Abstract
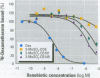
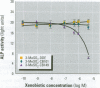
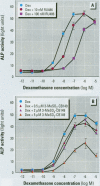
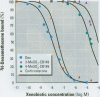
Persistent polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) metabolites were studied with respect to their interaction with the human glucocorticoid receptor (GR). 3-Methylsulphonyl-2,5,6,2',4',5'-hexachlorobiphenyl (3-MeSO2-CB149) was shown to compete with 3H-dexamethasone for binding to the GR, with an IC50 (concentration that inhibits 50%) of approximately 1 microM. Using GRAF cells expressing human GR, glucocorticoid responsive element, and a reporter enzyme, we demonstrated that 3-MeSO2-CB149 functionally acts as an antagonist at the GR (IC50 = 2.7 microM). In accordance with the receptor binding, the antagonism mainly appeared to be of a competitive nature. When studying the competitive binding of 24 methylsulfonyl PCBs (relative to dexamethasone) to GR from mouse liver cytosol, seven compounds had a higher affinity to GR than 3-MeSO2-CB149. Structure-activity relationship studies indicated that the presence of three chlorine atoms in the ortho-position and chlorine and methyl sulfone groups on either end of the molecule (4 and 4'-position) increased the affinity to GR. The relevance of this finding for human health is not known, but PCB methyl sulfones are ubiquitous pollutants present in mother's milk. The results stress the need for studying endocrine disruptors that affect hormonal systems other than sex and thyroidogenic hormones.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alksnis M., Barkhem T., Strömstedt P. E., Ahola H., Kutoh E., Gustafsson J. A., Poellinger L., Nilsson S. High level expression of functional full length and truncated glucocorticoid receptor in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Demonstration of ligand-induced down-regulation of expressed receptor mRNA and protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10078–10085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman A., Wachtmeister C. A. Synthesis of methanesulfonyl derivatives of 2,2-bis (4-chlorophenyl)-1,1-dichloroethylene (p,p'-DDE), present in seal from the Baltic. Acta Chem Scand B. 1977;31(1):90–91. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.31b-0090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrousos G. P., Laue L., Nieman L. K., Kawai S., Udelsman R. U., Brandon D. D., Loriaux D. L. Glucocorticoids and glucocorticoid antagonists: lessons from RU 486. Kidney Int Suppl. 1988 Oct;26:S18–S23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csaba G., Inczefi-Gonda A. Transgenerational effect of a single neonatal benzpyrene treatment on the glucocorticoid receptor of the rat thymus. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1998 Feb;17(2):88–92. doi: 10.1177/096032719801700203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard R. C., Riondel A., Muller A. F., Herrmann W., Baulieu E. E. RU 486: a steroid with antiglucocorticosteroid activity that only disinhibits the human pituitary-adrenal system at a specific time of day. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3879–3882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hontela A., Rasmussen J. B., Audet C., Chevalier G. Impaired cortisol stress response in fish from environments polluted by PAHs, PCBs, and mercury. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1992 Apr;22(3):278–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00212086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelce W. R., Stone C. R., Laws S. C., Gray L. E., Kemppainen J. A., Wilson E. M. Persistent DDT metabolite p,p'-DDE is a potent androgen receptor antagonist. Nature. 1995 Jun 15;375(6532):581–585. doi: 10.1038/375581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettel L. M., Murphy A. A., Morales A. J., Yen S. S. Clinical efficacy of the antiprogesterone RU486 in the treatment of endometriosis and uterine fibroids. Hum Reprod. 1994 Jun;9 (Suppl 1):116–120. doi: 10.1093/humrep/9.suppl_1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B. O., Lund J. Novel involvement of a mitochondrial steroid hydroxylase (P450c11) in xenobiotic metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 8;270(36):20895–20897. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.36.20895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norén K., Lundén A., Pettersson E., Bergman A. Methylsulfonyl metabolites of PCBs and DDE in human milk in Sweden, 1972-1992. Environ Health Perspect. 1996 Jul;104(7):766–772. doi: 10.1289/ehp.104-1469405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto A. M., Sonnenschein C., Chung K. L., Fernandez M. F., Olea N., Serrano F. O. The E-SCREEN assay as a tool to identify estrogens: an update on estrogenic environmental pollutants. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Oct;103 (Suppl 7):113–122. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]