Abstract
The simple organometallic, (μ-S2)Fe2(CO)6, serves as a precursor to synthetic analogues of the chemically rudimentary iron-only hydrogenase enzyme active site. The fundamental properties of the (μ-SCH2CH2CH2S)[Fe(CO)3]2 compound, including structural mobility and regioselectivity in cyanide/carbon monoxide substitution reactions, relate to the enzyme active site in the form of transition-state structures along reaction paths rather than ground-state structures. Even in the absence of protein-based active-site organization, the ground-state structural model complexes are shown to serve as hydrogenase enzyme reaction models, H2 uptake and H2 production, with the input of photo- or electrochemical energy, respectively.
Since the discoveries of hydrogenases (H2ases) in bacteria in 1931 (1, 2) and in Archaea in 1981 (3), their importance in all areas of natural sciences and their potential for technological application (for H2 production as well as efficient H2 uptake in fuel cells) (4, 5) have commanded extensive research effort. In fact, reports of the similarity in H2 uptake and splitting by organometallics such as Co2(CO)8 to produce HCo(CO)4, a species that could easily reproduce the enzymes' activity assay of H/D isotope scrambling in H2/D2O mixtures (6, 7), appeared before the knowledge of metal content in the enzymes! The fact that a bimetallic was chosen as example demonstrated remarkable prescience or, perhaps, just good luck (see below). The dicobaltoctacarbonyl analogy is attractive, particularly in view of the subsequent determination of binuclear organometallic active sites in both Fe-only and [NiFe]H2ases. Nevertheless, binuclear oxidative addition of H2, with concomitant homolytic splitting and formal conversion to two hydrides as in the H2/Co2(CO)8 reaction (8), is not accepted as the mechanism of H2 activation in the metallohydrogenases. From pH-dependent studies it was shown that H2 splitting and presumably H2 formation occur in a heterolytic H+/H− manner (9–11). Subsequent removal of electrons from the metal hydride accounts for an energy-efficient use of H2 as a cellular fuel: H2 ⇄ 2H+ + 2e−. The reverse process produces H2, which is the direction of reactivity to which most [Fe]H2ases are committed (12, 13).
The heterolytic splitting of dihydrogen as a low-energy route to metal hydrides that are reactive toward reducible substrates has been known for decades (14, 15). The requirements for the binding of H2, producing stable (η2–H2)M complexes, are also well understood (16, 17). One of the assemblies that nature has produced for such processes, perfected by evolution over billions of years and exacting exquisite control over H2 binding and release, is the subject of this article.
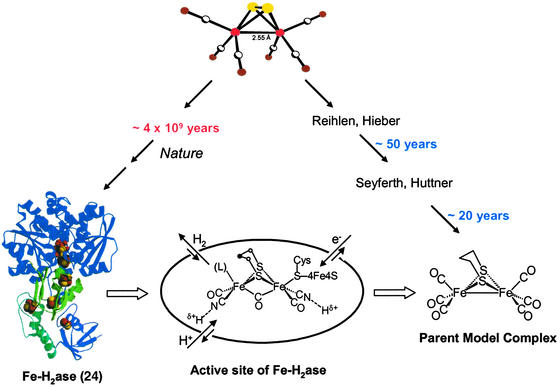
In our view, which is related to those expressed by Wächtershäuser (18), Adams and Stiefel (19), as well as Fontecilla-Camps and coworkers (20), the ultimate ancestor of the distinctly organometallic active site of iron H2ases is diironhexacarbonyldisulfide, i.e., a fragment of the mineral iron sulfide, rendered molecular and mobilized by carbon monoxide (Fig. 1). Over the course of 4 billion years it has been developed by nature, perhaps initially as a template on which condensations of atoms and small molecules created rudimentary organic moieties, perhaps peptidic-like polymers. Later the catalyst became internalized within the protein, evolving to be protected from the oxidizing environment of a maturing Earth. An entirely different biosynthetic scheme would then be obligatory, resulting in a controlled synthesis of an extraordinary and sophisticated catalytic site. The existence and immobilization of diatomic ligands in the metallohydrogenases, both in [NiFe]H2ase (21–23) and [Fe]H2ase (24–29), is truly remarkable in current biochemistry in that carbon monoxide and cyanide are typically poisonous to all life forms.
Figure 1.
Representation of the evolution of CO-mobilized iron sulfide in nature to yield the active site of [Fe]H2ase and in chemists' laboratories to yield model complexes. [The structure of [Fe]H2ase is reprinted with permission from Peters et al. (24) (Copyright 1998 American Association for the Advancement of Science).]
Although such a catalytic role of CO-mobilized iron sulfide in chemical evolution as expressed above has not been substantiated, it finds some support in experiments that have linked low valent primordial carbonylated iron–sulfur compounds to the synthesis of pyruvate in conditions that mimicked hydrothermal vents and ancient environments (30). This concept readily suggests easy synthetic access to compounds that should model the active site of Fe-only H2ase, which also begins with (μ-S2)Fe2(CO)6 (refs. 31 and 32; Fig. 1).
On an entirely different time scale, chemists have established the ability of the diirondisulfide of (μ-S2)Fe2(CO)6 unit to mediate organic transformations at sulfur (33, 34), including the synthesis of model complexes (35) of import to the discussion below. The parent model, (μ-pdt)Fe2(CO)6 (pdt = −S(CH2)3S−), (35) is a complex that reproduces the Fe2S2 core fairly faithfully (36), including the three-light-atom S-to-S linker (Fig. 1). It reacts with cyanide with complete regioselectivity in CN−/CO exchange, yielding one cyanide on each iron, (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)2(CN)]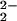 (36–38). The coordination geometry of the dinuclear model complexes is that of a binuclear unit consisting of two edge-bridged square pyramids. The formal oxidation state of the iron is +1, and, to achieve an 18-electron count on each iron, a metal—metal bond is required, consistent with the observed Fe⋅⋅⋅Fe distance of 2.5 Å.
(36–38). The coordination geometry of the dinuclear model complexes is that of a binuclear unit consisting of two edge-bridged square pyramids. The formal oxidation state of the iron is +1, and, to achieve an 18-electron count on each iron, a metal—metal bond is required, consistent with the observed Fe⋅⋅⋅Fe distance of 2.5 Å.
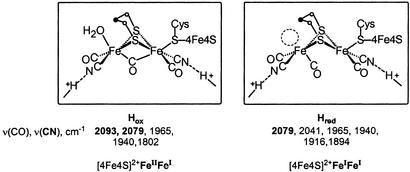
The [Fe]H2ase active-site structure (39) defines what was known to be an unusual [6Fe6S] cluster, referred to as the H cluster or hydrogen-producing cluster. Protein crystallography resolved the H cluster into two components. A typical [4Fe4S] cluster is cysteine-bridged to an unusual [2Fe2S] unit. The former is one of several [4Fe4S] ferredoxin units positioned 12.5 Å apart that define the electron-transfer path from the buried active site to the exterior of the protein, a feature observed in structures of all metallohydrogenases. The [2Fe2S] unit is of similar composition and overall geometry as the organometallic model complexes with an Fe2S2 butterfly core and an Fe⋅⋅⋅Fe distance of 2.6 Å. They differ in the orientation of the two-edge-bridged square pyramids: The model complexes place “open” sites underneath the μ-S2Fe2 unit; the binuclear active site has one square pyramid inverted with respect to the other. This gives the appearance of an open site on a single iron in one form of the enzyme, denoted by the dashed circle in Fig. 2. The apparent open site in the reduced form, Hred (25, 26), of the enzyme, presumed to be FeIFeI, might be occupied by a hydrogenic species, H2 or H−, undetected by protein crystallography. The site is definitely occupied by H2O in the oxidized form, Hox (24), and by CO in the CO-inhibited, oxidized form of the enzyme (27). The latter, established by both crystallography and IR spectroscopy (40, 41), is a strong indicator of substrate site binding.
Figure 2.
Structures, ν(CO), ν(CN) stretching frequencies (26), and possible oxidation-state assignments of the oxidized (Hox) and reduced (Hred) forms of the [Fe]H2ase (44) (Fe⋅⋅⋅Fe distances are 2.6 Å for both).
The identity of the three light atoms that link sulfurs in the enzyme active site cannot be unambiguously determined by protein crystallography. If, as initially modeled (25), all three are carbon, propane dithiolate would be an entirely new organic cofactor in biochemistry. A supposition that the central atom might be a heteroatom such as nitrogen (26), introducing an internal base proximal to the H2-binding or H2-producing site and well positioned to either deliver or extract protons, is attractive (42). However, it is not, at the time of this writing, verifiable; the biosynthesis of [Fe]H2ase remains unknown. A synthetic route to (μ-SCH2N(Me)CH2S)[Fe(CO)3]2 derived from condensation of methyl amine and formaldehyde (Eq. 1) lends support to the supposition that iron sulfide might template small-molecule transformation to an elaborated organic moiety (43).
 |
1 |
The inverted square pyramid that exists in the Fe2S2 unit on the iron distal to the [4Fe4S] cluster in the reduced form of [Fe]H2ase places a CO underneath the Fe—Fe vector. Its bonding character depends on the enzyme redox level. IR spectral studies have found three different oxidation levels based on stretching frequencies of the diatomic ligands in [Fe]H2ase (26). The results of Hox and Hred corroborate the differences established in x-ray crystal structures, which found movement of the bridging CO in the Hox to terminal in Hred (Fig. 2). Note that the mobile CO is trans to the cysteine sulfur that bridges to the proximal [4Fe4S] cluster. Thus as electrons enter or leave the dinuclear active-site cluster, the μ-CO is well situated to moderate charge differences with only minor structural changes. Interpretation of Mössbauer (44) and EPR data (45, 46) and correlation of IR spectra with model compounds (40) permit oxidation-state assignments of FeIIFeI to Hox and FeIFeI to Hred. The [4Fe4S] cluster maintains a +2 redox level in these two states, Hox and Hred (44–46).
This bridging CO (≈1,800 cm−1) in Hox, which may exist as semibridging (≈1,850 cm−1) or terminal (1,895 cm−1) in the Hred, is one of the active-site features that small-molecule models have not yet been able to reproduce as ground-state, stable moieties. A second is the paramagnetic oxidized form of the enzyme, i.e., the FeIIFeI mixed-valent species. Such a lack of stability signals the important role of the protein in evolving or developing the active site to perform difficult functions with ease. Desirable properties as are elusive in thermodynamically stable model compounds, the structures of which are dictated solely by first coordination sphere requirements of metal and ligand, require structural forms of higher energy, similar to intermediates or transition states along reaction paths or molecular rearrangement profiles. This is a statement of the entatic-state principle as expressed by Vallee and Williams in 1968 (47). The following summary of fundamental properties of {(μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)2L]2 (L = CO, CN−, PMe3)} model complexes provided the basis for this conclusion.
Stereochemical Nonrigidity of (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)3]2 Model Complexes
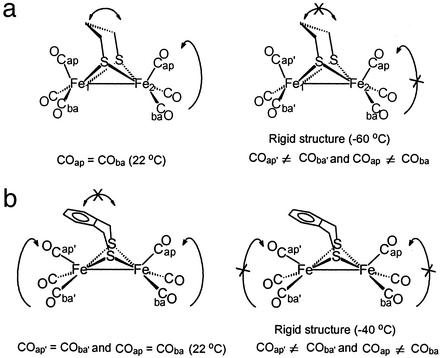
An obvious structural feature of the (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)3]2 complexes is the ease with which molecular rearrangements occur. Stereochemical nonrigidity exists in the iron dithiacyclohexane moiety of (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3]2 as shown by variable-temperature 1H-NMR studies (48). In contrast, at 22°C the bridge is fixed in the (μ-o-xyldt)[Fe(CO)3]2, making the two iron atoms nonequivalent (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Stereochemical nonrigidity of (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3]2 (a) and (μ-o-xyldt)[Fe(CO)3]2 (b).
Variable-temperature 13C-NMR spectra established the intramolecular dynamics of the carbonyls in (μ-SRS)Fe2(CO)6 to be restricted to basal/apical CO site exchange in individual Fe(CO)3 units (ref. 48; Fig. 3). This study found a lower rotational barrier for the (μ-o-xyldt)[Fe(CO)3]2 as compared with the other members of the series. Relief of the repulsive interaction of the arene group with the apical CO ligand, i.e., a steric assist to rotation, accounts for the lower barrier. This conclusion was corroborated and extended by density functional theory computations (49).
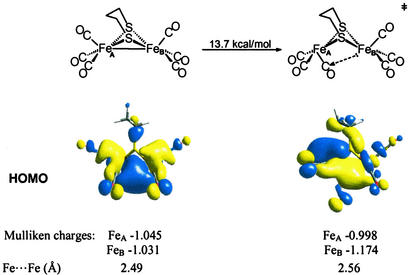
Fig. 4 presents results of density functional theory computations of the intramolecular CO-site exchange processes in (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3]2 (49). The computed activation barrier of 13.7 kcal/mol is consistent with that estimated from the NMR coalescence temperatures. More interesting is the change in the highest occupied molecular orbitals resulting from structural differences of ground-state and transition-state structures. The optimized transition-state geometry is not a simple 60° staggering of the eclipsed Fe(CO)3 units in the ground-state structure. Rather, as the rotation occurs, the CO that comes underneath the Fe—Fe bond vector develops a slight bend concomitant with overall flattening of the rotated S2Fe(CO)3 unit.
Figure 4.
Polarization of Fe—Fe bond electron density upon Fe(CO)3 unit rotation in (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3]2 as shown by the highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMOs) and the Mulliken charges.
If the ground-state (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3]2 is viewed as a symmetrical edge-bridged square pyramid, the transition state for Fe(CO)3 rotation shows that one square pyramid is inverted relative to the other. Further consequences are: (i) there develops a partial disruption and lengthening of the Fe—Fe bond; (ii) the Fe—Fe bond density is polarized toward the unrotated iron; (iii) this polarized bond density is partially dispersed onto the CO group that lies underneath the Fe—Fe vector; and (iv) a charge disparity develops with the iron of the rotated Fe(CO)3 unit being ≈0.2 units more positive and presenting itself with an apparent open site.
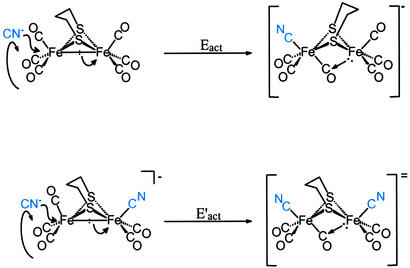
It did not go unnoticed that the transition-state structure of the model complex in such a rotated state, as shown in Fig. 4, resembled that of the reduced enzyme active site, perhaps implying that the latter has been trapped in a high-energy conformation, locked by H-bonding and other protein interactions in a position so as to readily perform functions of the catalyst. For example, if a better electron-donating ligand were to be trans to the incipient bridging CO group, a stronger donation from FeB to the μ-CO should be possible, better “fixing” the structure. This position is occupied by the S of cysteine bridged to [4Fe4S] cluster in the enzyme active site. The steric interaction of the central unit in the irondithiacyclohexane ring is also expected to stabilize the rotated state. Such expectations gained credibility with further computations of isomeric forms of (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3][Fe(CO)2(CN)]− (49). Consistent with NMR results, the lowest barrier to rotation is for the Fe(CO)3 unit within the monocyano derivative (Eq. 2). The computations again found a steric assist to the rotation process.
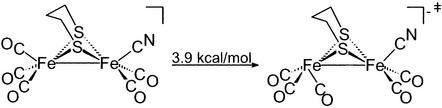 |
2 |
The dependence of configurational mobility on the steric nature of μ-SRS and the electronic character of the substituent ligand helped account for the R dependence in the cyanide substitution reactions, described below.
Chemical- and Regioselectivity in CN−/CO Exchange Reactions in (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)3]2: Reaction Profiles
Detailed kinetic studies (Eqs. 3 and 4) established the CN−/CO substitution process in (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)3]2 [R = −CH2CH2− (edt), −CH2CH2CH2− (pdt), or −CH2C6H4CH2−(o-xyldt)], which yields the disubstituted derivatives, (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)2(CN)]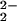 , is a two-step process in which both steps follow associative (SN2) pathways (48).
, is a two-step process in which both steps follow associative (SN2) pathways (48).
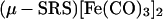 |
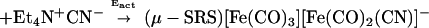 |
3 |
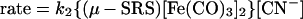 |
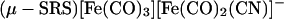 |
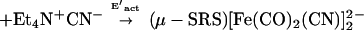 |
4 |
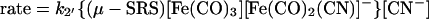 |
The relative rates of addition of the cyanides has an R-dependent reactivity pattern that cannot be explained based on the electronic effect of the μ-SRS bridge; as indicated by the ν(CO) stretching frequencies of the (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)3]2, all the bridges have similar electron donor abilities. For μ-SRS = μ-o-xyldt, E′act is greater than Eact, whereas for μ-pdt, the opposite order was observed, Eact > E′act! The latter result was unexpected, because nucleophilic attack of an anion on an anion typically results in rate inhibition. The origin of what appeared to be a cooperative effect of the first cyanide for addition of the second became a focus of study that involved the fundamental structural characteristics of dithiolatodiironhexacarbonyl complexes described above. The fact that the (μ-o-xyldt)[Fe(CO)3]2 that has a lower barrier of Fe(CO)3 unit rotation demonstrated faster CN−/CO reactivity suggests a connection between the mobility of the Fe(CO)3 unit and the reactivity of the molecule toward CN−. This relationship is embodied in the mechanism expressed in Fig. 5 as a possibility of CN−/CO substitution reaction pathway. It resolves the overall activation energy, Eact(overall), into two processes: CN− attack, Eact(CN− attack); and rotation, Eact(rot'n) (Eq. 5).
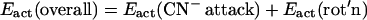 |
5 |
Thus the proposed mechanism for the CN− displacement of CO given in Fig. 5 provides rationale for the cooperative effect of the intrinsic cyanide during the nucleophilic attack of the second CN−. The SN2 character of the cyanide reaction results in displacement of the Fe—Fe bond density concomitant with rotation of the Fe(CO)3 unit, positioning one CO underneath the Fe—Fe vector and aiding in delocalizing the electron density that was displaced toward the unrotated iron. According to this mechanism the second CN− finds a lower rotational barrier due to the presence of the already coordinated anionic CN− ligand, which stabilizes the resulting bridging CO and the rotated form of the inverted square pyramid. This explains the similarity of the activation parameters for the second CN− addition for both the aliphatic (pdt and edt) and aromatic (o-xyldt) bridges. In the case of the (μ-o-xyldt)[Fe(CO)3]2 there is an assist even for the first CN− attack. It comes from the repulsive CO/arene interaction that lowers the rotational barrier and, as a result, the activation energy for the first CN− addition. Because this assist is missing from the edt completely and is less substantial for the pdt bridge, the first CN− attack finds a higher activation barrier in these binuclear complexes of aliphatic bridges as compared with the aromatic ο-xyldt.
Figure 5.
Proposed mechanism for the two-step CN−/CO substitution reaction in (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3]2 to yield (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)2(CN)]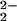 .
.
Such a hypothesis as presented for the CN−/CO substitution mechanism has been supported by density functional theory calculations of the Fe(CO)3 unit rotation in (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3]2, which compared the various transition-state possibilities of (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3]2 and (μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)3][Fe(CO)2CN]− as discussed earlier. That the second CN− attack process might have a similar barrier to the first bespeaks the increased stabilization of the rotated Fe(CO)3 unit when the adjacent iron atom is rendered more electron-rich in the Fe(CO)2(CN) form.
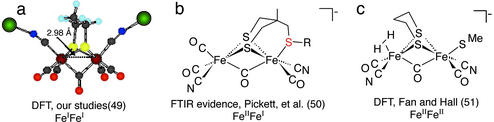
The extent of the actual bridging character of that CO group positioned beneath the Fe—Fe vector increases as the entering CN− docks into the opened coordination position on iron. This conclusion is based on density functional theory computations of the reaction profile of the CN−/CO substitution process, which includes the intermediate shown in Fig. 6a (49). In this study a sodium cyanide ion pair in the form of CN−⋅⋅⋅Na+ was used instead of CN− to avoid the charge difference between the species involved in the process. More definite evidence for such a μ-CO as might be in the CO-inhibited, oxidized form of the enzyme comes from Fourier transform IR spectral data of an electrochemically generated FeIIFeI, Fe2S3 complex, which shows an almost precise match of the ν(CN), ν(CO) values with those of the enzyme (Fig. 6b; ref. 50). The η2–H2 complex indicated in Fig. 6c results from the theoretical modeling of the functioning enzyme active site (51); its binding or stabilization requires d6 FeII.
Figure 6.
Calculated and observed diiron complexes with a bridging CO group, closer structural analogues to the active site of [Fe]H2ase.
The Quest for Models that Function as Does the [Fe]H2ase Active Site
H2 Uptake.
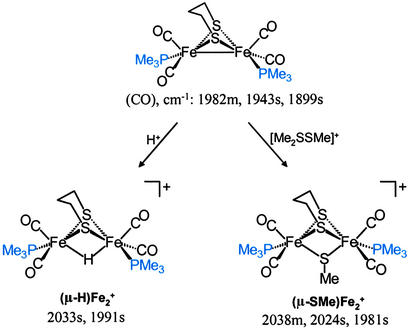
The structural match of the rotated, transition-state form of (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)3]2 model complexes with the enzyme active site does not provide a functional similarity. The all-carbonyl complex does not take up a proton, nor does it bind molecular H2. In a reduced FeIFeI form the enzyme active site performs the former, whereas the latter requires the one-electron more-oxidized form, FeIIFeI. Although Pickett and coworkers (50) have reported evidence for such a species from spectroelectrochemical studies, such a stable mixed-valent species is not achieved easily in the chemist's laboratory. However, the binuclear FeIFeI complexes, rendered more electron-rich by CO exchange with PMe3, react with electrophiles, E+, and engage the FeIFeI-bond density in binuclear oxidative addition, yielding FeIIFeII species in the form of (μ-E)(μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)2(PMe3)]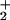 (Scheme S1; refs. 52–54).
(Scheme S1; refs. 52–54).
Scheme 1.
Binuclear oxidative addition of electrophiles H+ and SMe+ to FeIFeI.
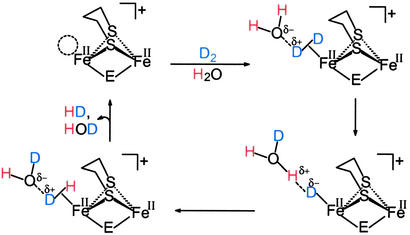
Both d6 Fe(II) binuclear complexes in Scheme S1 were shown to (i) have photochemically labile CO groups and (ii) mediate isotopic scrambling in H2/D2O or D2/H2O mixtures under photolytic conditions (52–54). Such H/D-exchange reactions are consistent with H2ase activity test reactions. A possible mechanism for this exchange is given in Scheme S2 in which the open site for H2 binding is positioned trans to the bridging ligand (H or SMe) similarly to the enzyme active site in which the H2 binds trans to the bridging CO group. In the presence of water, mixtures of H2 and D2 also show isotopic scrambling to HD, with both E = H or SMe. In the absence of water, only the (μ-H)(μ-pdt)[Fe(CO)2(PMe3)]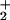 has the capability to catalyze H/D exchange in mixtures of H2 and D2 to produce HD (52, 53).
has the capability to catalyze H/D exchange in mixtures of H2 and D2 to produce HD (52, 53).
Scheme 2.
H/D exchange mechanism.
It must be stressed that the FeIIFeII-bridging hydride complexes serve to provide a functional model, the similarity to the enzyme active site of which rests in their binuclearity, their Fe2S2 core, and their ability to bind and heterolytically activate H2 or D2 at an FeII site. We do not wish to imply that a (μ-H)(μ-SRS)Fe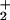 core exists in the enzyme active site. Rather the (μ-SRS)FeIIFeI core is created electrochemically from (μ-SRS)(FeI)2, generating a coordinately unsaturated, 16-e−, FeII center, the ground-state structure of which matches the expected transition state in our ligand substitution reactions in (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)3]2. It also matches the transition state and intermediate in the coordinately unsaturated (μ-E)(μ-SRS)FeII2 that serves to bind and activate H2.
core exists in the enzyme active site. Rather the (μ-SRS)FeIIFeI core is created electrochemically from (μ-SRS)(FeI)2, generating a coordinately unsaturated, 16-e−, FeII center, the ground-state structure of which matches the expected transition state in our ligand substitution reactions in (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)3]2. It also matches the transition state and intermediate in the coordinately unsaturated (μ-E)(μ-SRS)FeII2 that serves to bind and activate H2.
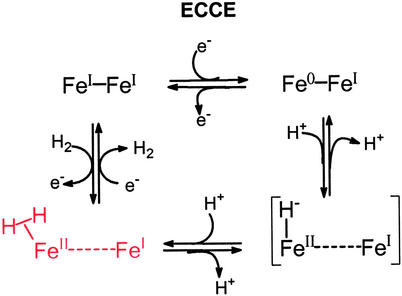
H2 Production Mechanisms.
The expected prominent intermediate in H2 uptake by the [Fe]H2ase active site shown below is, by microscopic reversibility, present in H2 production. Rates of proton and electron transfer to the site as well as H2 release account for the rapid rates of H2 production in [Fe]H2ases.
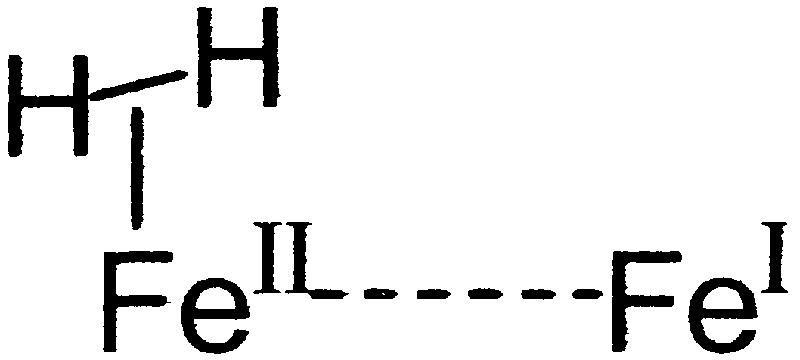 |
Thus the (η2–H2)FeII–FeI species is a principal in several electrochemical paths, deriving from iron(I) complexes as inaugural points. The electrochemical-chemical-chemical- electrochemical process expressed (clockwise from FeI–FeI) in Scheme S3 (D. Chong, I.P.G., M. L. Miller, R. Mejia-Rodriguez, and M.Y.D., unpublished data) has reduction to the Fe0FeI mixed-valent species preceding protonation. This mechanism applies to the neutral FeI–FeI model complexes, (μ-SRS)[Fe(CO)2L]2 (L = CO or PMe3), in the presence of acetic acid in CH3CN solvent. Electrochemical studies in our laboratories (D. Chong, I.P.G., M. L. Miller, R. Mejia-Rodriguez, and M.Y.D., unpublished data) and others (55) verify catalytic H2 production at potentials that depend on the donor ability of L and to a lessor extent on the nature of R. The all-CO complex better stabilizes the reduced Fe0FeI intermediate, and produces H2 at potentials ≈500 mV more positive than the complex with L = PMe3. The latter complex, however, enjoys greater stability over long periods of electrolysis. It is also expected (as yet not demonstrated) to be more apt to participate in the reverse, H2 uptake electrocatalytic process as the PMe3 ligand better stabilizes FeII. The mixture of carbon monoxide and cyanide ligands (with H bonding to the cyanide-nitrogen) permits such catalytic tuning and control in the enzyme active site.
Scheme 3.
Mechanism for electrocatalytic production of H2.
Conclusions
The fundamental characteristics that lead to H2ase-like reactivity in the binuclear complexes that serve as structural models of [Fe]H2ase provide a firm reference point for the oxidation states that are needed for H+ or H2 uptake and correlate redox levels with directionality of H2 reactivity. The extremely fast turnovers of H2 production in the [Fe]H2ase (estimated at 9,000 molecules of H2 per sec at 30°C for Desulfovibrio desulfuricans) (56) suggest that major structural rearrangements are not occurring during the catalytic process. Thus the structural integrity of the “rotated” state, or inverted square pyramid shown below as the H2 production form of the active site, permits electron density to flow from the [4Fe4S] “wire” into the Fe—Fe bond. Polarization onto the distal iron results in monocentric oxidative addition of a proton to Fe0 and generates FeII–H and, after addition of the second proton, the η2–H2. Although release of H2 is rapid in an electron-rich environment, the site accommodates binding H2 as a nucleophile, when electron flow is reversed into the [4Fe4S] cluster. The CO that was terminal and permitted Fe⋅⋅⋅Fe contact in the H2-producing mode now becomes bridging to better stabilize electron-deficient structures.
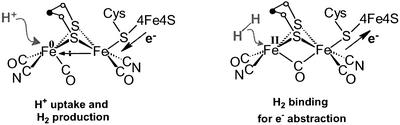 |
The reversibility of the reaction performed by the H2ase enzyme may rest in the minimal active-site conformational changes. Protonation of the FeIFeI model complexes in their ground states yields stable bridging hydrides that are not susceptible to subsequent protonation without the input of electrons at electropotentials much more negative that those observed in the enzyme. The formation of the bridging hydrides is prevented in a similarly reduced form of the active site of the enzyme by virtue of the rotated structure that positions a CO group beneath the Fe—Fe bond vector.
Of the many binuclear active sites now known to exist in metalloenzymes, that of the [Fe]H2ase is arguably the simplest. It is attached to the protein by only one covalently bound ligand and a few H bonds. The points of catalytic control are subtle and apparently involve low energy and minor molecular motions within the first coordination sphere once it is poised in an orientation conducive to its chemical performance.
Acknowledgments
We thank group members Dr. Daesung Chong, Rosario Mejia-Rodriguez, Chao-Yi Chiang, Matt Miller, and Jesse Tye for their contributions. We are grateful to our collaborators, Professor Michael B. Hall and Dr. Lisa M. Thomson of the Laboratory of Molecular Simulations (Texas A&M University), and to the Supercomputing Facility at Texas A&M University for computer time. We acknowledge financial support from National Science Foundation Grant CHE-0111629 and contributions from the R. A. Welch Foundation.
Abbreviation
- H2ase
hydrogenase
Footnotes
This paper was submitted directly (Track II) to the PNAS office.
References
- 1.Stephenson M, Stickland L H. Biochem J. 1931;25:205–214. doi: 10.1042/bj0250205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Adams M W W, Mortenson L E, Chen J-S. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;594:105–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(80)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Graf E-G, Thauer R K. FEBS Lett. 1981;136:165–169. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cammack R, Frey M, Robson R, editors. Hydrogen as a Fuel. London: Taylor & Francis; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hoffmann P. Tomorrow's Energy: Hydrogen, Fuel Cells, and Prospects for a Cleaner Planet. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Farkas A, Farkas L, Yudkin J. Proc R Soc London Ser B. 1934;115:373–379. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Krasna A I, Rittenberg D. J Am Chem Soc. 1954;76:3015–3020. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ungváry F. J Organomet Chem. 1972;36:363–370. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lespinat P A, Berlier Y, Fauque G, Czechowski M, Dimom B, LeGall J. Biochimie. 1986;68:55–61. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Teixeira M, Fauque G, Moura I, Lespinat P A, Berlier Y, Prickril B, Peck H D, Jr, Xavier A V, LeGall J, Moura J J G. Eur J Biochem. 1987;167:47–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Albracht S P J. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1188:167–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vignais P M, Billoud B, Meyer J. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2001;25:455–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2001.tb00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Frey M. Chembiochem. 2002;3:153–160. doi: 10.1002/1439-7633(20020301)3:2/3<153::AID-CBIC153>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Halpern J, Milne J B. Proc Int Congr Catal, 2nd. 1960;1:445–457. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Halpern J. J Organomet Chem. 1980;200:133–144. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kubas G J, Ryan R R, Swanson B I, Vergamini P J, Wasserman H J. J Am Chem Soc. 1984;106:451–452. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kubas G J. Acc Chem Res. 1988;21:120–128. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wächtershäuser G. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1992;58:85–201. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(92)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Adams M W W, Stiefel E I. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2000;4:214–220. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(99)00077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Garcin E, Vernède X, Hatchikian E C, Volbeda A, Frey M, Fontecilla-Camps J C. Structure (London) 1999;7:557–566. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Volbeda A, Garcin E, Piras C, De Lacey A L, Fernandez V M, Hatchikian E C, Frey M, Fontecilla-Camps J C. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118:12989–12996. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bagley K A, Van Garderen C J, Chen M, Duin E C, Albracht S P J, Woodruff W H. Biochemistry. 1994;33:9229–9236. doi: 10.1021/bi00197a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pierik A J, Roseboom W, Happe R P, Bagley K A, Albracht S P J. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:3331–3337. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.6.3331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Peters J W, Lanzilotta W N, Lemon B J, Seefeldt L C. Science. 1998;282:1853–1858. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5395.1853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nicolet Y, Piras C, Legrand P, Hatchikian C E, Fontecilla-Camps J C. Structure (London) 1999;7:13–23. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nicolet Y, De Lacey A L, Vernède X, Fernandez V M, Hatchikian E C, Fontecilla-Camps J C. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:1596–1601. doi: 10.1021/ja0020963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lemon B J, Peters J W. Biochemistry. 1999;38:12969–12973. doi: 10.1021/bi9913193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Van der Spek T M, Arendsen A F, Happe R P, Yun S, Bagley K A, Stufkens D J, Hagen W R, Albracht S P J. Eur J Biochem. 1996;237:629–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0629p.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pierik A J, Hulstein M, Hagen W R, Albracht S P J. Eur J Biochem. 1998;258:572–578. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2580572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cody G D, Boctor N Z, Filley T R, Hazen R M, Scott J H, Sharma A, Yoger H S., Jr Science. 2000;289:1337–1340. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5483.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Reihlen H, Gruhl A, Hessling G. Liebigs Ann Chem. 1929;472:268–287. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hieber W, Spacu P. Z Anorg Allg Chem. 1937;233:852–864. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Seyferth D, Henderson R S, Song L-C. Organometallics. 1982;1:125–133. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Seyferth D, Womack G B, Gallagher M K, Cowie M, Hames B W, Fackler J P, Jr, Mazany A M. Organometallics. 1987;6:283–294. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Winter A, Zsolnai L, Huttner G. Z Naturforsch, B: Anorg Chem, Org Chem. 1982;37:1430–1436. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lyon E J, Georgakaki I P, Reibenspies J H, Darensbourg M Y. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1999;38:3178–3180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schmidt M, Contakes S M, Rauchfuss T B. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:9736–9737. [Google Scholar]
- 38. Le Cloirec, A., Best, S. P., Borg, S., Davies, S. C., Evans, D. J., Hughes, D. L. & Pickett, C. J. (1999) Chem. Commun., 2285–2286.
- 39.Nicolet Y, Lemon B J, Fontecilla-Camps J C, Peters J W. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:138–143. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01536-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.De Lacey A L, Stadler C, Cavazza C, Hatchikian E C, Fernandez V M. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:11232–11233. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen Z, Lemon B J, Huang S, Swartz D J, Peters J W, Bagley K A. Biochemistry. 2002;41:2036–2043. doi: 10.1021/bi011510o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fan H-J, Hall M B. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:3828–3829. doi: 10.1021/ja004120i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Li H, Rauchfuss T B. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:726–727. doi: 10.1021/ja016964n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Popescu C V, Münck E. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:7877–7884. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pereira A S, Tavares P, Moura I, Moura J J G, Huynh B H. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:2771–2782. doi: 10.1021/ja003176+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bennett B, Lemon B J, Peters J W. Biochemistry. 2000;39:7455–7460. doi: 10.1021/bi992583z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vallee B L, Williams R J. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1968;59:498–505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lyon E J, Georgakaki I P, Reibenspies J H, Darensbourg M Y. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:3268–3278. doi: 10.1021/ja003147z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Georgakaki, I. P., Thomson, L. M., Lyon, E. J., Hall, M. B. & Darensbourg, M. Y. (2003) Coord. Chem. Rev., in press.
- 50. Razavet, M., Borg, S. J., George, S. J., Best, S. P., Fairhurst, S. A. & Pickett, C. J. (2002) Chem. Commun., 700–701. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 51.Cao Z X, Hall M B. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:3734–3742. doi: 10.1021/ja000116v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhao X, Georgakaki I P, Miller M L, Yarbrough J C, Darensbourg M Y. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:9710–9711. doi: 10.1021/ja0167046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zhao X, Georgakaki I P, Miller M L, Mejia-Rodriguez R, Chiang C-Y, Darensbourg M Y. Inorg Chem. 2002;41:3917–3928. doi: 10.1021/ic020237r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Georgakaki, I. P., Miller, M. L. & Darensbourg, M. Y. (2003) Inorg. Chem., in press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 55.Gloaguen F, Lawrence J D, Rauchfuss T B. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:9476–9477. doi: 10.1021/ja016516f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cammack R. Nature. 1999;397:214–215. doi: 10.1038/16601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]