Abstract
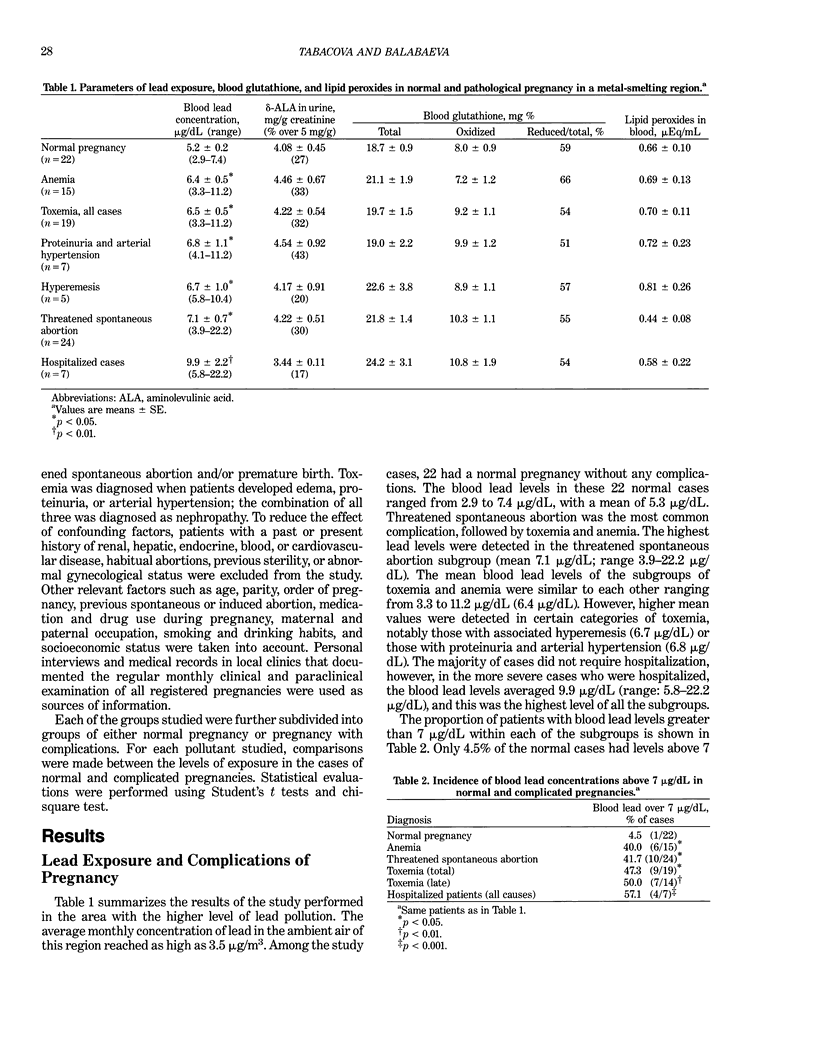
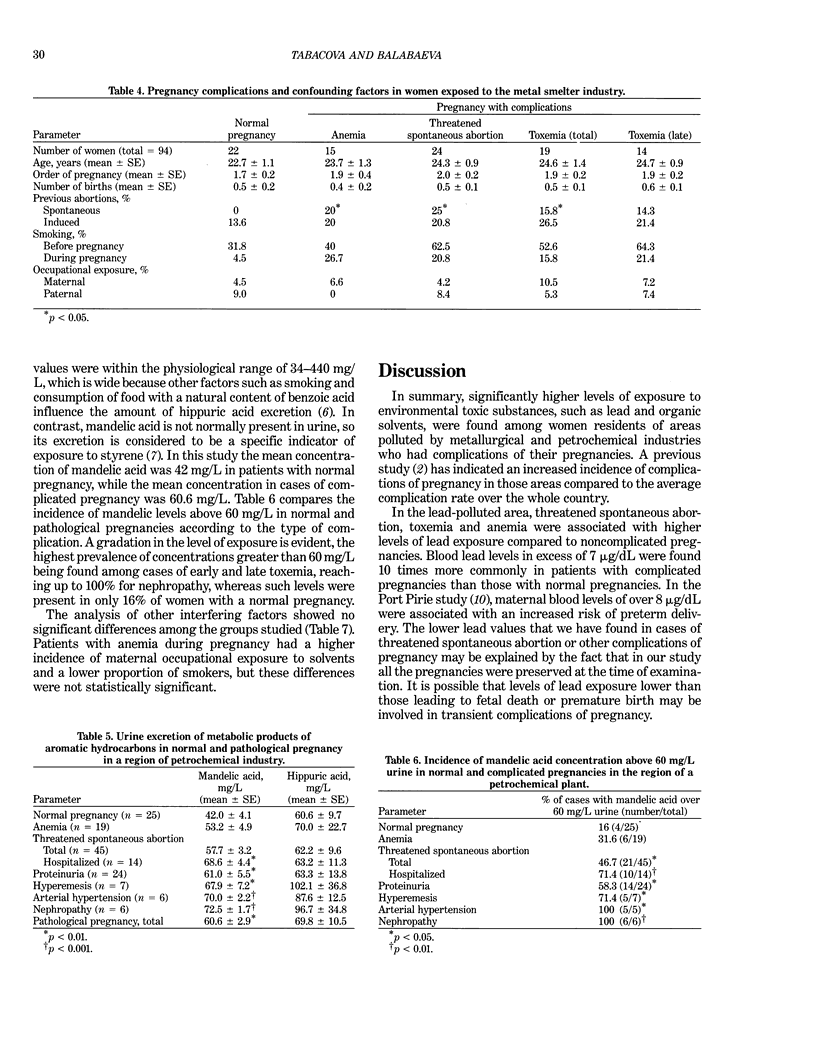
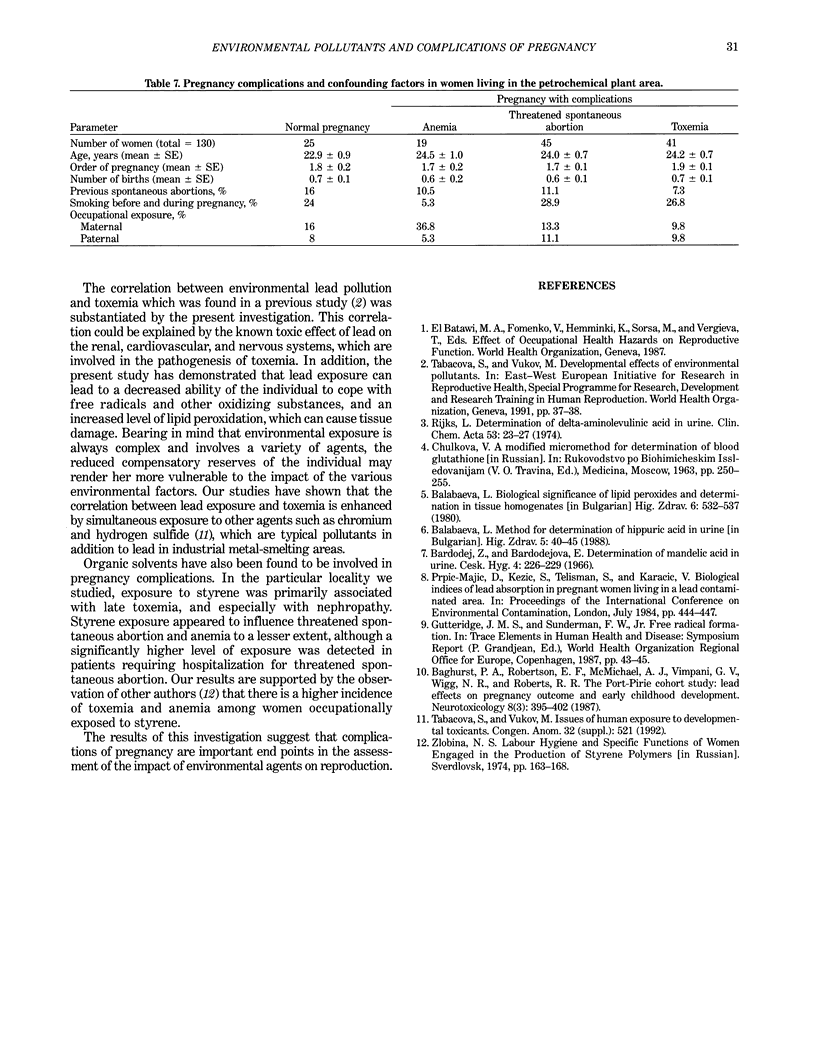
Certain complications of pregnancy, e.g., threatened spontaneous abortion, toxemia, emesis, and anemia, were studied in pregnant women living in industrial areas contaminated by smelters and the petrochemical industry. Exposure to lead or aromatic hydrocarbons was assessed in parallel by the determination of these agents or their metabolites in blood and urine. Comparison of respective exposure levels was made between women with normal pregnancies and those with complications. Significantly higher levels of lead in blood and increased excretion of the metabolic products of organic solvents were found in women with complicated pregnancies compared to those with normal pregnancies. Threatened spontaneous abortion, toxemia, and anemia were associated with higher lead exposure in the vicinity of smelters. In these patients, evidence of disturbances of blood glutathione equilibrium and increased lipid peroxidation were found indicating a decreased ability to compensate for the effects of exposure. Styrene exposure in a petrochemical industrial area was associated mainly with late toxemia and nephropathy. Patients with these complications also had a tendency to elevated exposure to other aromatic hydrocarbons. It is suggested that complications of pregnancy may be induced by environmental agents at levels lower than those that result in pregnancy loss or preterm birth.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baghurst P. A., Robertson E. F., McMichael A. J., Vimpani G. V., Wigg N. R., Roberts R. R. The Port Pirie Cohort Study: lead effects on pregnancy outcome and early childhood development. Neurotoxicology. 1987 Fall;8(3):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijks L. G. A modification of the Berkó-Durkó method for the determination of delta-aminolevulinic acid in urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 May 31;53(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


