Abstract
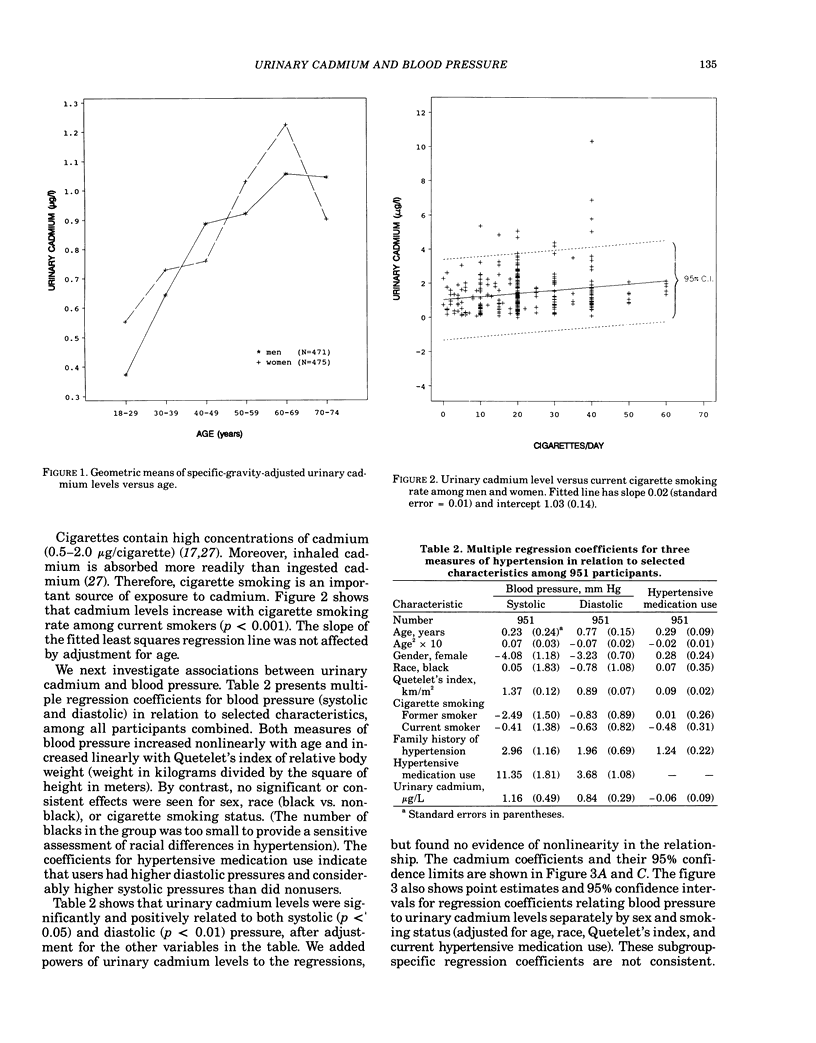
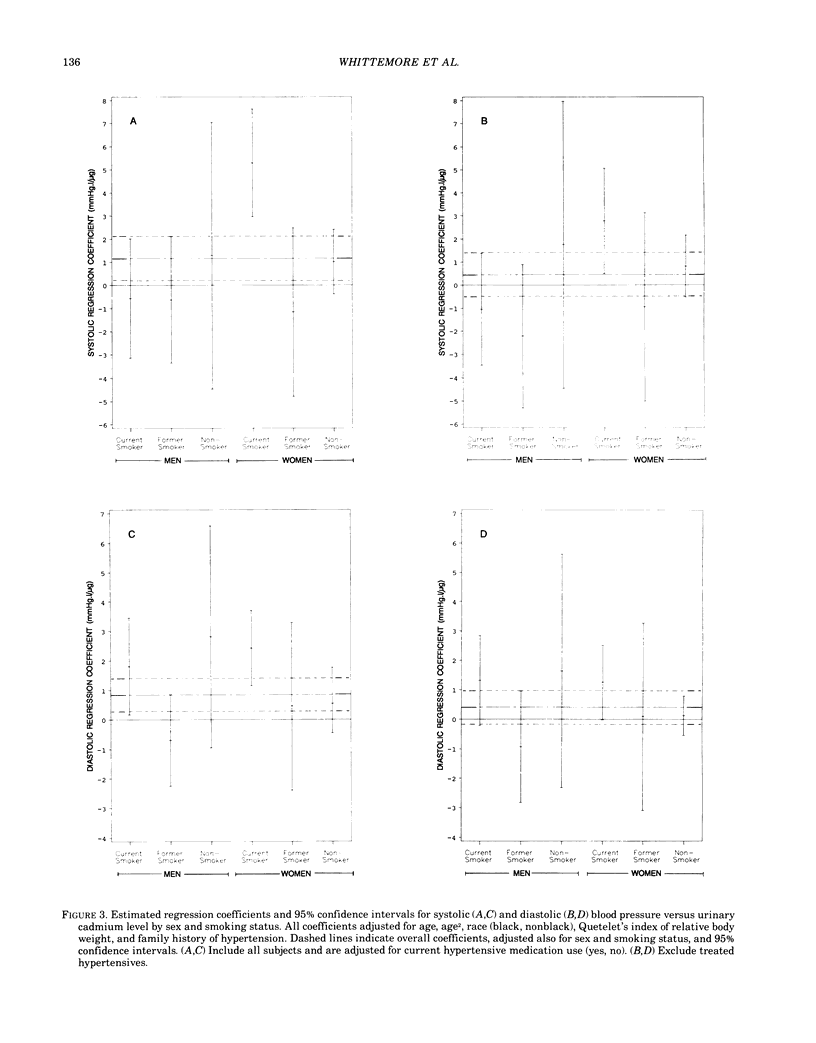
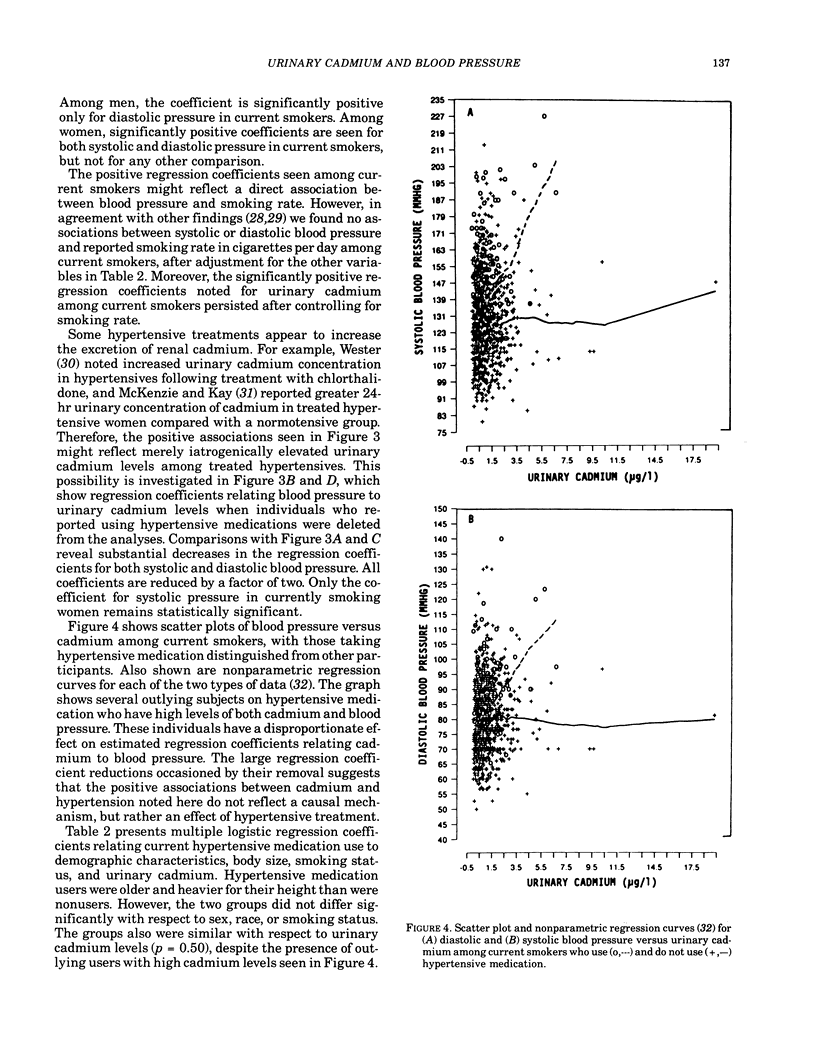
Relationships between urinary cadmium levels and blood pressure were examined in a sample of 951 adult men and women who participated in the Second National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (NHANES II). Among all participants, positive relationships were seen between urinary cadmium levels and both systolic and diastolic blood pressure (p less than 0.05 and p less than 0.01, respectively), after adjusting for age, sex, race, relative body weight, smoking status, and hypertensive medication use. However, analyses for subgroups determined by sex and smoking status were inconsistent. Among current smokers, urinary cadmium levels were significantly positively associated with both systolic and diastolic blood pressure for women, and with diastolic blood pressure for men. Yet among former smokers and lifelong nonsmokers of both sexes, urinary cadmium was not significantly associated with either systolic or diastolic blood pressure. Evidence that some hypertensive medications increase urinary cadmium excretion suggests that the positive associations seen among current smokers may reflect high urinary cadmium levels among hypertensives induced by hypertensive treatment. After treated hypertensives were removed from the analysis, regression coefficients relating blood pressure to cadmium dropped by a factor of two and lost statistical significance. We conclude that the present data provide little support for a causal association between systemic cadmium and hypertension at nonoccupational exposure levels. Further, conflicting results of previous studies may reflect failure to control adequately for age, smoking status, and hypertensive treatment.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballantyne D., Devine B. L., Fife R. Interrelation of age, obesity, cigarette smoking, and blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Br Med J. 1978 Apr 8;1(6117):880–881. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6117.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beevers D. G., Campbell B. C., Goldberg A., Moore M. R., Hawthorne V. M. Blood-cadmium in hypertensives and normotensives. Lancet. 1976 Dec 4;2(7997):1222–1224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beevers D. G., Cruickshank J. K., Yeoman W. B., Carter G. F., Goldberg A., Moore M. R. Blood-lead and cadmium in human hypertension. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1980 Sep;4(2-3):251–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins P. E., Dutton J., Evans C. J., Morgan W. D., Sivyer A., Elwood P. C. An in-vivo study of renal cadmium and hypertension. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;10(6):459–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb02085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elinder C. G., Kjellström T., Linnman L., Pershagen G. Urinary excretion of cadmium and zinc among persons from Sweden. Environ Res. 1978 Jun;15(3):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(78)90126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauser S. C., Bello C. T., Glauser E. M. Blood-cadmium levels in normotensive and untreated hypertensive humans. Lancet. 1976 Apr 3;1(7962):717–718. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)93091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene S. B., Aavedal M. J., Tyroler H. A., Davis C. E., Hames C. G. Smoking habits and blood pressure change: a seven year follow-up. J Chronic Dis. 1977 Jul;30(7):401–413. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(77)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellström T., Evrin P. E., Rahnster B. Dose-response analysis of cadmium-induced tubular proteinuria: a study of urinary beta2-microglobulin excretion among workers in a battery factory. Environ Res. 1977 Apr;13(2):303–317. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(77)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal N. E., Johnson D. E., Kraemer D. F., Pahren H. R. Normal levels of cadmium in diet, urine, blood, and tissues of inhabitants of the United States. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1979 Nov;5(6):995–1014. doi: 10.1080/15287397909529809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal N. E. Urinary cadmium and beta 2-microglobulin: correlation with nutrition and smoking history. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1988;25(2):179–183. doi: 10.1080/15287398809531199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal N. E., Zirkes M. Urinary cadmium and beta 2-microglobulin: normal values and concentration adjustment. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1983 Apr-Jun;11(4-6):607–624. doi: 10.1080/15287398309530371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwerys R. R., Buchet J. P., Roels H. A., Brouwers J., Stanescu D. Epidemiological survey of workers exposed to cadmium. Arch Environ Health. 1974 Mar;28(3):145–148. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1974.10666455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. P., Jusko W. J., Coughlin L. L. Cadmium accumulation im man: influence of smoking, occupation, alcoholic habit and disease. J Chronic Dis. 1972 Dec;25(12):717–726. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(72)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M., Kay D. L. Urinary excretion of cadmium, zinc and copper in normotensive and hypertensive women. N Z Med J. 1973 Jul 25;78(495):68–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard K. Cadmium and hypertension. Lancet. 1977 Mar 26;1(8013):677–678. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. M., Erlanger M., Perry E. F. Increase in the systolic pressure of rats chronically fed cadmium. Environ Health Perspect. 1979 Feb;28:251–260. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7928251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. M., Jr, Erlanger M. W. Metal-induced hypertension following chronic feeding of low doses of cadmium and mercury. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Apr;83(4):541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. M., Jr, Erlanger M., Perry E. F. Elevated systolic pressure following chronic low-level cadmiun feeding. Am J Physiol. 1977 Feb;232(2):H114–H121. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1977.232.2.H114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. M., Jr, Erlanger M., Perry E. F. Hypertension following chronic, very low dose cadmium feeding (39900). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Oct;156(1):173–176. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revis N. W., Zinsmeister A. R. The relationship of blood cadmium level to hypertension and plasma norepinephrine level: A Romanian study. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Jun;167(2):254–260. doi: 10.3181/00379727-167-41159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHROEDER H. A. CADMIUM HYPERTENSION IN RATS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:62–66. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHROEDER H. A., VINTON W. H., Jr Hypertension induced in rats by small doses of cadmium. Am J Physiol. 1962 Mar;202:515–518. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.3.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Anderson R. J., Reading J. C. Chronic cadmium exposures associated with kidney function effects. Am J Ind Med. 1980;1(3-4):319–337. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700010309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staessen J., Bulpitt C. J., Roels H., Bernard A., Fagard R., Joossens J. V., Lauwerys R., Lijnen P., Amery A. Urinary cadmium and lead concentrations and their relation to blood pressure in a population with low exposure. Br J Ind Med. 1984 May;41(2):241–248. doi: 10.1136/oem.41.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thind G. S., Fischer G. M. Plasma cadmium and zinc in human hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Nov;51(5):483–486. doi: 10.1042/cs0510483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thun M. J., Osorio A. M., Schober S., Hannon W. H., Lewis B., Halperin W. Nephropathy in cadmium workers: assessment of risk from airborne occupational exposure to cadmium. Br J Ind Med. 1989 Oct;46(10):689–697. doi: 10.1136/oem.46.10.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wester P. O. Trace elements in serum and urine from hypertensive patients before and during treatment with chlorthalidone. Acta Med Scand. 1973 Dec;194(6):505–512. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1973.tb19482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


