Abstract
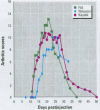
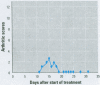
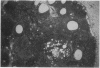
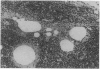
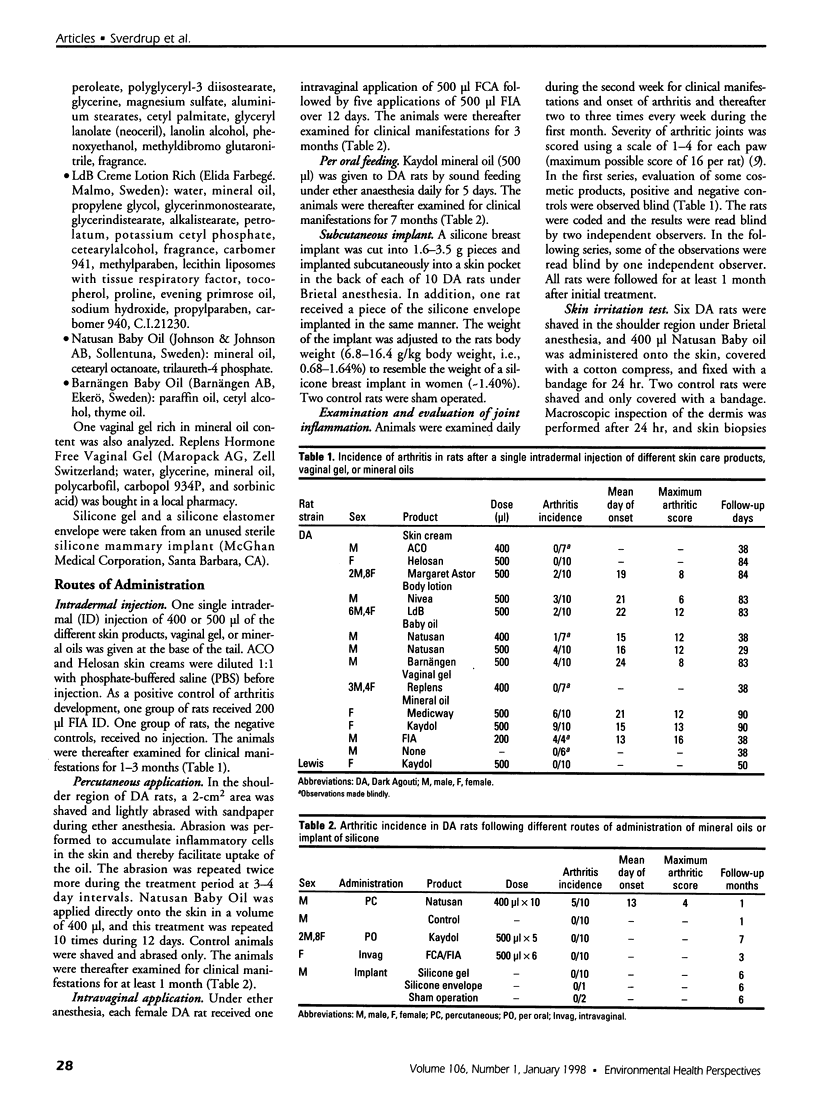
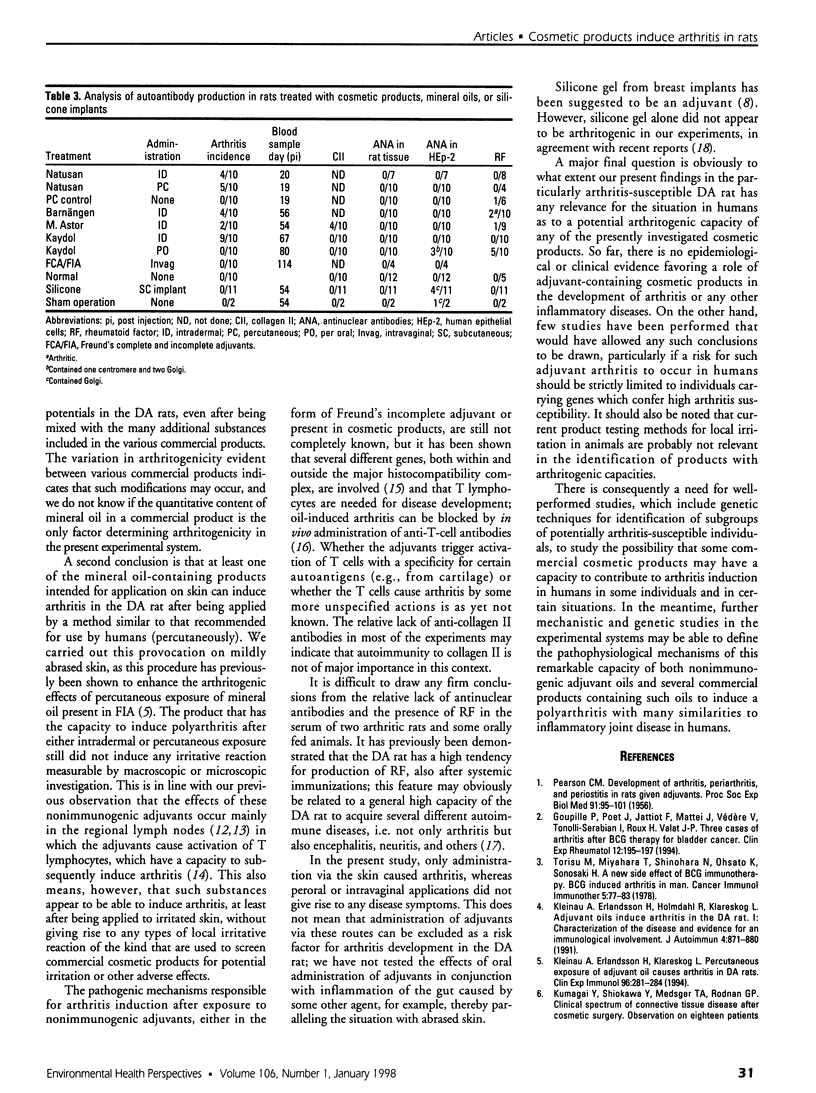
Many different agents, including mineral oil and silicone, have the capacity to act as immunological adjuvants, i.e., they can contribute to the activation of the immune system. Some adjuvants, including mineral oil, are known to induce arthritis in certain strains of rats after intradermal injection or percutaneous application. The aim of this study was to determine if common commercial cosmetic products containing mineral oil could induce arthritis in the highly susceptible DA (Dark Agouti) rat. Intradermal injection of five out of eight assayed cosmetic products without further additives resulted in arthritis with synovitis. One of the products induced a very aggressive arthritis, which had declined after 5-9 weeks. When this product was also assayed for arthritogenicity upon percutaneous administration, it induced a mild and transient arthritis in 5 out of 10 DA rats, whereas control animals showed no clinical signs of joint involvement. No arthritic reaction was seen in rats after peroral feeding with the most arthritogenic product or by intravaginal application of Freund's adjuvants. Silicone gel implants in DA rats did not cause arthritis. We conclude that mineral oils included in common commercially available products retain their adjuvant properties and are arthritogenic in the presently investigated arthritis-prone rat strain. There is yet no evidence that mineral oils present in cosmetics may contribute to arthritis in humans, but we suggest that this question should be subject to further investigation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eneström S., Hultman P. Immune-mediated glomerulonephritis induced by mercuric chloride in mice. Experientia. 1984 Nov 15;40(11):1234–1240. doi: 10.1007/BF01946653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goupille P., Poet J. L., Jattiot F., Mattei J. P., Védère V., Tonolli-Serabian I., Roux H., Valat J. P. Three cases of arthritis after BCG therapy for bladder cancer. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994 Mar-Apr;12(2):195–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg M. C., Perlmutter D. L., Medsger T. A., Jr, Nguyen K., Steen V., Weisman M. H., White B., Wigley F. M. Lack of association between augmentation mammoplasty and systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jul;39(7):1125–1131. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Goldschmidt T. J., Kleinau S., Kvick C., Jonsson R. Arthritis induced in rats with adjuvant oil is a genetically restricted, alpha beta T-cell dependent autoimmune disease. Immunology. 1992 Jun;76(2):197–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinau S., Dencker L., Klareskog L. Oil-induced arthritis in DA rats: tissue distribution of arthritogenic 14C-labelled hexadecane. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1995 May;17(5):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(95)00020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinau S., Erlandsson H., Holmdahl R., Klareskog L. Adjuvant oils induce arthritis in the DA rat. I. Characterization of the disease and evidence for an immunological involvement. J Autoimmun. 1991 Dec;4(6):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90050-M. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinau S., Erlandsson H., Klareskog L. Percutaneous exposure of adjuvant oil causes arthritis in DA rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 May;96(2):281–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinau S., Klareskog L. Oil-induced arthritis in DA rats passive transfer by T cells but not with serum. J Autoimmun. 1993 Aug;6(4):449–458. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1993.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson P., Kleinau S., Holmdahl R., Klareskog L. Homologous type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Characterization of the disease and demonstration of clinically distinct forms of arthritis in two strains of rats after immunization with the same collagen preparation. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):693–701. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentzen J. C., Issazadeh S., Storch M., Mustafa M. I., Lassman H., Linington C., Klareskog L., Olsson T. Protracted, relapsing and demyelinating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in DA rats immunized with syngeneic spinal cord and incomplete Freund's adjuvant. J Neuroimmunol. 1995 Dec 31;63(2):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(95)00153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentzen J. C., Olsson T., Klareskog L. Susceptibility to oil-induced arthritis in the DA rat is determined by MHC and non-MHC genes. Transplant Proc. 1995 Apr;27(2):1532–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müssener A., Klareskog L., Lorentzen J. C., Kleinau S. TNF-alpha dominates cytokine mRNA expression in lymphoid tissues of rats developing collagen- and oil-induced arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1995 Jul;42(1):128–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1995.tb03635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naim J. O., Lanzafame R. J., van Oss C. J. The adjuvant effect of silicone-gel on antibody formation in rats. Immunol Invest. 1993 Mar;22(2):151–161. doi: 10.3109/08820139309063397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. Development of arthritis, periarthritis and periostitis in rats given adjuvants. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jan;91(1):95–101. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERMYLEN C., DE VREKER R. A., VERSTRAETE M. A rapid enzymatic method for assay of fibrinogen fibrin polymerization time (FPT test). Clin Chim Acta. 1963 May;8:418–424. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]