Abstract
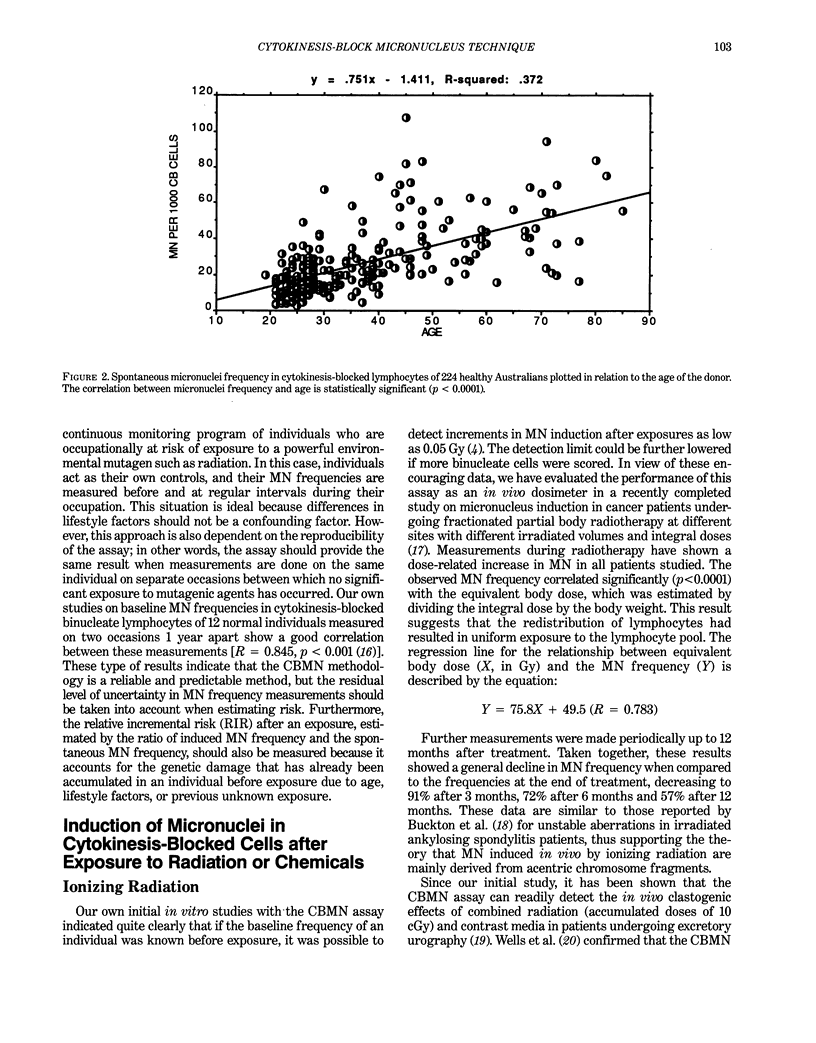
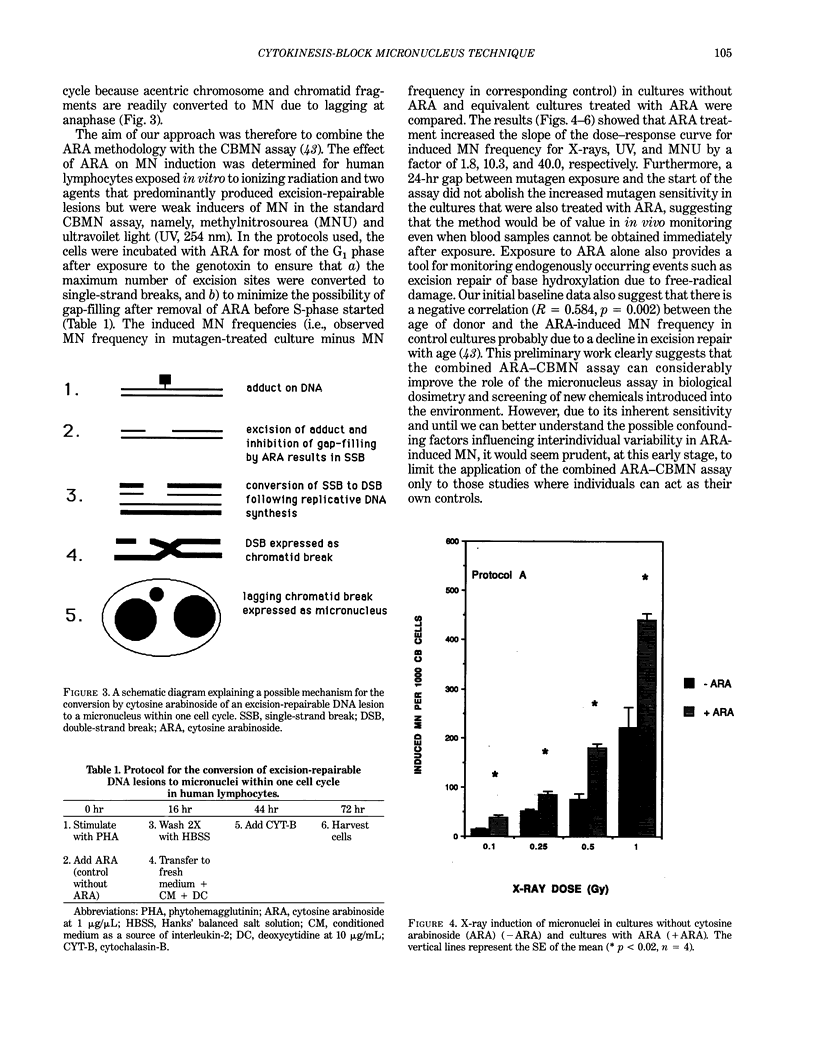
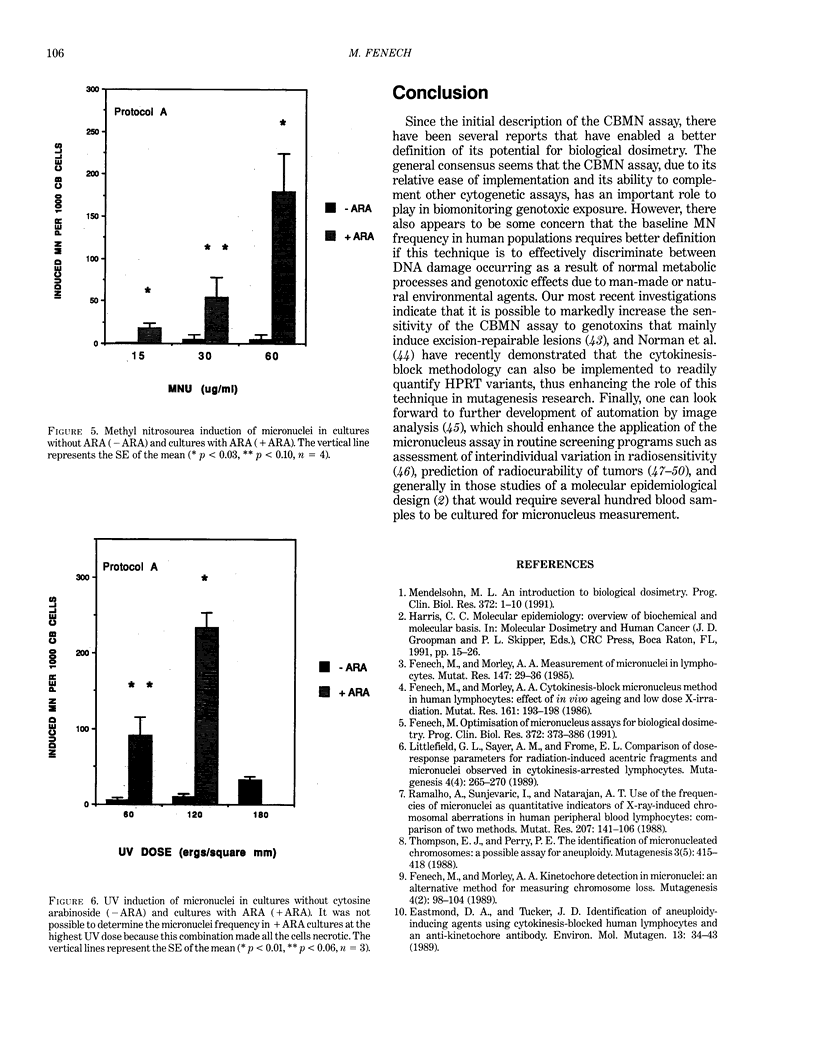
The development of the cytokinesis-block (CB) technique has made the human lymphocyte micronucleus assay (MN) a reliable and precise method for assessing chromosome damage. Recent studies in our laboratory have confirmed that this method is a sensitive indicator of in vivo radiation exposure in patients undergoing fractionated partial-body radiotherapy and rodents exposed to uniform whole-body irradiation, thus supporting the application of the cytokinesis-block micronucleus (CBMN) assay for biological dosimetry. To further define the use of this assay in biomonitoring, we have also undertaken extensive studies to determine the spontaneous level of MN in normal human populations and its relationship to various lifestyle factors. During the past year, we have also developed a new variation to the CBMN assay that enables the conversion of excision-repairable lesions to MN within one cell-cycle using cytosine arabinoside. With this method the slope of the in vitro dose-response curves was increased by a factor of 1.8 for X-rays, 10.3 for ultraviolet (254 nm) radiation, and approximately 40-fold for methylnitrosourea. Consequently, the CBMN assay can now be used not only to measure whole chromosome loss or chromosome breaks but also excision repair events. The versatility and simplicity of the CBMN assay together with new developments in automation should enable its successful application in monitoring exposed populations as well as identifying mutagen-sensitive individuals within a population.
Full text
PDF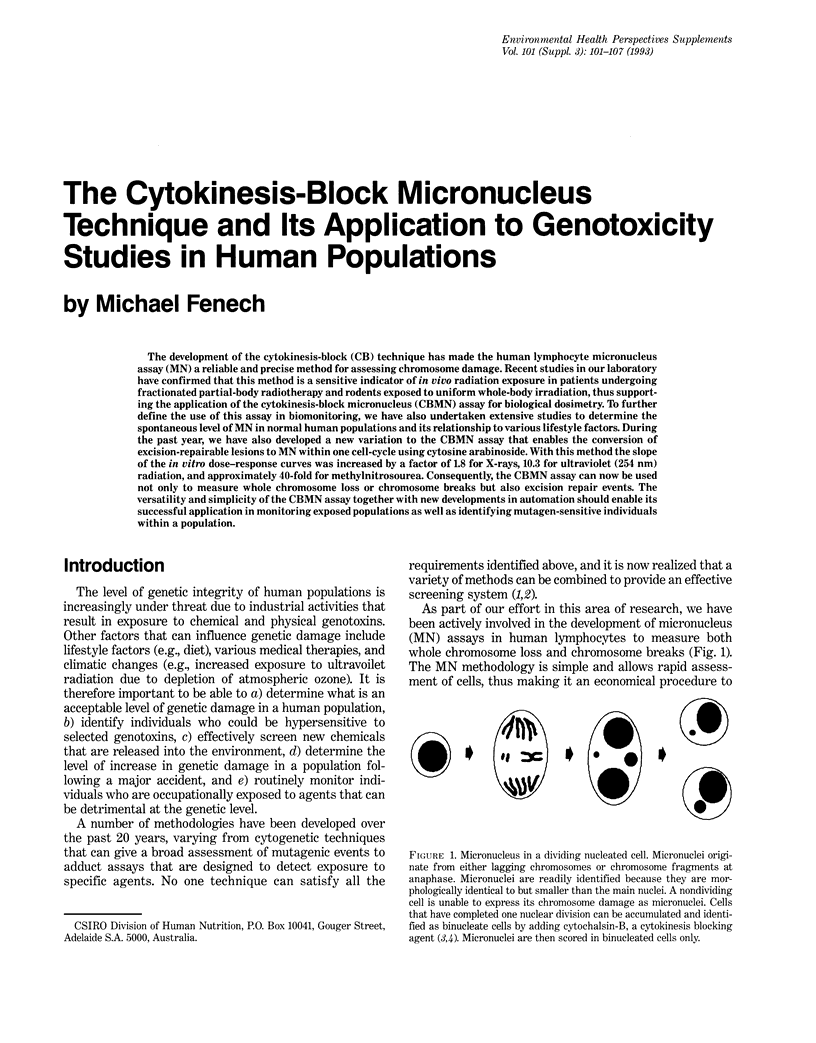



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Au W. W., Walker D. M., Ward J. B., Jr, Whorton E., Legator M. S., Singh V. Factors contributing to chromosome damage in lymphocytes of cigarette smokers. Mutat Res. 1991 Jun;260(2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(91)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasem A. N., Ali A. S. Establishment of dose-response relationships between doses of Cs-137 gamma-rays and frequencies of micronuclei in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1991 Feb;259(2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(91)90047-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ban S., Donovan M. P., Cologne J. B., Sawada S. Gamma-ray- and fission neutron-induced micronuclei in PHA stimulated and unstimulated human lymphocytes. J Radiat Res. 1991 Mar;32(1):13–22. doi: 10.1269/jrr.32.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckton K. E., Brown W. M., Smith P. G. Lymphocyte survival in men treated with x-rays for ankylosing spondylitis. Nature. 1967 Apr 29;214(5087):470–473. doi: 10.1038/214470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastmond D. A., Tucker J. D. Identification of aneuploidy-inducing agents using cytokinesis-blocked human lymphocytes and an antikinetochore antibody. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;13(1):34–43. doi: 10.1002/em.2850130104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erexson G. L., Kligerman A. D., Bryant M. F., Sontag M. R., Halperin E. C. Induction of micronuclei by X-radiation in human, mouse and rat peripheral blood lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1991 Oct;253(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(91)90132-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erexson G. L., Kligerman A. D., Halperin E. C., Honoré G. M., Allen J. W. Micronuclei in binucleated lymphocytes of mice following exposure to gamma radiation. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;13(2):128–132. doi: 10.1002/em.2850130207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M. F., Dunaiski V., Osborne Y., Morley A. A. The cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay as a biological dosimeter in spleen and peripheral blood lymphocytes of the mouse following acute whole-body irradiation. Mutat Res. 1991 Jun;263(2):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(91)90069-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M., Denham J., Francis W., Morley A. Micronuclei in cytokinesis-blocked lymphocytes of cancer patients following fractionated partial-body radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990 Feb;57(2):373–383. doi: 10.1080/09553009014552471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M., Morley A. A. Cytokinesis-block micronucleus method in human lymphocytes: effect of in vivo ageing and low dose X-irradiation. Mutat Res. 1986 Jul;161(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(86)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M., Morley A. A. Kinetochore detection in micronuclei: an alternative method for measuring chromosome loss. Mutagenesis. 1989 Mar;4(2):98–104. doi: 10.1093/mutage/4.2.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M., Morley A. A. Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1985 Feb-Apr;147(1-2):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(85)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M., Neville S. Conversion of excision-repairable DNA lesions to micronuclei within one cell cycle in human lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1992;19(1):27–36. doi: 10.1002/em.2850190106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M. Optimisation of micronucleus assays for biological dosimetry. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;372:373–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M. The cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay in nucleated cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;340B:195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. The molecular biology of nucleotide excision repair of DNA: recent progress. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;6:1–23. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1984.supplement_6.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Braselmann H., Bauchinger M. Screening for interindividual differences in radiosensitivity by means of the micronucleus assay in human lymphocytes. Radiat Environ Biophys. 1989;28(2):113–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01210295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocisová J., Srám R. J. Mutagenicity studies on paracetamol in human volunteers. III. Cytokinesis block micronucleus method. Mutat Res. 1990 May;244(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(90)90103-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kormos C., Köteles G. J. Micronuclei in X-irradiated human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1988 May;199(1):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90227-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlefield L. G., Sayer A. M., Frome E. L. Comparisons of dose-response parameters for radiation-induced acentric fragments and micronuclei observed in cytokinesis-arrested lymphocytes. Mutagenesis. 1989 Jul;4(4):265–270. doi: 10.1093/mutage/4.4.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masunaga S., Ono K., Abe M. A method for the selective measurement of the radiosensitivity of quiescent cells in solid tumors--combination of immunofluorescence staining to BrdU and micronucleus assay. Radiat Res. 1991 Mar;125(3):243–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masunaga S., Ono K., Wandl E. O., Fushiki M., Abe M. Use of the micronucleus assay for the selective detection of radiosensitivity in BUdR-unincorporated cells after pulse-labelling of exponentially growing tumour cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990 Aug;58(2):303–311. doi: 10.1080/09553009014551641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn M. L. An introduction to biological dosimetry. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;372:1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliore L., Parrini M., Sbrana I., Biagini C., Battaglia A., Loprieno N. Micronucleated lymphocytes in people occupationally exposed to potential environmental contaminants: the age effect. Mutat Res. 1991 Jan;256(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(91)90028-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliore L., Parrini M., Sbrana I., Biagini C., Battaglia A., Loprieno N. Micronucleated lymphocytes in people occupationally exposed to potential environmental contaminants: the age effect. Mutat Res. 1991 Jan;256(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(91)90028-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki-Paakkanen J., Walles S., Osterman-Golkar S., Norppa H. Single-strand breaks, chromosome aberrations, sister-chromatid exchanges, and micronuclei in blood lymphocytes of workers exposed to styrene during the production of reinforced plastics. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1991;17(1):27–31. doi: 10.1002/em.2850170105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A., Mitchell J. C., Iwamoto K. S. A sensitive assay for 6-thioguanine-resistant lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1988 May;208(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(88)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osanto S., Thijssen J. C., Woldering V. M., van Rijn J. L., Natarajan A. T., Tates A. D. Increased frequency of chromosomal damage in peripheral blood lymphocytes up to nine years following curative chemotherapy of patients with testicular carcinoma. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1991;17(2):71–78. doi: 10.1002/em.2850170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters L. J., Brock W. A., Johnson T., Meyn R. E., Tofilon P. J., Milas L. Potential methods for predicting tumor radiocurability. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Apr;12(4):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston R. J., Gooch P. C. The induction of chromosome-type aberrations in G1 by methyl methanesulfonate and 4-nitroquinoline-N,-oxide, and the non-requirement of an S-phase for their production. Mutat Res. 1981 Oct;83(3):395–402. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston R. J. The effect of cytosine arabinoside on the frequency of X-ray-induced chromosome aberrations in normal human leukocytes. Mutat Res. 1980 Jan;69(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser J. S., Moquet J. E., Lloyd D. C., Edwards A. A. Radiation induction of micronuclei in human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1988 May;199(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramalho A., Sunjevaric I., Natarajan A. T. Use of the frequencies of micronuclei as quantitative indicators of X-ray-induced chromosomal aberrations in human peripheral blood lymphocytes: comparison of two methods. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar-Apr;207(3-4):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(88)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinúes B., Nuñez E., Bernal M. L., Alcala A., Saenz M. A., Conde B. Micronucleus assay in biomonitoring of patients undergoing excretory urography with diatrizoate and ioxaglate. Mutat Res. 1991 Aug;260(4):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(91)90019-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorsa M., Anttila A., Järventaus H., Kubiak R., Norppa H., Nylander L., Pekari K., Pfäffli P., Vainio H. Styrene revisited--exposure assessment and risk estimation in reinforced plastics industry. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;372:187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorsa M., Pyy L., Salomaa S., Nylund L., Yager J. W. Biological and environmental monitoring of occupational exposure to cyclophosphamide in industry and hospitals. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;204(3):465–479. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tates A. D., van Welie M. T., Ploem J. S. The present state of the automated micronucleus test for lymphocytes. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990 Nov;58(5):813–825. doi: 10.1080/09553009014552191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson E. J., Perry P. E. The identification of micronucleated chromosomes: a possible assay for aneuploidy. Mutagenesis. 1988 Sep;3(5):415–418. doi: 10.1093/mutage/3.5.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titeler M., Lyon R. A., Glennon R. A. Radioligand binding evidence implicates the brain 5-HT2 receptor as a site of action for LSD and phenylisopropylamine hallucinogens. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1988;94(2):213–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00176847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomanin R., Ballarin C., Nardini B., Mastrangelo G., Sarto F. Influence of smoking habit on the frequency of micronuclei in human lymphocytes by the cytokinesis block method. Mutagenesis. 1991 Mar;6(2):123–126. doi: 10.1093/mutage/6.2.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandl E. O., Ono K., Kain R., Herbsthofer T., Hienert G., Höbarth K. Linear correlation between surviving fraction and the micronucleus frequency. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Nov;56(5):771–775. doi: 10.1080/09553008914552031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager J. W., Sorsa M., Selvin S. Micronuclei in cytokinesis-blocked lymphocytes as an index of occupational exposure to alkylating cytostatic drugs. IARC Sci Publ. 1988;(89):213–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoetelief J., Broerse J. J. Dosimetry for radiation accidents: present status and prospects for biological dosemeters. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990 Apr;57(4):737–750. doi: 10.1080/09553009014550901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


