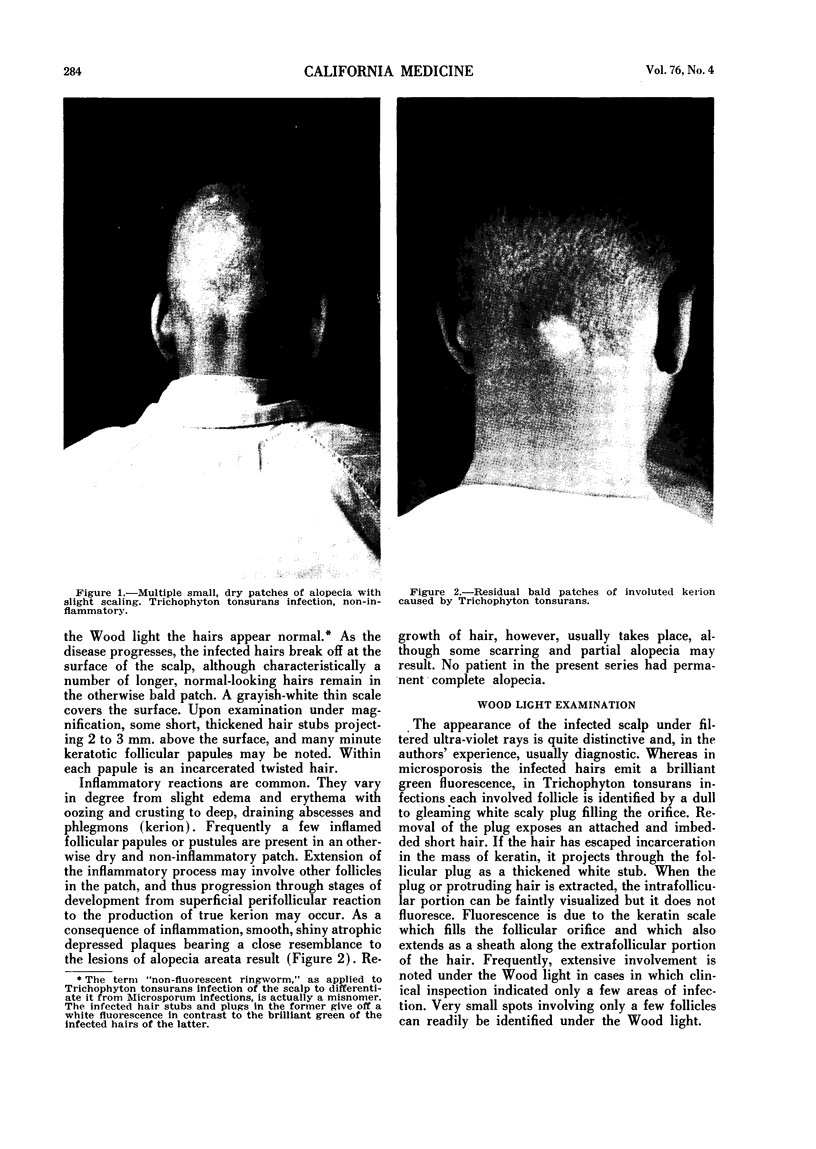
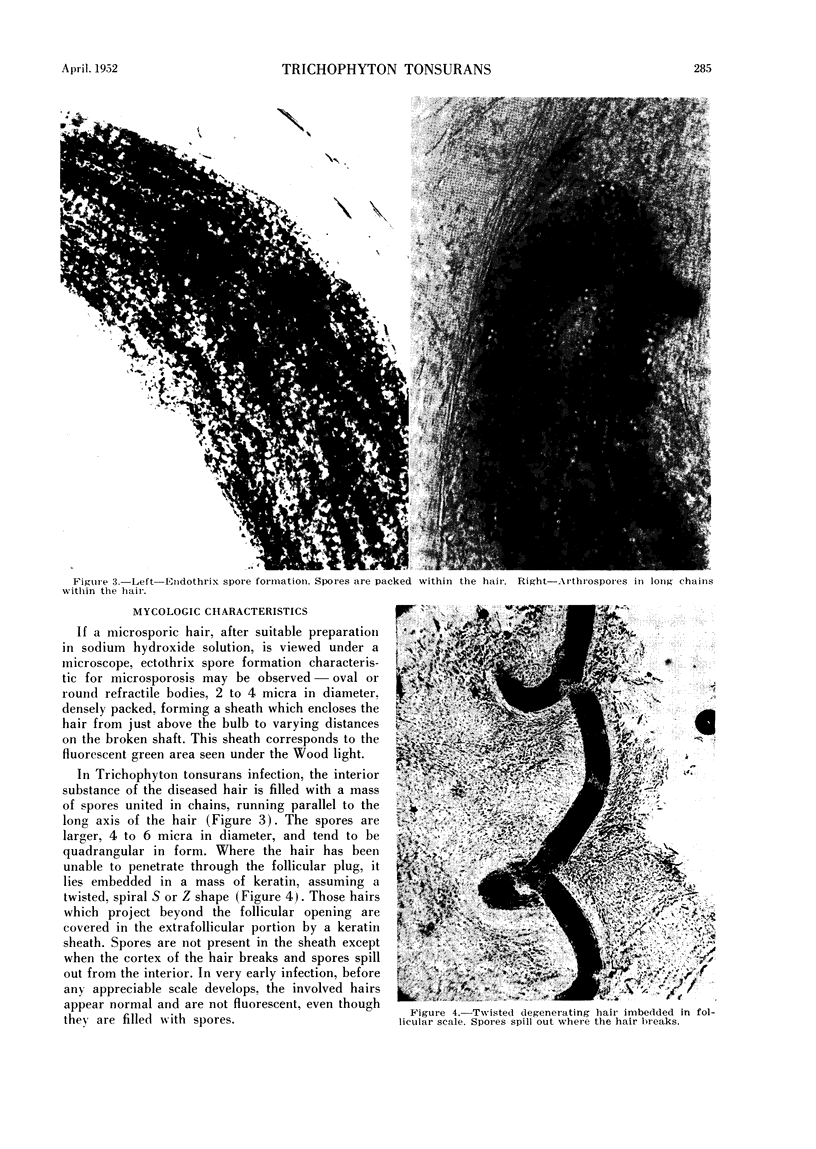
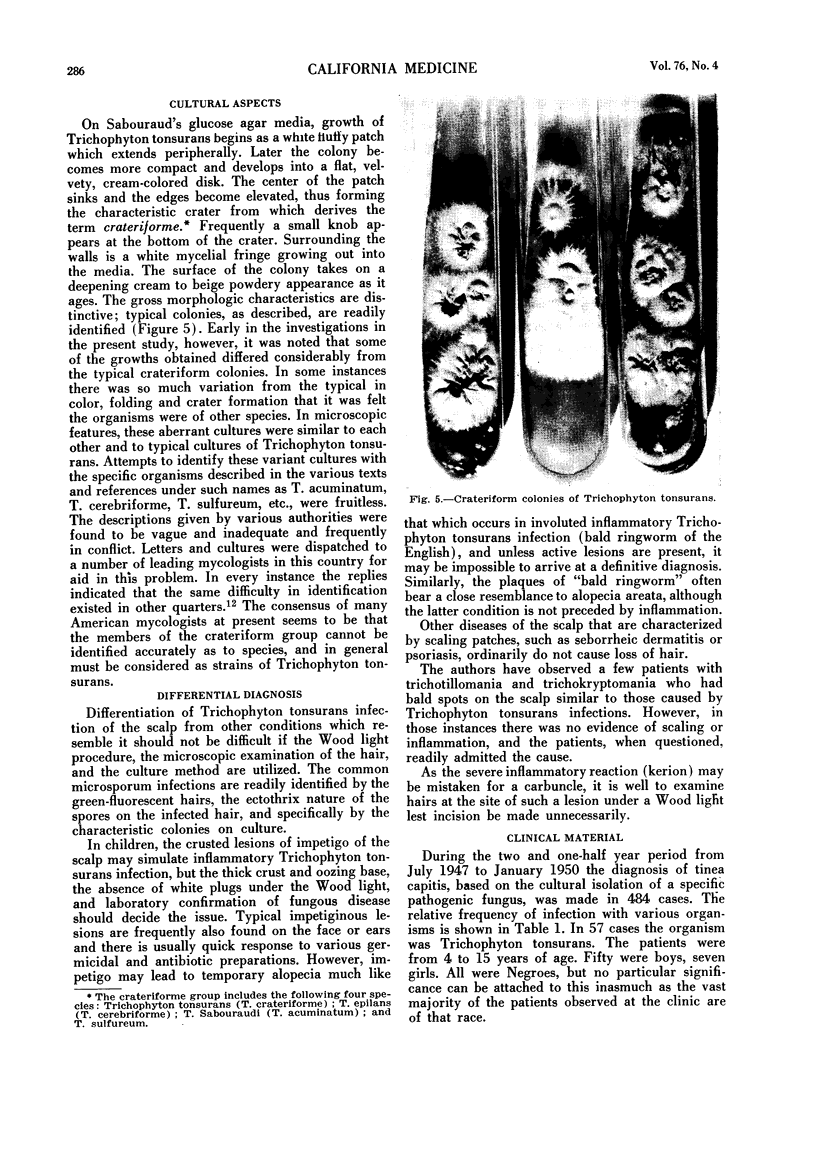
Abstract
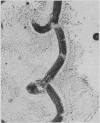
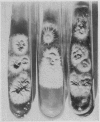
Of 484 cases of ringworm of the scalp observed in a period of two and a half years at a clinic in Los Angeles, 57 (11.78 per cent) were caused by Trichophyton tonsurans, an organism previously considered an infrequent cause of tinea capitis in the United States. The hairs at the site of infection with this organism are distinctively fluorescent when viewed under a Wood light—glowing white rather than green as do hairs infected with microsporum. Endothrix spore formation may be noted in microscopic examination of infected hairs. Material planted on Sabouraud's media grows as a typical crateriform colony. Occasionally variant growths on cultures are obtained.
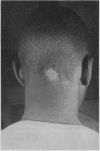
Trichophyton tonsurans may cause either dry, scaly lesions or inflammatory reaction. In the present series the incidence of cure was higher and the period of treatment shorter for patients with the inflammatory variety. Various antifungal preparations were employed for topical application and although the results were extremely variable, it was felt that some benefit was derived from their use. For lesions of the dry, non-inflammatory type, roentgen ray epilation appeared to be the treatment of choice.
Full text
PDF