Abstract
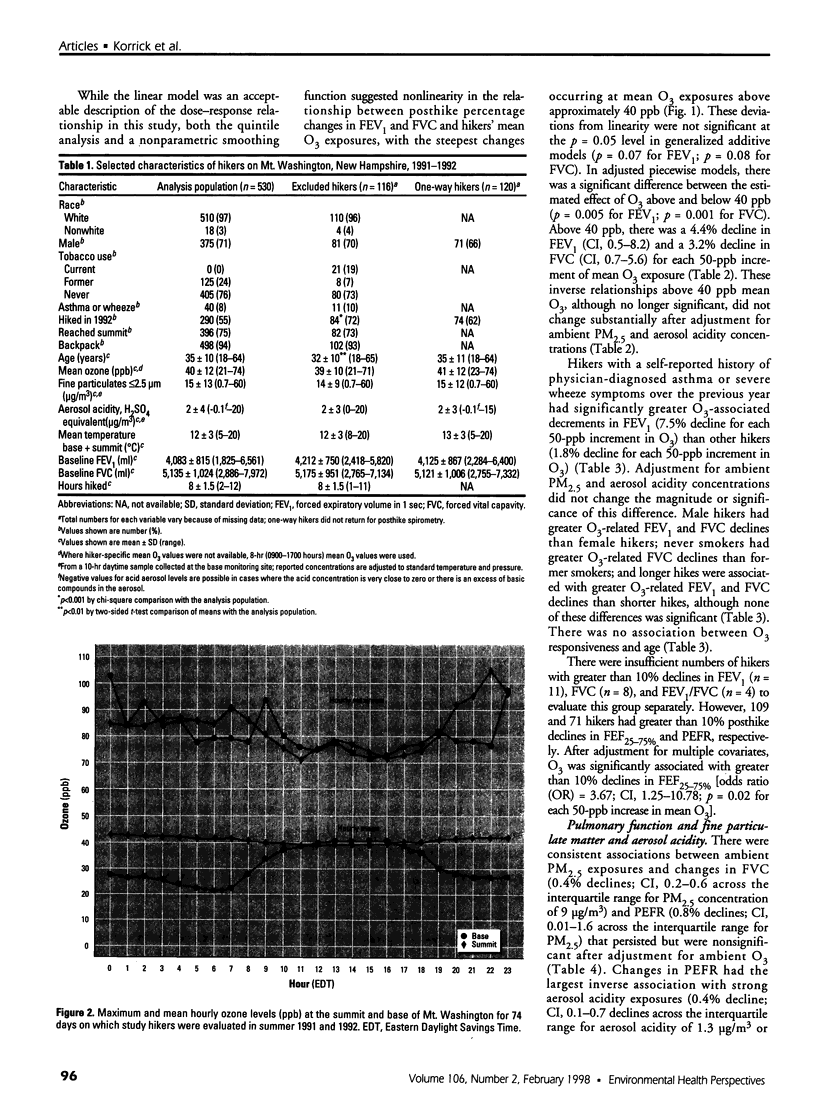
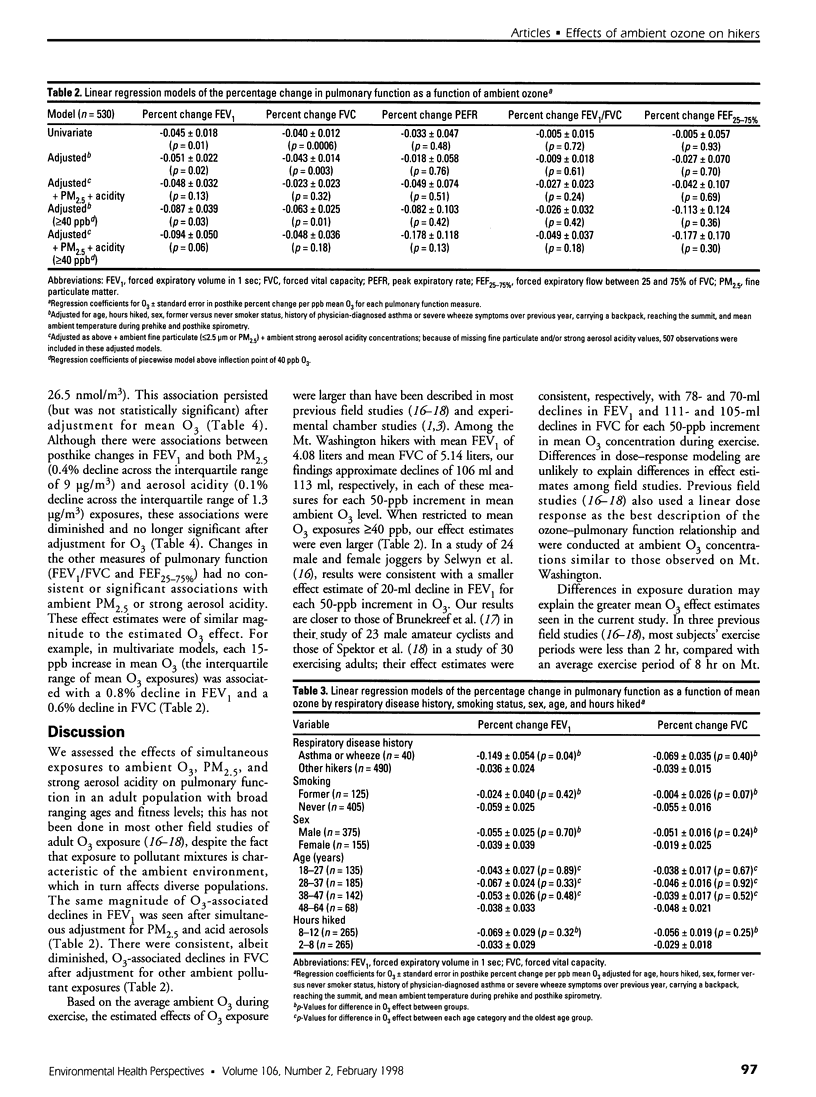
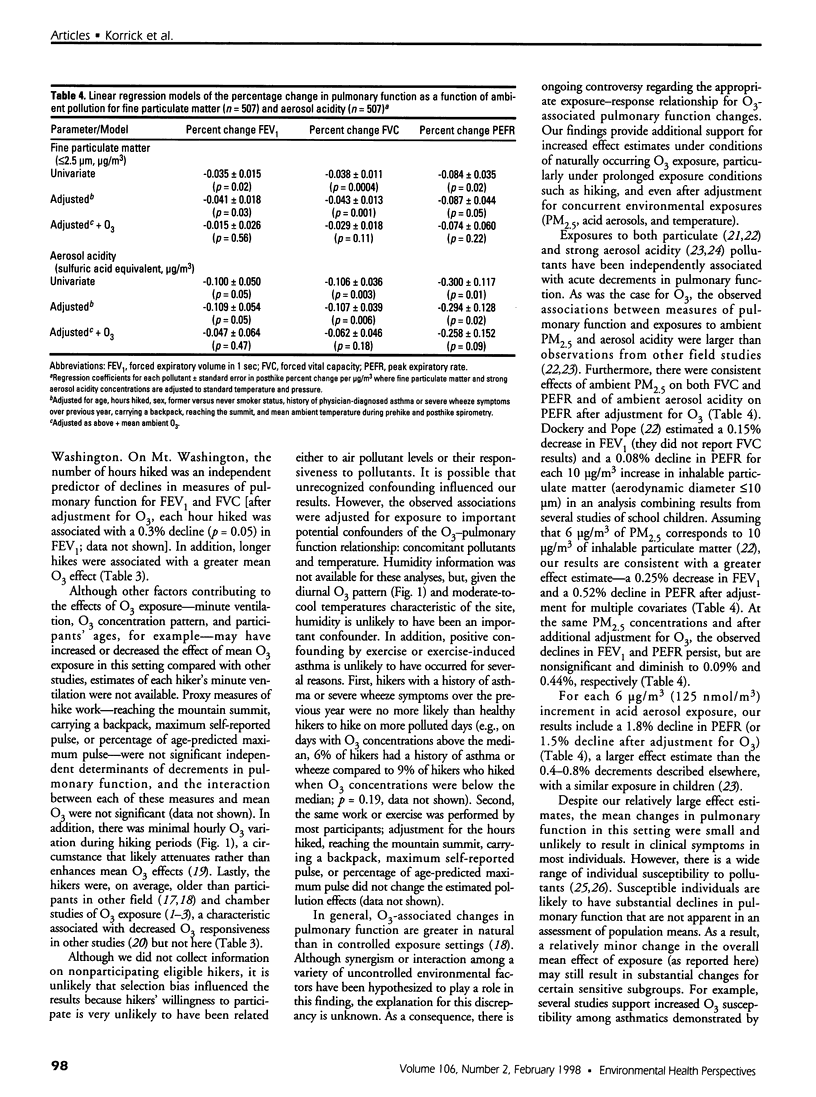
This study evaluated the acute effects of ambient ozone (O3), fine particulate matter (PM2.5), and strong aerosol acidity on the pulmonary function of exercising adults. During the summers of 1991 and 1992, volunteers (18-64 years of age) were solicited from hikers on Mt. Washington, New Hampshire. Volunteer nonsmokers with complete covariates (n = 530) had pulmonary function measured before and after their hikes. We calculated each hiker's posthike percentage change in forced expiratory volume in 1 sec (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), the ratio of these two (FEV1/FVC), forced expiratory flow between 25 and 75% of FVC(FEF25-75%), and peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR). Average O3 exposures ranged from 21 to 74 ppb. After adjustment for age,sex, smoking status (former versus never), history of asthma or wheeze, hours hiked, ambient temperature, and other covariates, there was a 2.6% decline in FEV1 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.4-4.7; p = 0.02] and a 2.2% decline in FVC (CI, 0.8-3.5; p =0.003) for each 50 ppb increment in mean O3. There were consistent associations of decrements in both FVC (0.4% decline; CI,0.2-0.6, p = 0.001) and PEFR (0.8% decline; CI, 0.01-1.6; p = 0.05) with PM2.5 and of decrements in PEFR (0.4% decline; CI, 0.1-0.7; p = 0.02) with strong aerosol acidity across the interquartile range of these exposures. Hikers with asthma or a history of wheeze (n = 40) had fourfold greater responsiveness to ozone than others. With prolonged outdoor exercise, low-level exposures to O3, PM2.5, and strong aerosol acidity were associated with significant effects on pulmonary function among adults. Hikers with a history of asthma or wheeze had significantly greater air pollution-related changes in pulmonary function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avol E. L., Linn W. S., Venet T. G., Shamoo D. A., Hackney J. D. Comparative respiratory effects of ozone and ambient oxidant pollution exposure during heavy exercise. J Air Pollut Control Assoc. 1984 Aug;34(8):804–809. doi: 10.1080/00022470.1984.10465814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunekreef B., Hoek G., Breugelmans O., Leentvaar M. Respiratory effects of low-level photochemical air pollution in amateur cyclists. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Oct;150(4):962–966. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.4.7921470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S., Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Analysis of airspace and interstitial mononuclear cell populations in human diffuse interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jul;118(1):7–15. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimeo M. J., Glenn M. G., Holtzman M. J., Sheller J. R., Nadel J. A., Boushey H. A. Threshold concentration of ozone causing an increase in bronchial reactivity in humans and adaptation with repeated exposures. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Sep;124(3):245–248. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockery D. W., Pope C. A., 3rd Acute respiratory effects of particulate air pollution. Annu Rev Public Health. 1994;15:107–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pu.15.050194.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folinsbee L. J., McDonnell W. F., Horstman D. H. Pulmonary function and symptom responses after 6.6-hour exposure to 0.12 ppm ozone with moderate exercise. JAPCA. 1988 Jan;38(1):28–35. doi: 10.1080/08940630.1988.10466349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazucha M. J., Folinsbee L. J., Seal E., Jr Effects of steady-state and variable ozone concentration profiles on pulmonary function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Dec;146(6):1487–1493. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.6.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstman D. H., Folinsbee L. J., Ives P. J., Abdul-Salaam S., McDonnell W. F. Ozone concentration and pulmonary response relationships for 6.6-hour exposures with five hours of moderate exercise to 0.08, 0.10, and 0.12 ppm. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Nov;142(5):1158–1163. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.5.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J. Q. Effect of ozone on respiratory responses in subjects with asthma. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Mar;103 (Suppl 2):103–105. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s2103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreit J. W., Gross K. B., Moore T. B., Lorenzen T. J., D'Arcy J., Eschenbacher W. L. Ozone-induced changes in pulmonary function and bronchial responsiveness in asthmatics. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Jan;66(1):217–222. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulle T. J., Sauder L. R., Hebel J. R., Chatham M. D. Ozone response relationships in healthy nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jul;132(1):36–41. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marple V. A., Rubow K. L., Turner W., Spengler J. D. Low flow rate sharp cut impactors for indoor air sampling: design and calibration. JAPCA. 1987 Nov;37(11):1303–1307. doi: 10.1080/08940630.1987.10466325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell W. F., Muller K. E., Bromberg P. A., Shy C. M. Predictors of individual differences in acute response to ozone exposure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Apr;147(4):818–825. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neas L. M., Dockery D. W., Koutrakis P., Tollerud D. J., Speizer F. E. The association of ambient air pollution with twice daily peak expiratory flow rate measurements in children. Am J Epidemiol. 1995 Jan 15;141(2):111–122. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. A., 3rd, Dockery D. W. Acute health effects of PM10 pollution on symptomatic and asymptomatic children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 May;145(5):1123–1128. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.5.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raizenne M. E., Burnett R. T., Stern B., Franklin C. A., Spengler J. D. Acute lung function responses to ambient acid aerosol exposures in children. Environ Health Perspect. 1989 Feb;79:179–185. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8979179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner B. Multivariate methods in ophthalmology with application to other paired-data situations. Biometrics. 1984 Dec;40(4):1025–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scannell C., Chen L., Aris R. M., Tager I., Christian D., Ferrando R., Welch B., Kelly T., Balmes J. R. Greater ozone-induced inflammatory responses in subjects with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Jul;154(1):24–29. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.154.1.8680687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spektor D. M., Lippmann M., Thurston G. D., Lioy P. J., Stecko J., O'Connor G., Garshick E., Speizer F. E., Hayes C. Effects of ambient ozone on respiratory function in healthy adults exercising outdoors. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):821–828. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





