Abstract
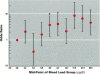
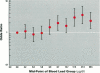
Long-term exposure to high concentrations of lead results in renal dysfunction. During a prospective study of environmental lead and pregnancy outcomes in 1502 women residing in two towns in Yugoslavia, we explored whether moderate exposure to lead results in increased rates of proteinuria. The geometric mean blood lead concentrations (BPb) were 17.1 and 5.1 micrograms/dl in the smelter and nonexposed towns, respectively. Increases in BPb were associated with increased odds ratios for both trace and > or = 1+ proteinuria, measured using a urinary dipstick. Comparing the women in the upper 10th percentile of exposure to those in the lowest 10th percentile, the adjusted odds ratio for > or = 1+ proteinuria was 4.5 (95% CI 1.5, 13.6). Similarly, the adjusted odds ratio for trace proteinuria was 2.3 (95% CI 1.3, 4.1). Similar to other studies showing associations between chronic exposure to lead and renal dysfunction, our data suggest that long-term exposure to environmental lead may be associated with proteinuria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchet J. P., Lauwerys R., Roels H., Bernard A., Bruaux P., Claeys F., Ducoffre G., de Plaen P., Staessen J., Amery A. Renal effects of cadmium body burden of the general population. Lancet. 1990 Sep 22;336(8717):699–702. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92201-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper W. C., Gaffey W. R. Mortality of lead workers. J Occup Med. 1975 Feb;17(2):100–107. doi: 10.1097/00043764-197502000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper W. C., Wong O., Kheifets L. Mortality among employees of lead battery plants and lead-producing plants, 1947-1980. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1985 Oct;11(5):331–345. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey D. A., MacGillivray I. The classification and definition of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Apr;158(4):892–898. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. M. Long term mortality study of chromate pigment workers who suffered lead poisoning. Br J Ind Med. 1984 May;41(2):170–178. doi: 10.1136/oem.41.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison J. M., Dunlop W. Renal hemodynamics and tubular function normal human pregnancy. Kidney Int. 1980 Aug;18(2):152–161. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. O., Parsons C. E. Potential errors in the measurement of total protein in male rat urine using test strips. Lab Anim. 1986 Jan;20(1):27–31. doi: 10.1258/002367786781062089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Factor-Litvak P., Graziano J. H., Kline J. K., Popovac D., Mehmeti A., Ahmedi G., Shrout P., Murphy M. J., Gashi E., Haxhiu R. A prospective study of birthweight and length of gestation in a population surrounding a lead smelter in Kosovo, Yugoslavia. Int J Epidemiol. 1991 Sep;20(3):722–728. doi: 10.1093/ije/20.3.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano J. H., Popovac D., Factor-Litvak P., Shrout P., Kline J., Murphy M. J., Zhao Y. H., Mehmeti A., Ahmedi X., Rajovic B. Determinants of elevated blood lead during pregnancy in a population surrounding a lead smelter in Kosovo, Yugoslavia. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Nov;89:95–100. doi: 10.1289/ehp.908995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano J. H., Slavkovic V., Factor-Litvak P., Popovac D., Ahmedi X., Mehmeti A. Depressed serum erythropoietin in pregnant women with elevated blood lead. Arch Environ Health. 1991 Nov-Dec;46(6):347–350. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1991.9934401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON D. A. A follow-up of cases of plumbism in children. Australas Ann Med. 1954 Aug;3(3):219–224. doi: 10.1111/imj.1954.3.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON D. A. Chronic nephritis in Queensland. Australas Ann Med. 1955 Aug;4(3):163–177. doi: 10.1111/imj.1955.4.3.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan W. R., Landis J. R., Schmouder R. L., Goldstein N. G., Harlan L. C. Blood lead and blood pressure. Relationship in the adolescent and adult US population. JAMA. 1985 Jan 25;253(4):530–534. doi: 10.1001/jama.253.4.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong C. D., Hanenson I. B., Lerner S., Hammond P. B., Pesce A. J., Pollak V. E. Occupational exposure to lead: effects on renal function. Kidney Int. 1980 Oct;18(4):489–494. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilis R., Gavrilescu N., Nestorescu B., Dumitriu C., Roventa A. Nephropathy in chronic lead poisoning. Br J Ind Med. 1968 Jul;25(3):196–202. doi: 10.1136/oem.25.3.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loiacono N. J., Graziano J. H., Kline J. K., Popovac D., Ahmedi X., Gashi E., Mehmeti A., Rajovic B. Placental cadmium and birthweight in women living near a lead smelter. Arch Environ Health. 1992 Jul-Aug;47(4):250–255. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1992.9938357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm D., Barnett H. A. A mortality study of lead workers 1925-76. Br J Ind Med. 1982 Nov;39(4):404–410. doi: 10.1136/oem.39.4.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Johnson H. M. Long-term mortality profile of heavily-exposed lead smelter workers. J Occup Med. 1982 May;24(5):375–378. doi: 10.1097/00043764-198205000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. E., Lipschitz D. A., Bieber C. P., Cook J. D. Measurement of serum ferritin by a 2-site immunoradiometric assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Sep;61(1):209–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J., Graziano J. H., Popovac D., Kline J. K., Mehmeti A., Factor-Litvak P., Ahmedi G., Shrout P., Rajovic B., Nenezic D. U. Past pregnancy outcomes among women living in the vicinity of a lead smelter in Kosovo, Yugoslavia. Am J Public Health. 1990 Jan;80(1):33–35. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri L. C., Hewitt D., Orser B. Blood lead and blood pressure: analysis of cross-sectional and longitudinal data from Canada. Environ Health Perspect. 1988 Jun;78:123–126. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8878123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli S. A micromethod for free erythrocyte porphyrins: the FEP test. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jun;81(6):932–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock S. J., Shaper A. G., Ashby D., Delves H. T., Clayton B. E. The relationship between blood lead, blood pressure, stroke, and heart attacks in middle-aged British men. Environ Health Perspect. 1988 Jun;78:23–30. doi: 10.1289/ehp.887823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovac D., Graziano J., Seaman C., Colakovic B., Popovac R., Osmani I., Haxhiu M., Begraca M., Bozovic Z., Mikic M. Elevated blood lead in a population near a lead smelter in Kosovo, Yugoslavia. Arch Environ Health. 1982 Jan-Feb;37(1):19–23. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1982.10667527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. Lead, blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease in men and women. Environ Health Perspect. 1991 Feb;91:71–75. doi: 10.1289/ehp.919171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selevan S. G., Landrigan P. J., Stern F. B., Jones J. H. Mortality of lead smelter workers. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Oct;122(4):673–683. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staessen J. A., Lauwerys R. R., Buchet J. P., Bulpitt C. J., Rondia D., Vanrenterghem Y., Amery A. Impairment of renal function with increasing blood lead concentrations in the general population. The Cadmibel Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 16;327(3):151–156. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207163270303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thysell H. A comparison between Albustix, Hema-Combistix, Labstix, the sulphosalicyclic-acid test, Heller's nitric-acid test, and a biuret method. Diagnosis of proteinuria. Acta Med Scand. 1969 May;185(5):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedeen R. P., Maesaka J. K., Weiner B., Lipat G. A., Lyons M. M., Vitale L. F., Joselow M. M. Occupational lead nephropathy. Am J Med. 1975 Nov;59(5):630–641. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedeen R. P., Malik D. K., Batuman V. Detection and treatment of occupational lead nephropathy. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Jan;139(1):53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]