Figure 5.
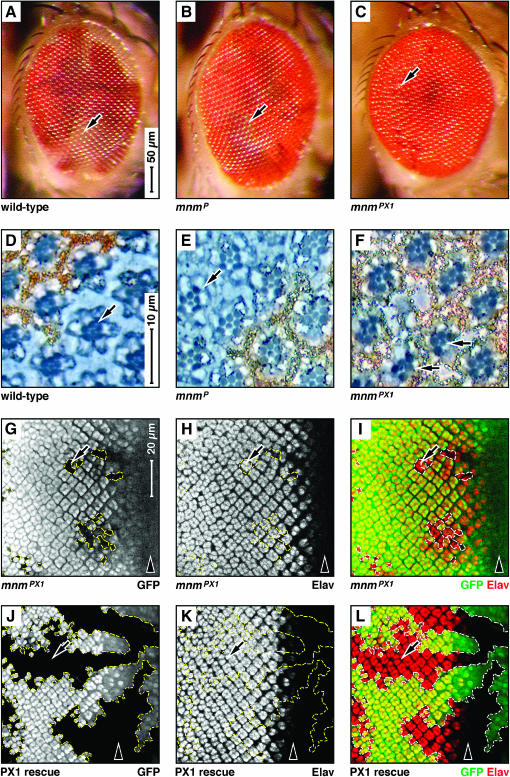
mnm loss-of-function affects eye development. (A–C) Scanning electron micrographs of female adult compound eyes containing ey:Flp-induced mosaic clones marked by white: dorsal, up; anterior, right; scale indicated in A. Genotypes: (A) wild type, (B) mnmP, and (C) mnmPX1. Note that the weak allele mnmP clones are as large as wild type (arrows in A and B) but that the null allele mnmPX1 leaves scars (arrow in C). (D–F) Sections of adult compound eyes containing eyeless:Flp-induced mosaic clones marked by white: dorsal, up; anterior, right; scale indicated in D. Genotypes: (D) wild type, (E) mnmP, and (F) mnmPX1. Note that the wild-type and mnm clones contain mutant (white−) photoreceptor cells (arrows in D–F). (G–L) Third instar eye-imaginal discs containing eyeless:Flp-induced mnmPX1 mosaic clones (outlined), negatively marked by GFP; anterior, right and to the same scale (bar in G). Arrowheads indicate the position of the morphogenetic furrow. (G and J) GFP in white; (H and K) Elav antigen in white; (I and L) GFP in green and Elav in red. Note that mnmPX1 clones are small, but express the differentiation marker Elav (arrow in G–I). (J–L) mnm rescuing transgene (see text). Note that the size of the mnmPX1 clones is entirely rescued (arrows).