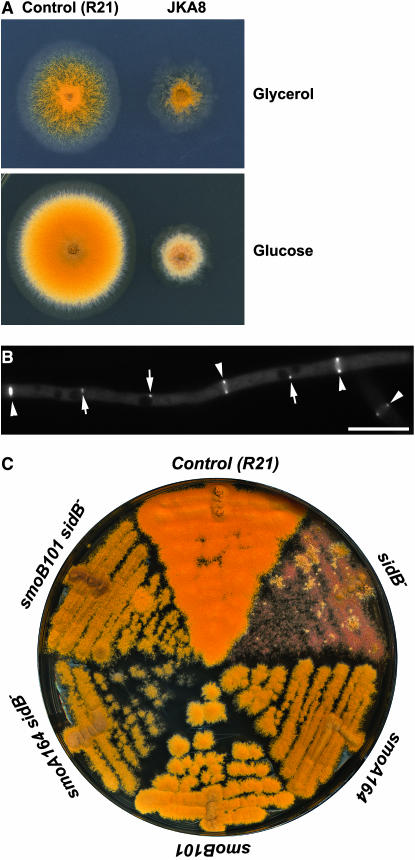
Figure 7.
smo mutations suppressed the loss-of-function sidB mutation. (A). The control (R21) and the alcA(p)∷GFP-sidB (JKA8) strains were grown on minimal medium with glycerol as the sole carbon source (top) and on rich medium containing glucose (bottom). Under inducing conditions (with glycerol), JKA8 produced a colony with reduced size, and it conidiated robustly. Under repressive conditions (with glucose), JKA8 failed to conidiate, while R21 demonstrated healthy conidiating capacity. (B) GFP–SIDB localized to both the spindle pole bodies (arrows) and the septation site (arrowheads) during septation. (C) smoA164 and smoB101 mutations restored conidiation when GFP–SIDB expression was turned off on medium containing glucose. But the double mutants produced colonies with reduced sizes compared to the control (R21) strain. Bar, 10 μm.