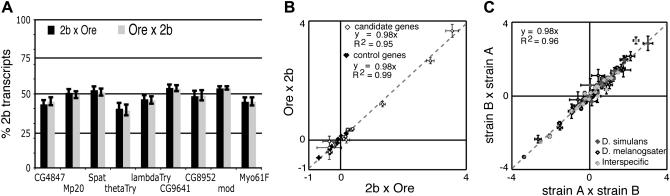
Figure 2.—
Allelic expression in reciprocal crosses indicates a lack of imprinting. (A) The percentage of total transcripts derived from the 2b allele in offspring from reciprocal crosses (2bO and O2b) is shown for imprinting candidate genes. The log2-transformed ratio of allelic expression, log2(Y2b/YOre), was fitted to the mixed model described in the main text. LS means derived from this model were used to calculate the percentage of the 2b allele in each sample. For example, if log2(Y2b/YOre) = 0, then Y2b/YOre = 2° = 1, and Y2b = 50%. Error bars indicate the 95% confidence interval surrounding each LS mean. Note that confidence intervals are not symmetric because the analysis of variance was performed on log-transformed data. LS means of relative allelic expression for 2bO and O2b flies were within 0.3 to 3 times the standard error of each other for all candidate genes. In all cases, this is <4.3 times the standard error (d.f. = 2) that defines the 95% confidence interval. (B) The LS mean and standard errors of log2(Y2b/YOre) are plotted for imprinting candidate genes (open diamonds) and control genes (solid diamonds). Expression in 2bO flies from a cross between 2b females and Ore males is shown on the x-axis, with expression in O2b flies from a cross of Ore females and 2b males shown on the y-axis. (C) Additional tests for imprinting from P. Wittkopp, B. Haerum and A. Clark (unpublished data) are shown. LS means are plotted in both panels with error bars indicating the standard error. Supplemental Table 2 (http://www.genetics.org/supplemental/) summarizes the genes, crosses, LS means, standard errors, and significance tests for all comparisons.