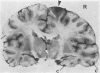
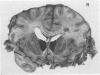
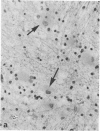
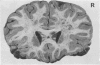
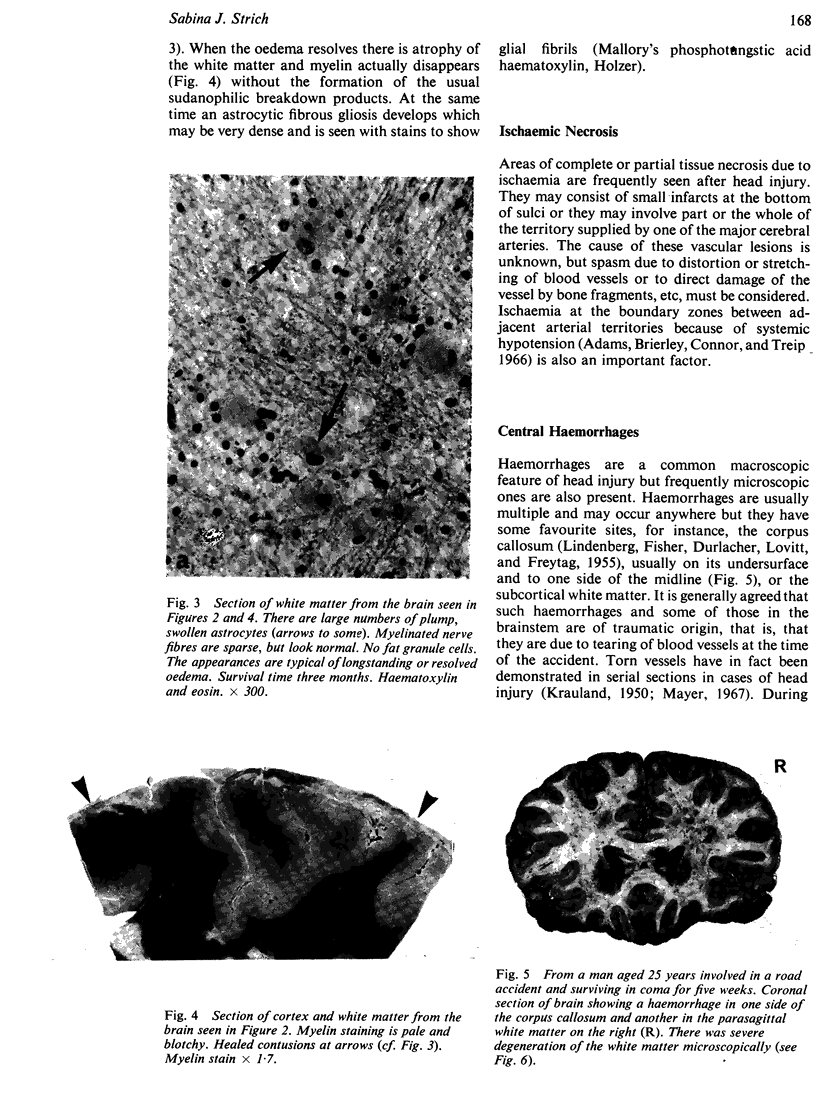
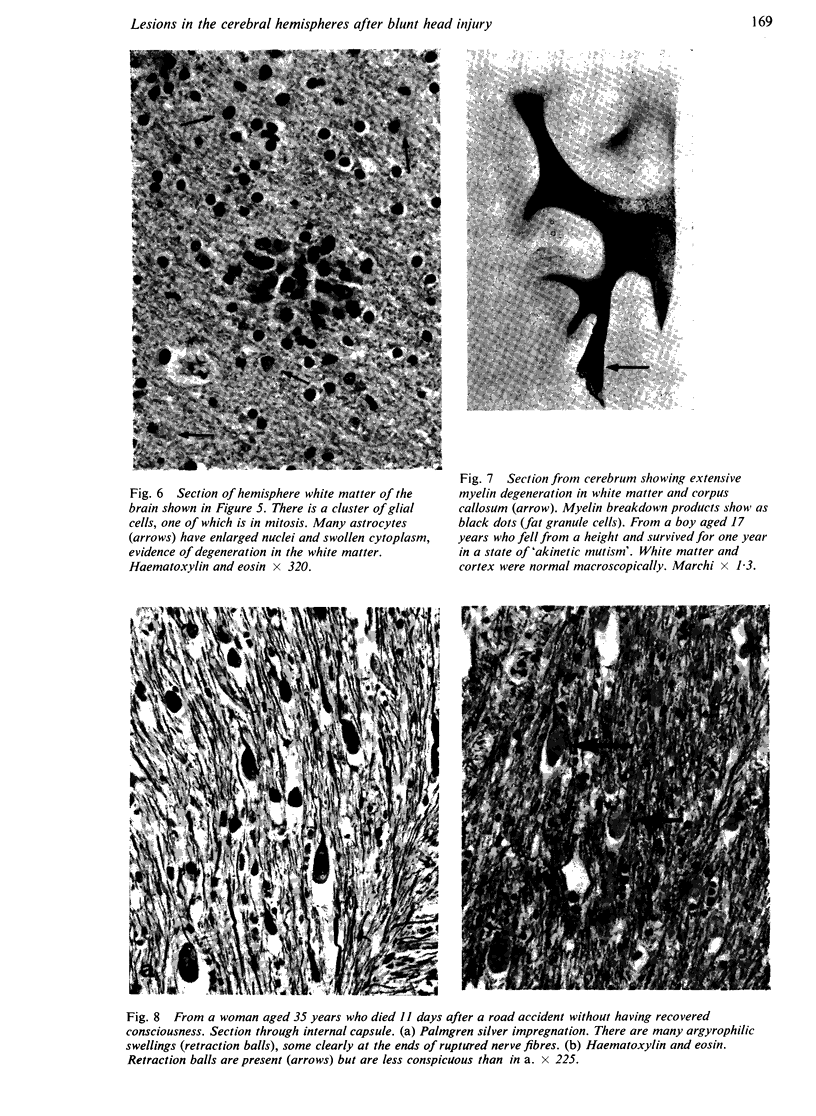
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. H., Brierley J. B., Connor R. C., Treip C. S. The effects of systemic hypotension upon the human brain. Clinical and neuropathological observations in 11 cases. Brain. 1966 Jun;89(2):235–268. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Ralston H. J., 3rd The cellular reaction to Wallerian degeneration in the central nervous system of the cat. Brain Res. 1969 May;13(3):444–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Strich S. J. Histological observations on Wallerian degeneration in the spinal cord of the baboon, Papio papio. Acta Neuropathol. 1969;12(4):314–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00809128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLYAS F. SILVER IMPREGNATION METHOD FOR MICROGLIA. Acta Neuropathol. 1963 Nov 5;3:206–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00687068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS A. G. A new theory on the dynamics of brain concussion and brain injury. J Neurosurg. 1958 Sep;15(5):548–561. doi: 10.3171/jns.1958.15.5.0548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLATZO I., PIRAUX A., LASKOWSKI E. J. The relationship between edema, blood-brain-barrier and tissue elements in a local brain injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1958 Oct;17(4):548–564. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195810000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzo I. Presidental address. Neuropathological aspects of brain edema. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jan;26(1):1–14. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196701000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENBERG R., FISHER R. S., DURLACHER S. H., LOVITT W. V., Jr, FREYTAG E. Lesions of the corpus callosum following blunt mechanical trauma to the head. Am J Pathol. 1955 Mar-Apr;31(2):297–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer E. T. Zentrale Hirnschäden nach Einwirkung stumpfer Gewalt auf den Schädel. Hirstammläsionen. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1967;210(3):238–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00367551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin N. C. Neuropathological changes in the white matter following head injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jan;26(1):77–84. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196701000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ommaya A. K., Faas F., Yarnell P. Whiplash injury and brain damage: an experimental study. JAMA. 1968 Apr 22;204(4):285–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ommaya A. K. Trauma to the nervous system. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1966 Dec;39(6):317–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer D. R. Microscopic lesions in the brain following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Aug;31(4):299–306. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.4.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerless S. J., Rewcastle N. B. Shear injuries of the brain. Can Med Assoc J. 1967 Mar 11;96(10):577–582. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLIER K., UNTERHARNSCHEIDT F. [Mechanism and pathomorphology of brain damage after blunt cranial trauma]. Hefte Unfallheilkd. 1963;76:1–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRICH S. J. Diffuse degeneration of the cerebral white matter in severe dementia following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 Aug;19(3):163–185. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.3.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strich S. J. Notes on the Marchi method for staining degenerating myelin in the peripheral and central nervous system. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Apr;31(2):110–114. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.2.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterharnscheidt F., Higgins L. S. Traumatic lesions of brain and spinal cord due to nondeforming angular acceleration of the head. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1969 Spring;27(1):127–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]