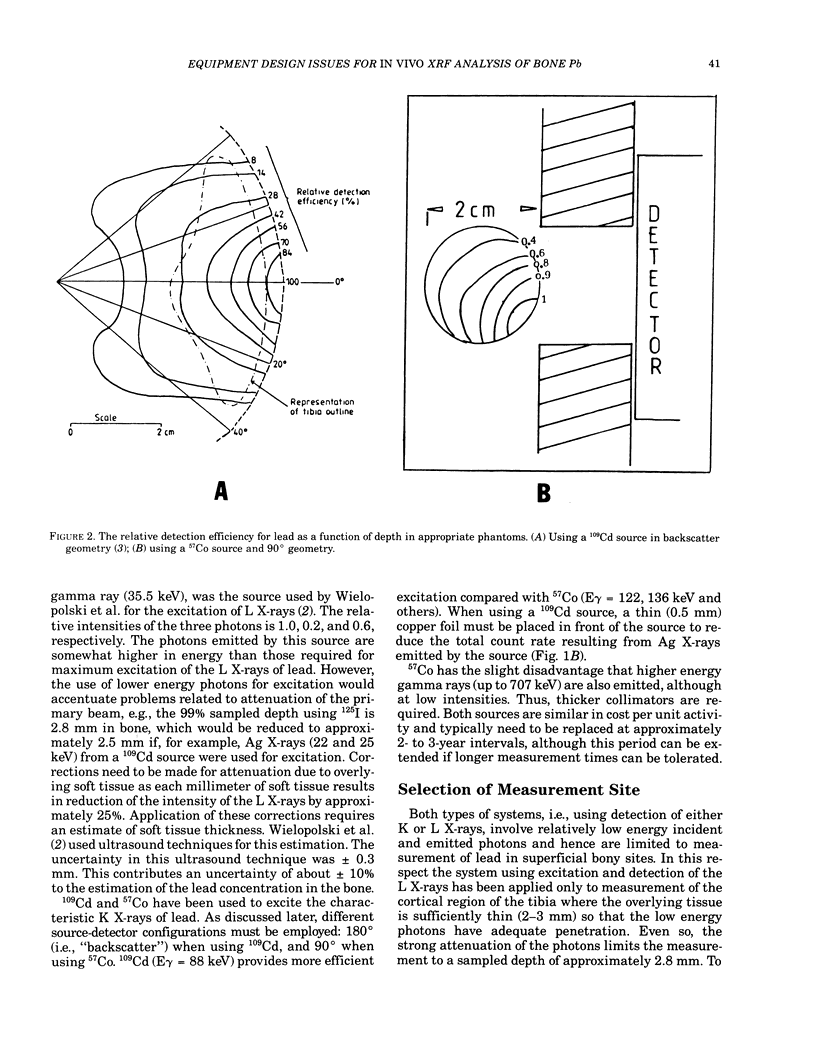
- Somervaille L. J., Chettle D. R., Scott M. C. In vivo measurement of lead in bone using x-ray fluorescence. Phys Med Biol. 1985 Sep;30(9):929–943. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/30/9/005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielopolski L., Rosen J. F., Slatkin D. N., Vartsky D., Ellis K. J., Cohn S. H. Feasibility of noninvasive analysis of lead in the human tibia by soft x-ray fluorescence. Med Phys. 1983 Mar-Apr;10(2):248–251. doi: 10.1118/1.595244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


