Abstract
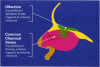
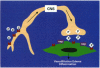
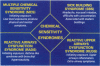
Neurogenic inflammation as a pathway distinct from antigen-driven, immune-mediated inflammation may play a pivotal role in understanding a broad class of environmental health problems resulting from chemical exposures. Recent progress in understanding the mediators, triggers, and regulation of neurogenic inflammation is reviewed. Evidence for and speculations about a role for neurogenic inflammation in established disorders such as asthma, rhinitis, contact dermatitis, migraine headache, and rheumatoid arthritis are presented. The sick building syndrome and multiple chemical sensitivity syndrome have been defined as clinical entities in which exposure to chemical inhalants gives rise to disease. Current data on the existence of chemical irritant receptors in the airway and skin are discussed; neurogenic inflammation arising from stimulation of chemical irritant receptors is a possible model to explain many of the aspects of chemical sensitivities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J. Neurogenic inflammation and asthma. J Asthma. 1992;29(3):165–180. doi: 10.3109/02770909209099025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Neurogenic inflammation in airways. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1991;94(1-4):303–309. doi: 10.1159/000235392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borson D. B., Brokaw J. J., Sekizawa K., McDonald D. M., Nadel J. A. Neutral endopeptidase and neurogenic inflammation in rats with respiratory infections. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Jun;66(6):2653–2658. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.6.2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S. M., Weiss M. A., Bernstein I. L. Reactive airways dysfunction syndrome (RADS). Persistent asthma syndrome after high level irritant exposures. Chest. 1985 Sep;88(3):376–384. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.3.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzzi M. G., Moskowitz M. A. The trigemino-vascular system and migraine. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1992 Apr;40(4):313–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavagnaro J., Lewis R. M. Bidirectional regulatory circuit between the immune and neuroendocrine systems. Year Immunol. 1989;4:241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahl L. A. Antidromic vasodilatation and neurogenic inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;37(2):275–300. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M. R. The worker with multiple chemical sensitivities: an overview. Occup Med. 1987 Oct-Dec;2(4):655–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Jacoby D. B., Djokic T. D., Rubinstein I., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Virus induces airway hyperresponsiveness to tachykinins: role of neutral endopeptidase. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Oct;67(4):1504–1511. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.4.1504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C. Peptides and neurogenic inflammation. Br Med Bull. 1987 Apr;43(2):386–400. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazelius B., Brodin E., Olgart L., Panopoulos P. Evidence that substance P is a mediator of antidromic vasodilatation using somatostatin as a release inhibitor. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Oct;113(2):155–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönblad M., Konttinen Y. T., Korkala O., Liesi P., Hukkanen M., Polak J. M. Neuropeptides in synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Dec;15(12):1807–1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto I., Ueki I. F., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Neutral endopeptidase modulates tachykinin-induced increase in vascular permeability in guinea pig skin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;88(3):288–293. doi: 10.1159/000234808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby D. B., Tamaoki J., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Influenza infection causes airway hyperresponsiveness by decreasing enkephalinase. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jun;64(6):2653–2658. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.6.2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó-Gábor A., Szolcsányi J. Action of rare earth metal complexes on neurogenic as well as on bradykinin-induced inflammation. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 May;22(5):366–371. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohrogi H., Nadel J. A., Malfroy B., Gorman C., Bridenbaugh R., Patton J. S., Borson D. B. Recombinant human enkephalinase (neutral endopeptidase) prevents cough induced by tachykinins in awake guinea pigs. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):781–786. doi: 10.1172/JCI114236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Lundblad L., Saria A., Anggård A. Inhibition of cigarette smoke-induced oedema in the nasal mucosa by capsaicin pretreatment and a substance P antagonist. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;326(2):181–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00517317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggs W. J., Cleveland C. H., Jr Rhinolaryngoscopic examination of patients with the multiple chemical sensitivity syndrome. Arch Environ Health. 1993 Jan-Feb;48(1):14–18. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1993.9938388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggs W. J. Health effects of indoor air pollution. N C Med J. 1992 Jul;53(7):354–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel J. A. Neutral endopeptidase modulates neurogenic inflammation. Eur Respir J. 1991 Jun;4(6):745–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen G. D. Mechanisms of activation of the sensory irritant receptor by airborne chemicals. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1991;21(3):183–208. doi: 10.3109/10408449109089879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obal F., Jr, Opp M., Cady A. B., Johannsen L., Postlethwaite A. E., Poppleton H. M., Seyer J. M., Krueger J. M. Interleukin 1 alpha and an interleukin 1 beta fragment are somnogenic. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):R439–R446. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.3.R439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedimonte G., Nadel J. A., Umeno E., McDonald D. M. Sendai virus infection potentiates neurogenic inflammation in the rat trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Feb;68(2):754–760. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.2.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein I., Iwamoto I., Ueki I. F., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Recombinant neutral endopeptidase attenuates substance P-induced plasma extravasation in the guinea pig skin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;91(3):232–238. doi: 10.1159/000235122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D., Thompson J. E., Scypinski L., Dusser D., Nadel J. A., Borson D. B. Toluene diisocyanate increases airway responsiveness to substance P and decreases airway neutral endopeptidase. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI113424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shim C., Williams M. H., Jr Effect of odors in asthma. Am J Med. 1986 Jan;80(1):18–22. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein S. D. Advances in understanding the pathophysiology of headache. Neurology. 1992 Mar;42(3 Suppl 2):6–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stankus R. P., Menon P. K., Rando R. J., Glindmeyer H., Salvaggio J. E., Lehrer S. B. Cigarette smoke-sensitive asthma: challenge studies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988 Sep;82(3 Pt 1):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(88)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka D. T., Grunstein M. M. Vasoactive effects of substance P on isolated rabbit pulmonary artery. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Apr;58(4):1291–1297. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.4.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The American Academy of Allergy and Immunology, 48th annual meeting. Orlando, Florida, March 6-11, 1992. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Jan;89(1 Pt 2):145–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddman R., Grunditz T., Larsson A., Sundler F. Sensory innervation of the ear drum and middle-ear mucosa: retrograde tracing and immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Apr;252(1):141–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00213835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. A. Recent field studies of personal and indoor exposures to environmental pollutants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Apr 30;641:7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb16527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]