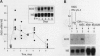Abstract
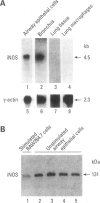
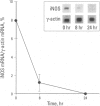
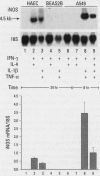
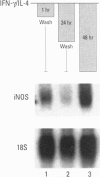
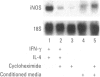
Nitric oxide is an important mediator of inflammatory responses in the lung and a key regulator of pulmonary vascular and bronchomotor tone. We have shown that the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) isoform is continuously expressed in human airway epithelium at mRNA and protein/activity levels in vivo. However, removal of epithelial cells from the in vivo airway environment resulted in rapid loss of iNOS expression, which suggested that expression is dependent upon conditions and/or factors present in the airway. To investigate the mechanisms responsible for maintenance of expression in vivo, we evaluated regulation of iNOS expression in primary human airway epithelial cells. Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) was sufficient for induction of iNOS in primary human airway epithelial cells (HAEC) in vitro, and interleukin-4 (IL-4) potentiated the expression through stabilization of iNOS mRNA. The IFN-gamma/IL-4-induced iNOS expression in HAEC was delayed in onset and prolonged with expression up to 1 week. Furthermore, transfer of overlying culture media [conditioned media (CM)] to other HAEC led to iNOS induction. Interestingly, IFN-gamma/IL-4 induction of iNOS was dependent on new protein synthesis, whereas CM induction of iNOS was not. IFN-gamma and IL-4 activated signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT1 and STAT6) in HAEC, but CM transfer to HAEC produced even higher levels of STAT1 activation than achieved by direct addition of cytokines. Thus, IFN-gamma/IL-4, which occurs in human lung lining fluid, led to iNOS expression in human airway epithelium through production of soluble mediators and stabilization of mRNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike T., Noguchi Y., Ijiri S., Setoguchi K., Suga M., Zheng Y. M., Dietzschold B., Maeda H. Pathogenesis of influenza virus-induced pneumonia: involvement of both nitric oxide and oxygen radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 19;93(6):2448–2453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.6.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano K., Chee C. B., Gaston B., Lilly C. M., Gerard C., Drazen J. M., Stamler J. S. Constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression, regulation, and activity in human lung epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10089–10093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Nitric oxide and airway disease. Ann Med. 1995 Jun;27(3):389–393. doi: 10.3109/07853899509002592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman J. S., Koppenol W. H. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol. 1996 Nov;271(5 Pt 1):C1424–C1437. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.5.C1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Park S. H., Aust A. E. Participation of nitric oxide and iron in the oxidation of DNA in asbestos-treated human lung epithelial cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1996 Feb 1;326(1):152–157. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1996.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles I. G., Palmer R. M., Hickery M. S., Bayliss M. T., Chubb A. P., Hall V. S., Moss D. W., Moncada S. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a cDNA encoding an inducible nitric oxide synthase from the human chondrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11419–11423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Lowenstein C. J., Shapiro R. A., Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Wang S. C., Nakayama D. K., Simmons R. L., Snyder S. H., Billiar T. R. Molecular cloning and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase from human hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo F. H., De Raeve H. R., Rice T. W., Stuehr D. J., Thunnissen F. B., Erzurum S. C. Continuous nitric oxide synthesis by inducible nitric oxide synthase in normal human airway epithelium in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo F. H., Uetani K., Haque S. J., Williams B. R., Dweik R. A., Thunnissen F. B., Calhoun W., Erzurum S. C. Interferon gamma and interleukin 4 stimulate prolonged expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in human airway epithelium through synthesis of soluble mediators. J Clin Invest. 1997 Aug 15;100(4):829–838. doi: 10.1172/JCI119598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque S. J., Flati V., Deb A., Williams B. R. Roles of protein-tyrosine phosphatases in Stat1 alpha-mediated cell signaling. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 27;270(43):25709–25714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.43.25709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Treisman R. Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: mechanisms and specificity. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Schindler U., Henzel W. J., Ho T. C., Brasseur M., McKnight S. L. An interleukin-4-induced transcription factor: IL-4 Stat. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1701–1706. doi: 10.1126/science.8085155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iademarco M. F., Barks J. L., Dean D. C. Regulation of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression by IL-4 and TNF-alpha in cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):264–271. doi: 10.1172/JCI117650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssens S. P., Shimouchi A., Quertermous T., Bloch D. B., Bloch K. D. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding human endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14519–14522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamijo R., Harada H., Matsuyama T., Bosland M., Gerecitano J., Shapiro D., Le J., Koh S. I., Kimura T., Green S. J. Requirement for transcription factor IRF-1 in NO synthase induction in macrophages. Science. 1994 Mar 18;263(5153):1612–1615. doi: 10.1126/science.7510419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobzik L., Bredt D. S., Lowenstein C. J., Drazen J., Gaston B., Sugarbaker D., Stamler J. S. Nitric oxide synthase in human and rat lung: immunocytochemical and histochemical localization. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;9(4):371–377. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/9.4.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb J. P., Paul-Eugene N., Damais C., Yamaoka K., Drapier J. C., Dugas B. Interleukin-4 stimulates cGMP production by IFN-gamma-activated human monocytes. Involvement of the nitric oxide synthase pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9811–9816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Look D. C., Pelletier M. R., Holtzman M. J. Selective interaction of a subset of interferon-gamma response element-binding proteins with the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) gene promoter controls the pattern of expression on epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):8952–8958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R., Bilbe G., Rediske J., Lotz M. Inducible nitric oxide synthase from human articular chondrocytes: cDNA cloning and analysis of mRNA expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Sep 21;1208(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Xie Q. W. Regulation of biosynthesis of nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13725–13728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietraforte D., Tritarelli E., Testa U., Minetti M. gp120 HIV envelope glycoprotein increases the production of nitric oxide in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Feb;55(2):175–182. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R. A., Barnes P. J., Springall D. R., Warren J. B., Kwon O. J., Buttery L. D., Wilson A. J., Geller D. A., Polak J. M. Expression of inducible nitric oxide in human lung epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 30;203(1):209–218. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R. A., Springall D. R., Warren J. B., Kwon O. J., Buttery L. D., Wilson A. J., Adcock I. M., Riveros-Moreno V., Moncada S., Polak J. Inducible nitric oxide synthase is increased in murine lung epithelial cells by cytokine stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 15;198(3):835–843. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands W. A., Bulut V., Severn A., Xu D., Liew F. Y. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis by interleukin-4 may involve inhibiting the activation of protein kinase C epsilon. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Oct;24(10):2345–2350. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:621–651. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.003201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Walter U. NO at work. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):919–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Laubach V. E., Reep B. R., Wood E. R. Purification and cDNA sequence of an inducible nitric oxide synthase from a human tumor cell line. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 2;32(43):11600–11605. doi: 10.1021/bi00094a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Griffith O. W. Mammalian nitric oxide synthases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1992;65:287–346. doi: 10.1002/9780470123119.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey W. R., Xue C., Klinghofer V., Barlow J., Pollock J. S., Förstermann U., Johns R. A. Immunochemical detection of inducible NO synthase in human lung. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):L722–L727. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.6.L722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz A., Oguchi S., Cicatiello L., Esumi H. Dual mechanism for the control of inducible-type NO synthase gene expression in macrophages during activation by interferon-gamma and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8324–8333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R. Transcriptional regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Laubach V. E., Alley E. W., Edwards K. A., Sherman P. A., Russell S. W., Murphy W. J. Transcriptional basis for hyporesponsiveness of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase gene to lipopolysaccharide/interferon-gamma. J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Apr;59(4):575–585. doi: 10.1002/jlb.59.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vera M. E., Shapiro R. A., Nussler A. K., Mudgett J. S., Simmons R. L., Morris S. M., Jr, Billiar T. R., Geller D. A. Transcriptional regulation of human inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2) gene by cytokines: initial analysis of the human NOS2 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 6;93(3):1054–1059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]